Green Future: Sustainable Energy and Innovations
Sustainable Energy: Renewable Resources and Future Energy Trends
In today's world, the rapidly increasing demand for energy and the limitations of fossil fuels have intensified the need for sustainable energy sources. In this context, renewable energy resources have emerged as environmentally friendly and long-term energy solutions. In this article, we will delve into the importance of sustainable energy, renewable resources, and future energy trends.
Renewable Energy Sources:
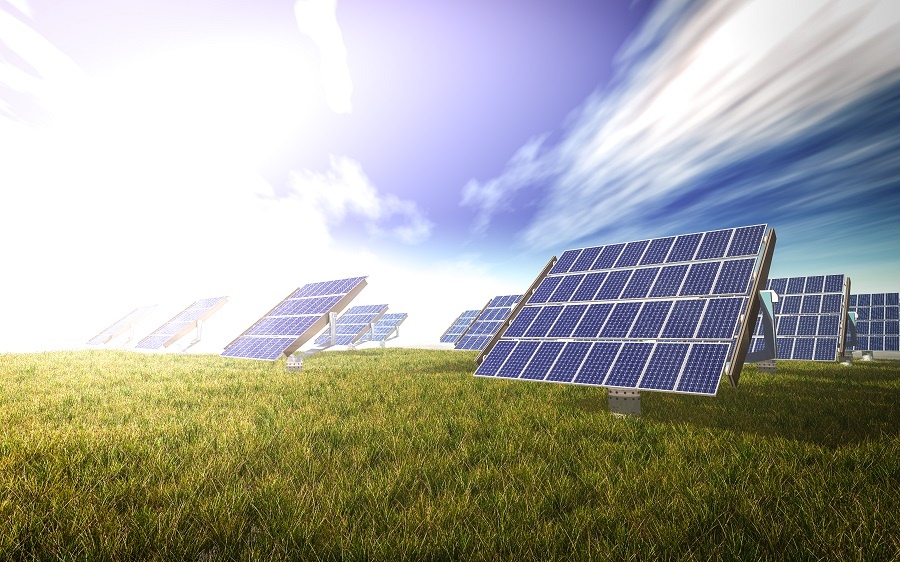
Solar energy, harnessed through solar panels for electricity production, stands as a paramount renewable source. The daily sunlight received by the Earth offers an inexhaustible potential for energy. Wind energy, another significant source, utilizes wind turbines to generate electricity. Advancements such as offshore wind farms enhance the potential of wind energy. Hydropower, derived from water sources, contributes to electricity production through large dams. Bioenergy, involving organic materials like agricultural residues and bioethanol, diversifies the sustainable energy portfolio. Geothermal energy taps into the heat beneath the Earth's surface for power generation.
Advancing Technology and Innovative Solutions:
Rapid developments in renewable energy technologies shape the future trends of energy. Increasing efficiency in solar panels has led to reduced costs, making solar energy more widely accessible. Improvements in wind turbine design enhance the effective utilization of wind energy. Energy storage technologies balance the fluctuating nature of renewable energy sources, contributing to increased energy security. Smart grids enable more efficient management of energy production and consumption.
Financial and Social Support:
Financial investments in renewable energy projects, along with governmental support through incentives and tax reductions, encourage the development of sustainable energy projects. Moreover, the growing awareness and support for sustainable energy within communities enhance societal acceptance of such projects.
Global Climate Change and Urgent Energy Transformation:
Global climate change emphasizes the increasing importance of sustainable energy. Greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels are major contributors to global warming. Hence, an urgent energy transformation is necessary, demanding the rapid adoption of sustainable energy sources.
Sustainable Energy and Employment Opportunities:
The renewable energy sector creates new employment opportunities. Various fields, such as the development, assembly, maintenance, and management of renewable energy projects, offer a range of job prospects. This, in turn, contributes to economic growth.
Challenges in Transitioning to Sustainable Energy:
The transition to sustainable energy is not without its challenges. Factors such as the cost of energy storage technologies, energy security concerns, and the modification of existing energy infrastructure influence the transition process.
International Collaboration and Energy Diplomacy:
Sustainable energy plays a crucial role in international collaboration and energy diplomacy. Cross-border energy trade, technology transfers, and collaborative projects contribute to making sustainable energy a global priority.
