Natural Agriculture
Introduction:
Natural agriculture is a method of farming that emphasizes the use of natural processes and minimal human intervention. It is based on the principles of ecology and is often referred to as sustainable or regenerative agriculture.
Some key practices of natural agriculture include:
- Using cover crops to improve soil health and fertility
- Implementing crop rotations to reduce pest and disease pressure
- Using compost and other organic matter to build soil fertility
- Using natural pest control methods, such as companion planting and encouraging beneficial insects
- Avoiding synthetic fertilizers and pesticides
- Using non-mechanized equipment and techniques, such as hand tools and animal power, to minimize soil compaction and erosion

Practise and history of Natural Agriculture:
Natural agriculture is a farming method that emphasizes the use of natural processes and minimal human intervention. It is based on the principles of ecology and is often referred to as sustainable or regenerative agriculture. The practice of natural agriculture has a long history, with traditional farming practices that have been used for centuries in many cultures around the world.
In Asia, traditional farming practices such as Fukuoka's Natural Farming in Japan, and Sri Lanka's System of Rice Intensification (SRI) have been used for centuries. These practices are based on using natural processes to improve soil health and fertility and to control pests and diseases.
In the last few decades, there has been a renewed interest in natural agriculture, with farmers and researchers around the world experimenting with different techniques and practices. The development of the organic farming movement in the 1940s and 1950s helped to raise awareness of the benefits of natural agriculture and bring it to a larger audience.
In recent years, natural agriculture has gained popularity as a way to address the negative impacts of industrial agriculture, such as soil depletion, pesticide and fertilizer pollution and loss of biodiversity. Many farmers are now turning to natural agriculture as a way to improve the health and resilience of their farms, while also reducing their environmental footprint.
Benefits of Natural Agriculture:
There are several benefits of natural agriculture:
- Environmental benefits: Natural agriculture promotes the health and biodiversity of the ecosystem by using natural processes and minimizing human intervention. It also reduces the farm's carbon footprint by using animal power and reducing the use of fossil fuels. Additionally, natural agriculture can improve soil health and fertility which is crucial for long-term crop productivity.
- Economic benefits: Natural agriculture can improve the profitability of the farm in the long-term by reducing the dependence on external inputs and improving soil health and fertility. Additionally, natural farmers often sell their products directly to consumers which can result in higher profit margins.
- Social benefits: Natural agriculture can have a positive impact on the surrounding community. By using traditional seed varieties, produce is more adapted to local conditions and can have a higher nutritional value. By using traditional farming techniques, farmers can also pass down their knowledge and skills to future generations, which helps to maintain local cultures and traditions.
- Nutritional benefits: Natural agriculture can increase the nutritional value of produce by avoiding the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides which can lead to more nutrient-dense crops.
- Resilience benefits: Natural agriculture can improve the resilience of the farm to climate change by using traditional seed varieties that are adapted to local conditions, and by building and maintaining healthy soil.
In summary, natural agriculture can have a wide range of benefits, including environmental, economic, social, nutritional, and resilience benefits. It is a sustainable and holistic approach to farming that emphasizes the use of natural processes and minimal human intervention. It can help to promote the health and biodiversity of the ecosystem, improve soil health and fertility, and can have a positive impact on the surrounding community.
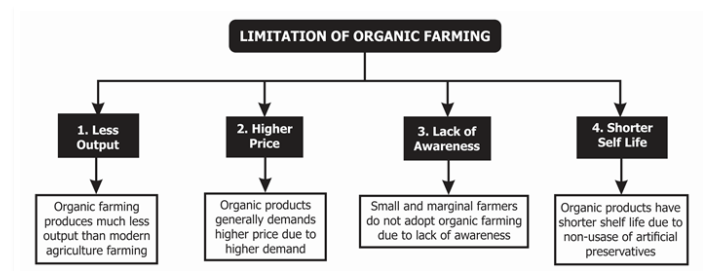
Drawbacks/Limitations of Natural Agriculture:
There are also some drawbacks of natural agriculture:
- Labor-intensive: Natural agriculture can be more labor-intensive than conventional farming, as it often requires more time and effort to implement.
- Lower yields: Natural agriculture may not produce as high of yields as conventional farming in the short term, as it focuses more on building soil health and biodiversity rather than maximizing production.
- Less predictable: Natural agriculture can be less predictable than conventional farming, as it relies more on natural processes and can be affected by factors such as weather and pest populations.
- Limited scalability: Some argue that natural agriculture may not be able to produce enough food to feed a growing global population, as it is more limited in scale than conventional farming.
- More expensive: Natural agriculture may have higher upfront costs for items such as cover crops, compost, and traditional seed varieties.
- Limited market: Natural agriculture products can be more expensive and harder to find in some areas, as these products are produced in limited quantities.
It's worth noting that the drawbacks of natural agriculture can vary depending on the specific context and location, and are not necessarily applicable to all natural farmers. Additionally, some of the drawbacks can be mitigated by using appropriate techniques and management strategies.
In summary, natural agriculture can have some drawbacks such as being labor-intensive, lower yields, less predictable, limited scalability, more expensive, and limited market. However, it's worth noting that the drawbacks of natural agriculture can vary depending on the specific context and location and some of them can be mitigated by using appropriate techniques and management strategies.
Aspects of Natural Agriculture:
Another key aspect of natural agriculture is the use of traditional and heirloom seed varieties. These varieties have been passed down through generations and are adapted to local conditions and climates. They are also often more resilient to pests and diseases and can better withstand extreme weather conditions. By using these traditional seed varieties, natural farmers can reduce their dependence on external inputs and improve the genetic diversity of their crops.
Another key aspect of natural agriculture is the use of animal power. Instead of relying on fossil fuels, natural farmers use animals such as horses and oxen to perform tasks such as plowing, planting and harvesting. This not only reduces the farm's carbon footprint, but it also improves soil health, reduces erosion, and improves the overall biodiversity of the farm ecosystem.
It's also worth noting that natural agriculture can also have a positive impact on the surrounding community. By using local seed varieties, produce is more adapted to local conditions and can have a higher nutritional value. By using traditional farming techniques, farmers can also pass down their knowledge and skills to future generations, which helps to maintain local cultures and traditions.
conclusion:
In conclusion, natural agriculture is a holistic and sustainable approach to farming that emphasizes the use of natural processes and minimal human intervention. It includes the use of traditional seed varieties, the maintenance of healthy soil, the use of animal power, and a focus on the overall ecosystem of the farm. The benefits of natural agriculture include environmental, economic, social, nutritional, and resilience benefits. It can help to promote the health and biodiversity of the ecosystem, improve soil health and fertility, and can have a positive impact on the surrounding community. However, natural agriculture also has some drawbacks such as being labor-intensive, lower yields, less predictable, limited scalability, more expensive, and limited market. It is important to consider the specific context and location when evaluating the benefits and drawbacks of natural agriculture and to use appropriate techniques and management strategies.




























































![Nekodex – Earn 20K+ NekoCoin ($20) [Highly Suggested]](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/b4f0a940-f27c-4168-8aaf-42f2974a82f0/1)






