The Impact of Social Media on Global Political Movements
Social media has transformed the landscape of global political movements, serving as both a tool for mobilization and a platform for dialogue. From facilitating grassroots activism to influencing public opinion and policy, social media's role in politics is profound and multifaceted.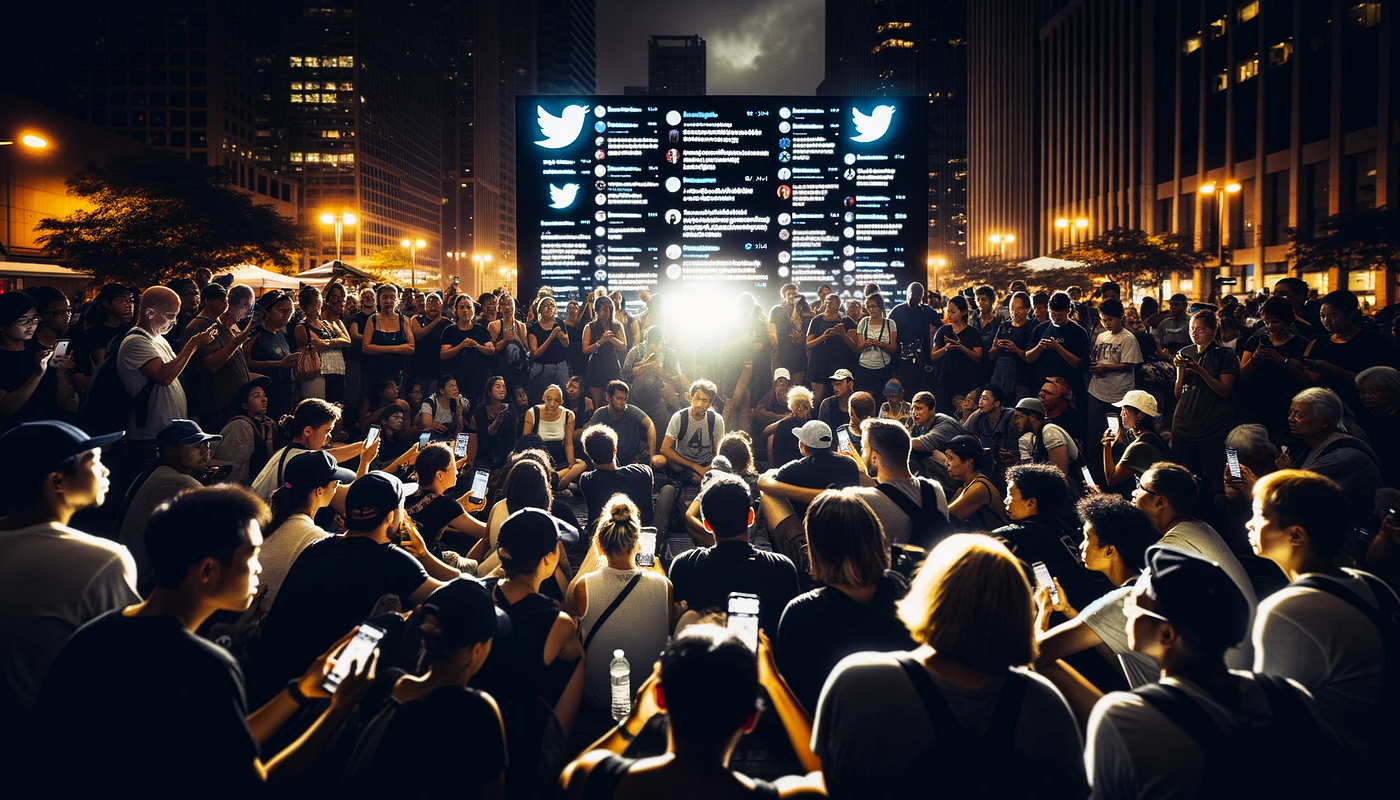 
This article explores the various ways in which social media has impacted global political movements, highlighting its benefits, challenges, and the implications for future political engagement.
Mobilization and Organization
Social media has revolutionized the way political movements organize and mobilize supporters. Platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram have enabled activists to reach a wide audience quickly and efficiently, often bypassing traditional media channels.
Rapid Dissemination of Information
Social media allows for the instantaneous sharing of information, which is crucial for organizing protests, rallies, and demonstrations. Activists can communicate logistical details, share real-time updates, and disseminate important messages to a large audience. This capability has been instrumental in movements such as the Arab Spring, where social media played a key role in coordinating protests across different countries.