Sustainable energy, providing eco-friendly and long-term energy solutions, addresses the future's energy demands. Rapid progress in renewable energy sources and technologies accelerates global energy transformation. In the future, the widespread adoption of renewable energy will not only provide clean energy but also contribute to economic growth, job creation, and environmental well-being. To ensure a sustainable future, it is crucial to increase investments in sustainable energy, raise awareness, and cultivate a culture of conscious energy consumption at every level from individuals to governments.
Sustainable energy also plays a pivotal role in combating energy poverty. Providing access to energy in developing countries is a fundamental aspect of sustainable development. Renewable energy sources offer an effective solution to supply energy to remote areas and empower rural communities.
Technological Integration and Smart Cities:
The integration of renewable energy technologies contributes to the development of smart cities. Cities worldwide are incorporating solar panels on rooftops, wind turbines in urban areas, and energy-efficient infrastructure. These innovations pave the way for environmentally conscious urban planning.
Public Awareness and Education:
Despite the advantages of sustainable energy, public awareness remains crucial. Educating communities about the benefits of renewable resources, energy efficiency, and the environmental impact of energy choices fosters a culture of responsible energy consumption.
Innovation in Energy Storage:
Continued research and development in energy storage technologies are vital for the advancement of sustainable energy. Efficient and cost-effective storage solutions are essential to address the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources and ensure a steady energy supply.
The Role of Electric Vehicles in Sustainable Transportation:
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is integral to achieving sustainability in transportation. As the EV infrastructure expands and battery technology improves, the transportation sector can significantly reduce its reliance on fossil fuels.
Challenges in Sustainable Energy Adoption:
While progress has been made, challenges persist in the widespread adoption of sustainable energy. The initial costs of implementing renewable energy technologies, resistance to change, and geopolitical factors affecting energy policies remain obstacles that need to be addressed.
Renewable Energy in Developing Economies:
The integration of sustainable energy in developing economies requires tailored solutions that consider economic constraints and energy demands. International support and collaboration are crucial to assisting these economies in their transition to sustainable energy.
Policy Frameworks and Government Initiatives:
Government policies and initiatives play a pivotal role in fostering the transition to sustainable energy. Clear regulatory frameworks, incentives for renewable energy projects, and commitment to international agreements contribute to a supportive environment for sustainable energy development.
Resilience Against Climate Change:
Sustainable energy adoption is closely linked to climate resilience. As the world faces the impacts of climate change, relying on renewable energy sources becomes imperative to build resilience against extreme weather events and environmental challenges.
Global Energy Transition and Economic Benefits:
The global transition to sustainable energy not only addresses environmental concerns but also brings substantial economic benefits. Investments in renewable energy projects stimulate economic growth, create jobs, and reduce dependence on fossil fuel imports.
Sustainable energy is a multifaceted solution that addresses environmental, social, and economic challenges. The ongoing global transition to renewable energy sources and the advancement of technology contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future. It requires collective efforts from individuals, communities, businesses, and governments to accelerate this transition and create a world powered by clean and sustainable energy.
Private Sector Engagement and Corporate Responsibility:
The involvement of the private sector is crucial in driving sustainable energy initiatives. Many corporations are recognizing the importance of adopting renewable energy practices, not only to reduce their carbon footprint but also as a strategy for long-term cost savings. Corporate responsibility in energy consumption positively influences supply chains and encourages sustainable practices across industries.
Community-Based Renewable Energy Projects:
Community-based renewable energy projects empower local communities to actively participate in and benefit from sustainable energy initiatives. These projects can range from small-scale solar installations to community-owned wind farms, fostering a sense of ownership and promoting decentralized energy production.
Emerging Technologies and Energy Innovations:
Constant advancements in technology lead to the emergence of new and innovative solutions in the energy sector. From breakthroughs in photovoltaic technology to advancements in energy-efficient appliances, these innovations contribute to making sustainable energy more accessible and efficient.
Cross-Sector Collaboration for Integrated Solutions:
Addressing complex challenges requires collaboration across various sectors. Cross-sector collaboration, involving energy experts, policymakers, environmentalists, and technologists, can lead to integrated solutions that consider social, economic, and environmental aspects in tandem.
Economic Benefits of Energy Efficiency:
Energy efficiency measures play a significant role in sustainable energy adoption. Implementing energy-efficient practices in industries, buildings, and transportation not only reduces energy consumption but also leads to substantial cost savings and increased competitiveness in the global market.
