The Graph
The Graph is a blockchain project that provides a database querying protocol and network infrastructure for decentralized applications (DApps). Operating on the Ethereum blockchain, The Graph enables developers to efficiently retrieve and query data in a fast and effective manner.
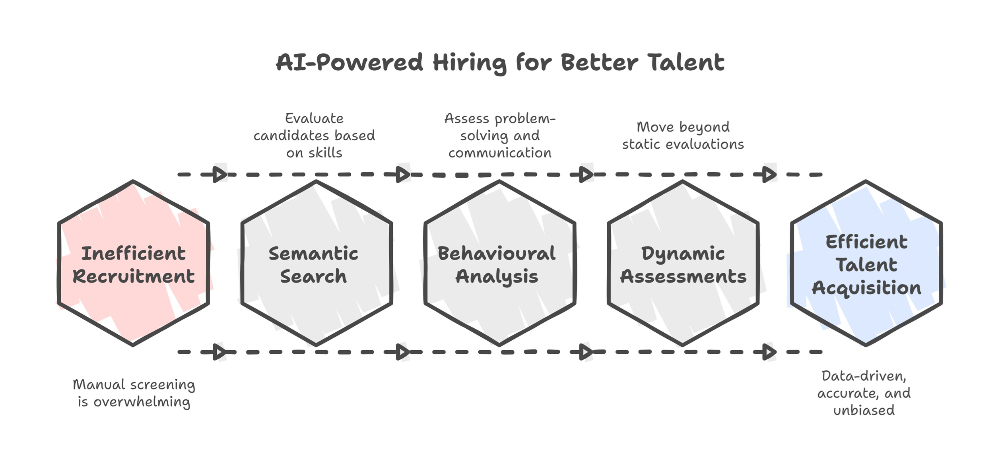
The primary objective of The Graph is to empower blockchain-based applications (DApps) to manage their database queries more efficiently. Similar to traditional databases, blockchain data can often be complex and scattered. The Graph offers a protocol to organize, index, and fetch this data rapidly.
Additionally, The Graph utilizes modular components called "subgraphs" to allow the creation of custom data structures for a specific DApp or protocol. This enables each DApp to build its own data structure tailored to its needs and retrieve only the data relevant to its requirements.
The core aim of The Graph project is to assist decentralized applications in achieving better performance, scalability, and flexibility in database queries.
The advantages of The Graph for blockchain projects include:
- Data Efficiency: The Graph enhances database queries, allowing developers faster access to blockchain data. This enables DApps to respond more quickly and operate more efficiently.
- Modular Data Structures: The concept of subgraphs enables each DApp to create its own custom data structure and access only the necessary data. This can reduce unnecessary data transfer, lowering network traffic and transaction costs.
- Scalability: The Graph may offer scalability advantages. Efficient management of database queries can reduce the load on the network, potentially increasing the capacity to serve a larger user base.
- Open Source and Community Engagement: The Graph project is open source and supported by a broad developer community. This allows for continuous development and updates to the project.
- Valuable Data Indexing: The Graph indexes blockchain data, providing developers with the capability to perform fast and effective queries. This is a crucial advantage for data analysis and enabling more complex functionality in DApps.
However, like any technological solution, the use and advantages of The Graph can vary depending on the project context, requirements, and other factors.
The disadvantages of The Graph include:
- Compatibility with Decentralization Principles: While The Graph operates on decentralized blockchain networks like Ethereum, it may not provide a sufficient level of decentralization for some users or projects. This could lead users to seek additional options and solutions.
- Data Update Delays: Due to the inherent structure of blockchains, adding new data to a blockchain can take a certain amount of time, resulting in delays in updating data on The Graph. This can be a disadvantage for real-time applications.
- Developer Training: To fully leverage the potential of The Graph, developers may need to undergo a specific training process to understand and use the project correctly. This could require additional effort from some developers.
- Project Dependency: The dependency of DApps on The Graph means that if issues arise in the project lifecycle or if the project is halted during development or maintenance, DApps may encounter problems with data retrieval and querying.
- Network Costs: Solutions based on blockchain are generally associated with transaction costs. Using The Graph, especially since it operates on the Ethereum network, may include the gas costs of the Ethereum network.
As with any technological solution, the advantages and disadvantages of The Graph can vary depending on project requirements and use case scenarios. Therefore, conducting a detailed analysis to evaluate its suitability for a project is crucial.
Thank you all for reading. Don't forget to comment and follow.