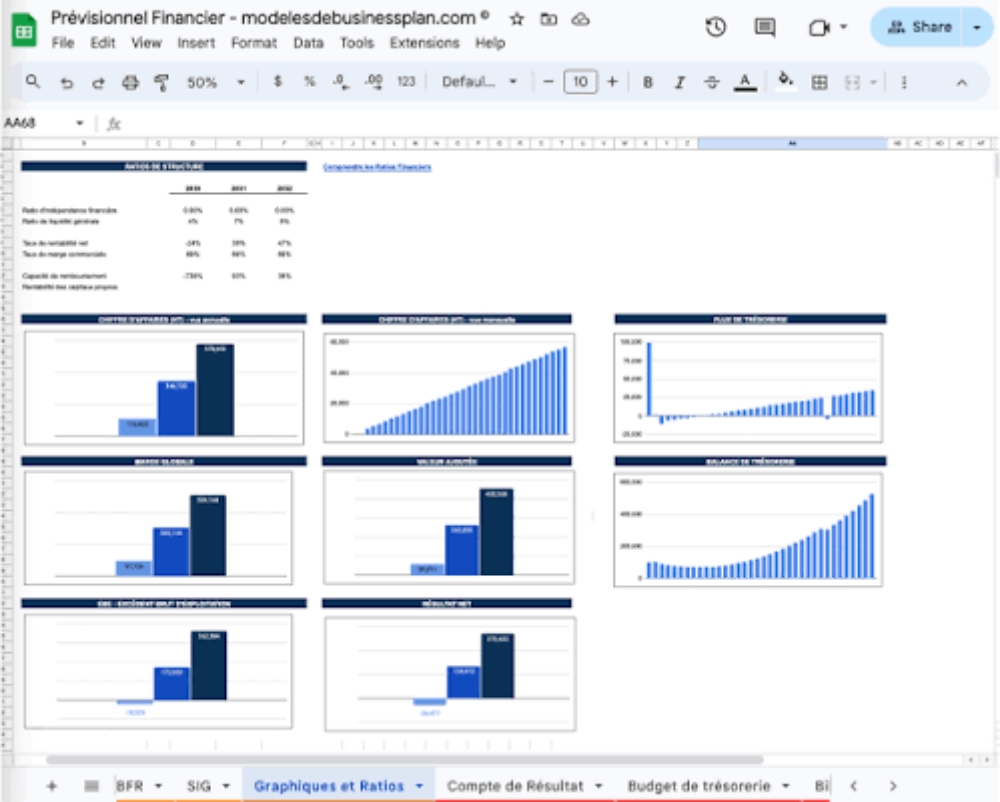
The Most Famous Stars in the Night Sky: How to Find and Identify Them
Stargazing is a timeless activity that has fascinated humanity for millennia. Whether you're an amateur astronomer or simply someone who enjoys looking up at the night sky, knowing how to find and identify the most famous stars can deepen your appreciation of the cosmos.
This article will guide you through the process of locating and recognizing these celestial beacons, enriching your stargazing experience.
The North Star: Polaris
 Polaris, commonly known as the North Star, holds a unique position in the night sky. Unlike other stars, Polaris remains almost stationary, marking the location of the north celestial pole. This has made it an invaluable navigational aid throughout history.
Polaris, commonly known as the North Star, holds a unique position in the night sky. Unlike other stars, Polaris remains almost stationary, marking the location of the north celestial pole. This has made it an invaluable navigational aid throughout history.
Finding Polaris
To locate Polaris, first find the Big Dipper (Ursa Major). The two stars at the end of the Big Dipper's bowl, known as the "pointer stars," point directly to Polaris. Following a line from these stars approximately five times the distance between them will lead you to the North Star. Polaris is the brightest star in the constellation Ursa Minor (the Little Dipper).
Significance in Navigation
Polaris' fixed position makes it a reliable guide for navigation. Mariners and explorers have used it for centuries to find their way across oceans and deserts. Its importance in the night sky cannot be overstated, as it provides a constant point of reference.
The Summer Triangle: Vega, Deneb, and Altair
 The Summer Triangle is an asterism, a recognizable pattern of stars, consisting of three bright stars: Vega, Deneb, and Altair. This triangle is prominent in the summer sky in the Northern Hemisphere and serves as a great starting point for stargazers.
The Summer Triangle is an asterism, a recognizable pattern of stars, consisting of three bright stars: Vega, Deneb, and Altair. This triangle is prominent in the summer sky in the Northern Hemisphere and serves as a great starting point for stargazers.