Empowering Developing Nations through Technology Transfer:
Facilitating the transfer of sustainable energy technologies to developing nations is essential for global progress. International cooperation in sharing knowledge, expertise, and technology empowers these nations to leapfrog traditional, polluting energy sources and embrace cleaner alternatives.
Circular Economy Principles in Energy Production:
Applying circular economy principles to energy production involves minimizing waste, recycling materials, and reusing resources. These principles contribute to the overall sustainability of energy systems by reducing environmental impacts and promoting responsible resource management.
Investment in Research and Development:
Ongoing investment in research and development (R&D) is critical for unlocking new possibilities in sustainable energy. R&D initiatives focus on improving existing technologies, exploring novel solutions, and addressing challenges related to scalability, efficiency, and environmental impact.
Climate-Resilient Infrastructure:
Building climate-resilient infrastructure is integral to sustainable energy development. As extreme weather events become more frequent, infrastructure that can withstand and recover from such events ensures the reliability and longevity of energy systems.
Consumer Empowerment and Demand-Side Management:
Empowering consumers with information about their energy consumption and promoting demand-side management strategies contribute to a more sustainable energy landscape. Smart grids, energy-efficient appliances, and consumer awareness campaigns encourage responsible energy use.
Global Governance for Sustainable Energy:
Establishing effective global governance mechanisms is vital for coordinating efforts, setting international standards, and addressing transboundary issues in the transition to sustainable energy. Global cooperation ensures that nations work collectively towards shared goals, fostering a united front against climate change.
In the quest for sustainable energy, a holistic approach encompassing technological innovation, cross-sector collaboration, corporate responsibility, and global governance is imperative. The journey towards a sustainable energy future requires continuous dedication, adaptability to emerging technologies, and a commitment to fostering a balance between societal needs and environmental preservation. As stakeholders from all sectors contribute to this shared vision, the prospect of a sustainable and resilient global energy landscape becomes increasingly attainable.
Public Policy and Incentives:
Effective public policies and incentives play a pivotal role in shaping the transition to sustainable energy. Governments worldwide can encourage the adoption of renewable energy by implementing supportive policies, such as feed-in tariffs, tax credits, and renewable portfolio standards. These measures not only stimulate investment in sustainable energy projects but also create a conducive environment for innovation and market growth.
Decentralized Energy Systems:
The move towards decentralized energy systems is gaining momentum as technology allows for smaller-scale, local energy production. Decentralized systems, including microgrids and distributed renewable energy sources, enhance energy resilience, reduce transmission losses, and empower local communities to have greater control over their energy supply.
Energy Justice and Inclusivity:
Promoting energy justice and inclusivity is integral to the sustainable energy transition. Ensuring that all communities, regardless of socio-economic status, have access to clean and affordable energy is essential. Inclusivity in decision-making processes and equitable distribution of the benefits of sustainable energy projects contribute to a fair and just energy transition.
Hydrogen as a Clean Energy Carrier:
The role of hydrogen as a clean energy carrier is gaining prominence. Green hydrogen, produced using renewable energy sources, holds promise as a versatile and clean energy carrier for various sectors, including industry and transportation. Continued research and development in hydrogen technologies are crucial for unlocking its full potential in the energy transition.
Green Finance and Investment:
The financial sector plays a crucial role in supporting the transition to sustainable energy. Green finance initiatives, sustainable investment funds, and socially responsible investment strategies contribute to channeling funds towards environmentally friendly projects. Investors increasingly recognize the importance of sustainable practices for long-term financial stability.
Electricity Market Reforms:
Reforming electricity markets is essential for accommodating the integration of renewable energy sources. Market designs that facilitate grid flexibility, fair compensation for renewable energy producers, and efficient electricity trading contribute to a more resilient and adaptive energy market.
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS):
Carbon capture, utilization, and storage technologies offer a potential solution for mitigating emissions from existing industrial processes. CCUS technologies can capture CO2 emissions from power plants and industrial facilities, preventing them from entering the atmosphere. Continued research and investment in CCUS are crucial for its widespread implementation.
Responsible Mining for Renewable Technologies:
The production of renewable energy technologies, such as solar panels and batteries, relies on critical minerals and metals. Ensuring responsible mining practices, including ethical sourcing and recycling of these materials, is essential to avoid environmental and social impacts associated with mining activities.
