What are Bear and Bull Markets?
A bull market is generally characterized by an upward trend in asset prices. The technical definition of a bull market is that the market value of assets rises 20% above its highest value in the last 52 weeks. In a bull market, economic growth rate is high, unemployment level is low and investor confidence is high. In a bull market, investors' tendency to take risks increases as they have optimistic expectations for the future.
How Does a Bull Market Form?
The most important factors that prepare the formation of the bull market:
- High Growth Rate: In a high-growth economy, consumption expenditures increase. Companies with increased sales contribute to employment growth by increasing their investments and capacities. Sustainable economic growth provides investors with optimistic expectations about the markets and encourages them to invest by taking more risks.
- Increased Investor Confidence: Increasing investors' confidence that asset prices will rise causes the prices of stocks or other financial assets to rise.
- Decreasing Unemployment Rate: Decreasing unemployment rate strengthens investor expectations that expenses will increase and companies' profits will increase.
How to Invest in a Bull Market?
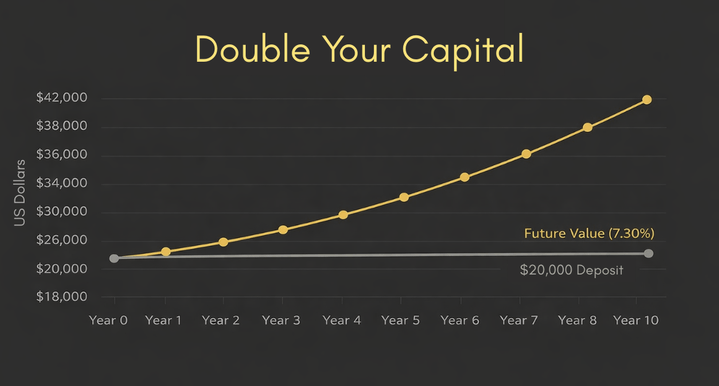
Research results have shown that historically bull markets have lasted longer than bear markets. Accordingly, the bear market lasts on average 1.4 years, and the bull market lasts 9 years. This determination plays an important role in shaping the investment strategies that investors choose in bear and bull markets. In a bull market, the expectation of a high return on investment prevails.
- Taking a Long Position: It is a more appropriate approach to take a long position in a bull market where the expectation of an increase in asset prices is high, the risk is relatively low and the risk/return ratio is high.
- Buying Low-Priced Assets: It would be more appropriate to maximize the return on investment by investing in assets whose market price is lower than their book value, instead of assets that are more in demand and whose prices increase excessively in the bull market.
- Long-Term Investment: Since the bull market is long-term, investors can invest in assets that will provide higher profits in the long term by adopting longer-term investment strategies instead of making profits through daily trading.
- Portfolio Diversification: Although the bull market is long-lasting, it is important for investors to diversify their portfolios according to their risk tolerance and sectors in order to distribute their risks and maximize their profits.
Bull Market Examples
Kaynak:
https://www.doviz.com/makale/ayi-ve-boga-piyasasi-nedir/129
@Metehan
@Arden