Grassroots Engagement
Social media platforms facilitate grassroots engagement by allowing individuals to participate in political discourse and activism from anywhere. This accessibility empowers ordinary citizens to contribute to political movements, amplifying diverse voices that might otherwise be marginalized.
Crowdsourcing and Fundraising
Activists use social media to crowdsource ideas, gather feedback, and raise funds for their causes. Online petitions, crowdfunding campaigns, and call-to-action posts are common methods for mobilizing resources and support.
Global Solidarity and Networking
Social media connects activists and supporters globally, fostering solidarity and knowledge exchange across borders. Movements like #BlackLivesMatter and #MeToo have transcended national boundaries, uniting people in a shared cause and creating a global network of advocacy.
Shaping Public Opinion and Discourse
Social media's influence extends beyond mobilization; it plays a critical role in shaping public opinion and discourse. The platforms provide a space for dialogue, debate, and the dissemination of diverse perspectives.
Amplification of Marginalized Voices
Social media gives a platform to voices that are often excluded from mainstream media. Activists, marginalized groups, and independent journalists use social media to highlight issues that may not receive adequate coverage, thereby influencing public awareness and opinion.
Viral Campaigns and Hashtags
Viral campaigns and hashtags can bring significant attention to specific issues, sparking widespread discussion and engagement. Hashtags like #FridaysForFuture, led by climate activist Greta Thunberg, have raised global awareness about climate change, influencing public discourse and policy debates.
Challenging Narratives and Counter-Narratives
Social media allows users to challenge dominant narratives and present counter-narratives. This democratization of information enables a broader range of perspectives to be heard, contributing to a more nuanced understanding of complex political issues.
Influencing Media and Political Agendas
The rapid spread of information on social media can influence traditional media coverage and political agendas. Journalists and policymakers often monitor social media trends to gauge public sentiment and identify emerging issues, which can lead to shifts in coverage and policy focus.
Challenges and Risks
While social media offers numerous benefits for political movements, it also presents significant challenges and risks. These include the spread of misinformation, the potential for echo chambers, and concerns about privacy and security.
Misinformation and Disinformation
The rapid dissemination of information on social media can lead to the spread of misinformation and disinformation. False or misleading content can easily go viral, influencing public perception and potentially undermining the credibility of political movements.
Echo Chambers and Polarization
Social media algorithms often prioritize content that aligns with users' existing beliefs and preferences, creating echo chambers that reinforce biases and contribute to political polarization. This can hinder constructive dialogue and compromise efforts to build consensus.
Surveillance and Censorship
Activists face risks of surveillance and censorship by governments or other actors. Authoritarian regimes may monitor social media activity, suppress dissenting voices, and restrict access to platforms to control the narrative and stifle opposition.
Data Privacy and Security
The collection and use of personal data by social media platforms raise concerns about privacy and security. The misuse of data can lead to targeted political manipulation and exploitation, as seen in the Cambridge Analytica scandal, where data was used to influence voter behavior.
The Future of Political Movements in the Digital Age
The digital age presents both opportunities and challenges for political movements. As social media continues to evolve, so too will its impact on politics. The future will likely see increased integration of digital tools in political activism, alongside ongoing debates about regulation, ethics, and the role of technology in society.
Digital Activism and New Technologies
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and virtual reality could further transform political activism. These technologies offer new ways to organize, secure, and visualize information, potentially enhancing the effectiveness of political movements.
Regulation and Ethical Considerations
The role of social media in politics raises important questions about regulation and ethics. Policymakers and technology companies will need to address issues related to content moderation, data privacy, and the prevention of harmful activities such as misinformation campaigns and cyberbullying.
Hybrid Movements and Offline Actions
While social media is a powerful tool for mobilization, effective political movements often combine online activism with offline actions. The interplay between digital and real-world activities will continue to be crucial in achieving lasting change.
Global Collaboration and Local Contexts
The global reach of social media enables international collaboration and solidarity, but political movements must also consider local contexts and dynamics. Effective activism requires an understanding of the specific cultural, social, and political factors that influence each region.
Conclusion
Social media has indelibly altered the landscape of global political movements, providing tools for mobilization, shaping public discourse, and amplifying diverse voices. However, the challenges it presents, such as misinformation, polarization, and privacy concerns, must be navigated carefully.
As political movements continue to leverage social media, the balance between harnessing its power and addressing its pitfalls will be critical in shaping the future of political activism and democratic engagement.