Unlocking the Enigma of Zero-Knowledge Proofs

Understanding Zero-Knowledge Proofs:
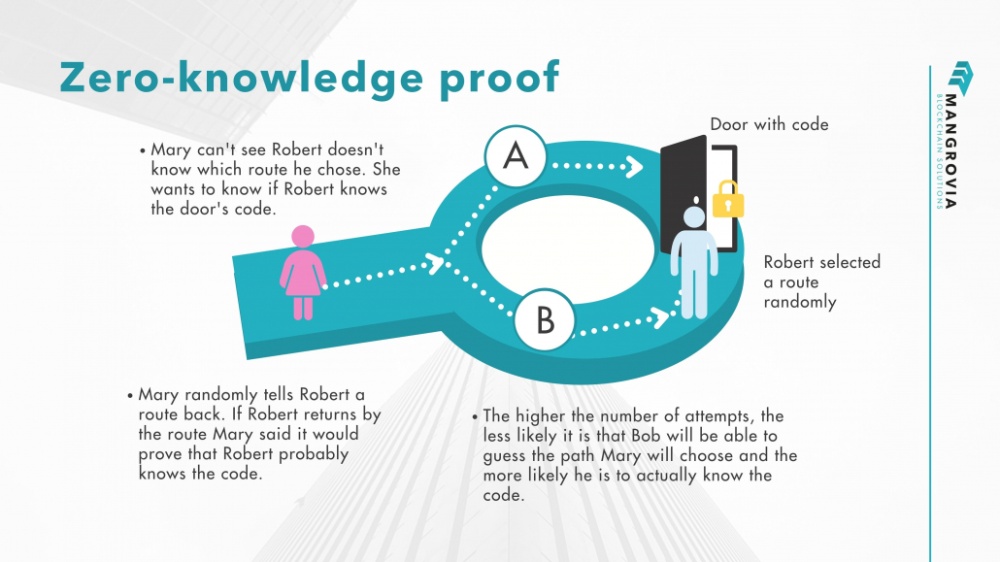
Zero-knowledge proofs, in the realm of cryptography, refer to a method where one party (the prover) can convince another party (the verifier) that they know a specific piece of information without revealing the information itself. This is achieved through a series of interactive protocols where the prover demonstrates knowledge of a secret without actually disclosing it.
Key Components of Zero-Knowledge Proofs:
- The Secret:
- At the core of a zero-knowledge proof is the existence of a secret or a piece of information that the prover aims to convince the verifier of knowing. This secret could be a password, a cryptographic key, or any sensitive data.
- Interactive Protocols:
- The proof involves a series of interactive protocols between the prover and the verifier. During these interactions, the prover provides evidence of their knowledge without explicitly revealing the secret. These protocols are designed to be efficient, ensuring that the verification process is quick and reliable.
- Completeness, Soundness, and Zero-Knowledge:
- A zero-knowledge proof must satisfy three fundamental properties: completeness (the honest prover convinces the honest verifier), soundness (a dishonest prover cannot convince an honest verifier), and zero-knowledge (the verifier learns nothing about the secret).
Applications of Zero-Knowledge Proofs:
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies:
- Zero-knowledge proofs have found extensive applications in blockchain and cryptocurrencies, enhancing privacy and security. Zcash, for example, utilizes a zero-knowledge proof called zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Arguments of Knowledge) to enable private transactions without disclosing the transaction details.
- Authentication and Access Control:
- Zero-knowledge proofs can be employed in authentication systems without revealing sensitive information. This is particularly useful in scenarios where proving identity is necessary, such as accessing secure facilities or logging into systems.
- Digital Voting:
- Zero-knowledge proofs have the potential to revolutionize digital voting systems by allowing voters to prove the validity of their vote without disclosing the actual vote. This ensures the integrity of the voting process while preserving individual privacy.
Challenges and Future Developments:
While zero-knowledge proofs offer promising solutions to privacy concerns, challenges such as implementation complexity and potential vulnerabilities still exist. Ongoing research and advancements aim to address these issues and further enhance the applicability of zero-knowledge proofs.
Conclusion:
Zero-knowledge proofs represent a groundbreaking advancement in the field of cryptography, offering a delicate balance between privacy and security. As our digital world continues to expand, the importance of preserving sensitive information becomes paramount. The ability to prove knowledge without divulging actual data opens up new possibilities for secure interactions and holds the potential to redefine how we approach privacy in the digital age.