Locating Vega
Vega is the brightest star in the constellation Lyra and the fifth-brightest star in the night sky. To find Vega, look directly overhead during midsummer evenings. It is one of the most luminous stars visible and easily distinguishable due to its brightness.
Finding Deneb
Deneb, part of the constellation Cygnus (the Swan), forms the top of the Northern Cross asterism. Look for a large cross shape in the sky, with Deneb marking the tail of the swan. It is less bright than Vega but still prominent.
Identifying Altair
Altair is the brightest star in the constellation Aquila (the Eagle). It lies almost directly south of Vega and Deneb, completing the Summer Triangle. Altair is easily identified by its proximity to two dimmer stars that form a straight line with it.
Significance in Astronomy
The Summer Triangle stars are not only prominent in the night sky but also significant in the study of stellar evolution. Vega, for instance, is often studied for its circumstellar disk, while Deneb is a luminous supergiant with considerable scientific interest.
Orion's Belt: Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka
 Orion's Belt is one of the most recognizable features in the night sky, consisting of three bright stars in a straight line: Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka. This belt is part of the larger Orion constellation, which is visible during winter months in the Northern Hemisphere.
Orion's Belt is one of the most recognizable features in the night sky, consisting of three bright stars in a straight line: Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka. This belt is part of the larger Orion constellation, which is visible during winter months in the Northern Hemisphere.
Finding Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka
To locate Orion's Belt, look for a prominent line of three stars in the southeastern sky during winter evenings. The belt is part of Orion, which also includes the bright stars Betelgeuse and Rigel. The belt stars are relatively close to each other and form a straight line, making them easy to identify.
Importance in Mythology and Culture
Orion's Belt has been significant in various mythologies and cultures. In Greek mythology, Orion was a mighty hunter. In ancient Egypt, the alignment of the pyramids of Giza is thought to correspond to the stars of Orion's Belt. The belt stars serve as a cultural and historical bridge across civilizations.
The Pleiades: The Seven Sisters
 The Pleiades, also known as the Seven Sisters, is an open star cluster in the constellation Taurus. It consists of seven visible stars that form a small, dipper-like shape. The Pleiades is one of the nearest star clusters to Earth and has been known since antiquity.
The Pleiades, also known as the Seven Sisters, is an open star cluster in the constellation Taurus. It consists of seven visible stars that form a small, dipper-like shape. The Pleiades is one of the nearest star clusters to Earth and has been known since antiquity.
Locating the Pleiades
To find the Pleiades, look for the bright constellation Taurus in the eastern sky during autumn and winter evenings. The Pleiades cluster is located near the bull's shoulder and appears as a tiny, shimmering cluster of stars. Binoculars can help in viewing more stars within the cluster.
Astronomical Significance
The Pleiades cluster is significant in the study of stellar formation and evolution. It contains hundreds of stars, though only a few are visible to the naked eye. The cluster's age and composition provide valuable information about the processes of star formation.
Cultural and Mythological Importance
The Pleiades have featured prominently in various mythologies. In Greek mythology, the seven sisters were the daughters of Atlas and Pleione. Many cultures have their own stories and legends associated with this star cluster, highlighting its universal appeal.
The Southern Cross: Crux
 Crux, commonly known as the Southern Cross, is a prominent constellation in the southern hemisphere. It consists of four main stars that form a cross shape. The Southern Cross is an important cultural symbol in many southern hemisphere countries.
Crux, commonly known as the Southern Cross, is a prominent constellation in the southern hemisphere. It consists of four main stars that form a cross shape. The Southern Cross is an important cultural symbol in many southern hemisphere countries.
Finding the Southern Cross
To locate the Southern Cross, look towards the southern sky. The constellation is easily recognizable due to its distinct cross shape. The two bright pointer stars, Alpha and Beta Centauri, can help guide you to Crux. Draw an imaginary line through these stars to find the cross.
Significance in Navigation
Like Polaris in the northern hemisphere, the Southern Cross has been a crucial navigational aid in the southern hemisphere. Its position in the sky indicates the direction of the South Pole, making it invaluable for travelers and navigators.
Conclusion
Stargazing can be a profoundly enriching experience, and knowing how to identify some of the most famous stars and constellations adds depth to this pastime. From the steadfast Polaris to the culturally rich Pleiades, these celestial landmarks serve as navigational aids, scientific interests, and cultural touchstones. As you gaze up at the night sky, take a moment to appreciate the stories and science behind these shining beacons.
References
NASA - Orion Constellation
Sky & Telescope - Finding Polaris
EarthSky - Summer Triangle
The Pleiades: Facts about the "Seven Sisters" star cluster
Britannica - Polaris