Blockchain Technology in Energy Transactions:
Blockchain technology is increasingly being explored for its potential in enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency in energy transactions. Decentralized and transparent blockchain platforms can facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading, enable traceability of renewable energy certificates, and streamline energy transactions.
Climate Adaptation Strategies:
In addition to mitigating greenhouse gas emissions, sustainable energy efforts should integrate climate adaptation strategies. Adapting to the impacts of climate change, such as rising sea levels and extreme weather events, ensures the long-term viability of energy infrastructure and minimizes vulnerabilities in the face of a changing climate.
Educational Initiatives for Sustainability:
Education and awareness initiatives are instrumental in fostering a culture of sustainability. Educational programs at all levels, from schools to universities, contribute to building a knowledgeable and environmentally conscious workforce. Public awareness campaigns also empower individuals to make informed decisions about their energy consumption.
Crisis Resilience and Sustainable Energy:
As the world faces increasing uncertainties and crises, the resilience of sustainable energy systems becomes paramount. Building infrastructure and systems that can withstand disruptions, whether caused by natural disasters or other unforeseen events, ensures a reliable and continuous energy supply. Microgrids, energy storage solutions, and robust transmission networks contribute to the resilience of sustainable energy infrastructure.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Energy Optimization:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the energy sector by optimizing energy production, distribution, and consumption. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to enhance energy efficiency, predict energy demand patterns, and optimize the operation of renewable energy sources. The integration of AI technologies contributes to a smarter and more adaptive energy ecosystem.
Energy-Efficient Urban Planning:
Sustainable urban planning is a critical component of the broader sustainable energy transition. Designing cities with energy-efficient buildings, integrated public transportation, and green spaces reduces energy consumption and environmental impact. Smart city initiatives, incorporating IoT technologies, contribute to resource-efficient and livable urban environments.
Circular Economy in Battery Technologies:
As the demand for energy storage increases, particularly in the context of renewable energy integration and electric vehicles, adopting circular economy principles in battery technologies is essential. Designing batteries for recyclability, efficient materials recovery, and responsible disposal contribute to minimizing environmental impact and resource depletion.
Integration of Nature-Based Solutions:
Nature-based solutions, such as reforestation and green infrastructure, complement sustainable energy efforts by sequestering carbon, enhancing biodiversity, and mitigating the impacts of climate change. Integrating these solutions into sustainable energy projects creates synergies that benefit both ecosystems and human communities.
Renewable Energy for Water Desalination:
Water scarcity is a growing global concern, and the integration of renewable energy in water desalination processes presents a sustainable solution. Solar and wind-powered desalination technologies provide energy-efficient and environmentally friendly alternatives for meeting the increasing demand for freshwater in water-scarce regions.
Off-grid renewable energy solutions, such as solar home systems and mini-grids, play a crucial role in alleviating energy poverty in remote and underserved areas. These solutions provide access to clean and affordable energy, empowering communities and supporting socio-economic development.
E-Mobility and Sustainable Transportation:
The transition to e-mobility, including electric vehicles (EVs) and charging infrastructure, is a key aspect of sustainable transportation. EVs contribute to reducing air pollution, dependence on fossil fuels, and greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with broader efforts to create a sustainable and decarbonized transportation sector.
Inclusive Decision-Making in Energy Transition:
Ensuring inclusivity in decision-making processes related to the energy transition is vital. Engaging diverse stakeholders, including local communities, indigenous groups, and marginalized populations, fosters a more democratic and equitable transition to sustainable energy.
Health Benefits of Sustainable Energy:
The shift to sustainable energy sources brings significant health benefits by reducing air pollution and mitigating the impact of climate change on public health. Cleaner air, improved water quality, and a reduced reliance on fossil fuels contribute to creating healthier and more resilient communities.
International Collaboration for Climate Mitigation:
Addressing the global challenge of climate change requires strengthened international collaboration. Shared research initiatives, technology transfer, and coordinated efforts in climate mitigation contribute to a unified response to the urgent environmental challenges posed by the changing climate.
The evolution towards a sustainable energy future is an ongoing and collaborative journey that encompasses diverse technologies, strategies, and societal shifts. By embracing innovative solutions, fostering inclusivity, and prioritizing resilience in the face of challenges, the global community can navigate the complexities of the sustainable energy transition. Through continuous adaptation and shared commitment, a sustainable energy landscape can be realized, ensuring a harmonious balance between human needs and environmental stewardship.
Would you like to check out my other articles? You can follow the links below