Bitcoin as a Store of Value: Unraveling the Digital Gold Narrative
 Since its inception in 2009, Bitcoin has evolved from a mere experiment in decentralized digital currency to a financial phenomenon that has captured the imagination of investors and technologists alike. While Bitcoin's potential as a medium of exchange has been widely discussed, an increasingly prevalent narrative positions it as a "store of value," drawing parallels with traditional safe-haven assets like gold. In this essay, we will explore the key attributes that contribute to Bitcoin's emergence as a store of value and the implications of this evolving narrative.
Since its inception in 2009, Bitcoin has evolved from a mere experiment in decentralized digital currency to a financial phenomenon that has captured the imagination of investors and technologists alike. While Bitcoin's potential as a medium of exchange has been widely discussed, an increasingly prevalent narrative positions it as a "store of value," drawing parallels with traditional safe-haven assets like gold. In this essay, we will explore the key attributes that contribute to Bitcoin's emergence as a store of value and the implications of this evolving narrative.
Decentralization and Security:
One of the foundational principles of Bitcoin is its decentralized nature. Operated on a distributed ledger called the blockchain, Bitcoin operates without a central authority, making it resistant to censorship and manipulation. The decentralized network ensures the security and integrity of transactions, fostering trust among users. This inherent resilience has contributed to Bitcoin's perception as a reliable store of value in an era where concerns about centralization and manipulation of traditional financial systems loom large.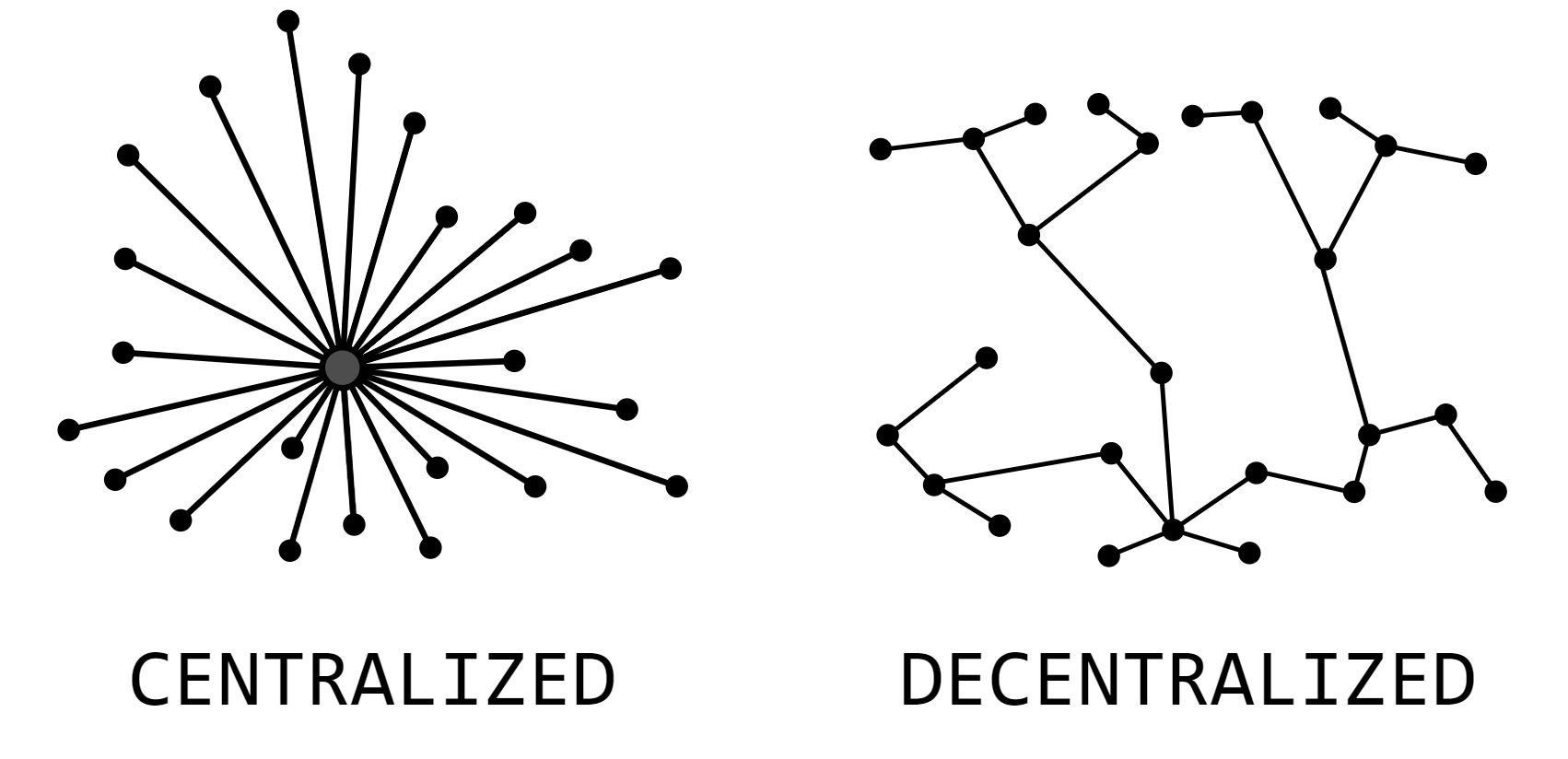
Limited Supply: Digital Gold Analogies
A defining characteristic that has fueled the store of value narrative is Bitcoin's capped supply. With a maximum limit of 21 million coins, Bitcoin scarcity is analogous to precious metals like gold. This scarcity is embedded in the protocol and mitigates the risk of inflation traditionally associated with fiat currencies. Investors, drawing parallels with gold's status as a hedge against inflation, view Bitcoin as "digital gold," a finite asset with the potential to retain value over time.
Immutable and Transparent Ledger:
Bitcoin's underlying technology, blockchain, provides an immutable and transparent ledger of all transactions. Every transaction is recorded and time-stamped, creating a transparent and publicly accessible record of ownership. This transparency adds an additional layer of trust for those seeking a store of value. The unforgeable nature of the blockchain ensures the integrity of the historical record, reinforcing Bitcoin's credibility as a reliable asset.
Global Accessibility and Portability:
Bitcoin's digital nature makes it highly accessible and portable, transcending geographical boundaries. This characteristic is particularly appealing in a globalized world where traditional store-of-value assets may face challenges related to cross-border transactions and storage. Bitcoin's ease of transfer and storage appeals to those seeking a borderless and efficient store of value, especially in regions where economic instability or capital controls are prevalent.
Market Adoption and Institutional Interest:
The narrative of Bitcoin as a store of value has gained traction with the growing adoption of cryptocurrencies. Institutional investors, including hedge funds and publicly traded companies, have started to recognize Bitcoin as a viable asset class for portfolio diversification. High-profile endorsements from influential figures and corporations have contributed to the mainstream acceptance of Bitcoin as a store of value, signaling a shift in the perception of cryptocurrencies from speculative instruments to long-term stores of wealth.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Bitcoin's evolution as a store of value is a multifaceted phenomenon driven by its decentralization, limited supply, transparency, global accessibility, and increasing institutional interest. The digital gold narrative has reshaped perceptions of Bitcoin from a mere speculative asset to a potential cornerstone of diversified investment portfolios. As the cryptocurrency ecosystem continues to mature and adapt to changing economic landscapes, the concept of Bitcoin as a store of value is likely to remain a focal point of discussion and exploration in the broader financial narrative.






































