What Distinguishes Obesity from Being Overweight?
Overweight and obesity are both terms used to describe a body mass index (BMI) that is higher than what is considered healthy. However, there is a difference between the two conditions.
Overweight is defined as a BMI of 25 to 29.9. Obesity is defined as a BMI of 30 or higher.
A BMI is a measure of body fat based on height and weight. It is calculated by dividing a person's weight in kilograms by their height in meters squared.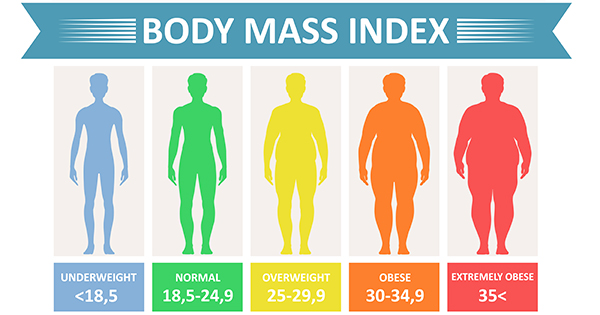
A BMI of 25 or higher is considered overweight because it is associated with an increased risk of developing health problems such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer.
A BMI of 30 or higher is considered obese because it is associated with an even greater risk of developing these health problems.
In addition to BMI, there are other factors that can help to distinguish obesity from being overweight. These factors include:
- Body fat distribution: People with obesity tend to have more body fat around their waist than people who are overweight. This is known as abdominal obesity, and it is a risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and other health problems.
- Waist-to-hip ratio: The waist-to-hip ratio is a measure of body fat distribution. It is calculated by dividing the waist circumference by the hip circumference. A waist-to-hip ratio of 0.8 or higher for women and 0.9 or higher for men is considered to be a risk factor for heart disease and other health problems.

- Physical activity: People with obesity are less likely to be physically active than people who are overweight. Physical activity can help to reduce body fat and improve health.
- Diet: People with obesity are more likely to eat a diet that is high in calories and unhealthy fats. A healthy diet can help to reduce body fat and improve health.
 If you are concerned about your weight, talk to your doctor. They can help you to determine if you are overweight or obese and can discuss treatment options with you.
If you are concerned about your weight, talk to your doctor. They can help you to determine if you are overweight or obese and can discuss treatment options with you.
Here are some tips for preventing or managing obesity:
- Eat a healthy diet: This includes eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It also means limiting your intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
- Be physically active: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity most days of the week.
- Lose weight gradually: Aim to lose 1-2 pounds per week.
- Make lifestyle changes that you can stick with: This includes finding healthy ways to manage stress, getting enough sleep, and avoiding smoking.
With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, it is possible to lose weight and improve your health.
Health Practitioner point of view on obesity:
As a health practitioner, I see the effects of obesity on a daily basis. Obesity is a complex disease that is caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, environment, and lifestyle. It is a serious health problem that can lead to a number of other health conditions, including heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer.
One of the most important things that I can do as a health practitioner is to help people understand the risks of obesity and to provide them with resources to help them lose weight and improve their health. I also work to dispel the myths about obesity and to help people understand that it is a treatable condition.
I believe that the best way to prevent obesity is to focus on prevention. This means teaching children about healthy eating and physical activity from a young age. It also means creating environments that make it easier for people to make healthy choices.
If you are concerned about your weight, talk to your doctor. They can help you to determine if you are overweight or obese and can discuss treatment options with you. There are many effective treatments for obesity, and with the right help, it is possible to lose weight and improve your health.
Here are some additional thoughts from a health practitioner's point of view:
- Obesity is a chronic disease, and it is important to treat it as such. This means making long-term lifestyle changes, not just trying to lose weight quickly.
- There is no one-size-fits-all treatment for obesity. The best treatment for you will depend on your individual needs and circumstances.
- It is important to be patient and persistent when trying to lose weight. It takes time and effort to make lasting changes.
- There are many resources available to help you lose weight and improve your health. Talk to your doctor, a registered dietitian, or a certified personal trainer for more information.
Is Obesity Hereditary?
Obesity is a complex disease that is caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, environment, and lifestyle. Genetics is thought to play a role in about 40% to 70% of the risk of obesity. This means that if you have a family history of obesity, you are more likely to be obese yourself.
There are a number of genes that have been linked to obesity. These genes affect how the body processes food, stores energy, and responds to hormones. Some genes are more common in people who are obese, but they do not guarantee that someone will be obese.
The environment also plays a role in obesity. This includes factors such as diet, physical activity, and stress. People who live in obesogenic environments, such as those with easy access to unhealthy food and limited opportunities for physical activity, are more likely to be obese.
Lifestyle factors also play a role in obesity. This includes factors such as diet, physical activity, and sleep. People who eat a lot of unhealthy food, do not get enough physical activity, and do not get enough sleep are more likely to be obese.
It is important to remember that obesity is not just a matter of willpower. It is a complex disease that is caused by a combination of factors. If you are concerned about your weight, talk to your doctor. They can help you to determine if you are at risk for obesity and can discuss treatment options with you.
Here are some additional thoughts on the role of genetics in obesity:
- Genes can make it more difficult to lose weight. People who have certain genes may have a harder time losing weight than people who do not have those genes. This is because the genes may affect how the body processes food and stores energy.
- Genes can make it more likely to gain weight. People who have certain genes may be more likely to gain weight than people who do not have those genes. This is because the genes may affect how the body responds to food and hormones.
- Genes can interact with the environment to increase the risk of obesity. For example, people who have certain genes may be more likely to gain weight if they live in an obesogenic environment.
It is important to remember that genes are not destiny. Even if you have a family history of obesity, you can still lose weight and improve your health. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, it is possible to lose weight and improve your health.