How do liquidity pools work?
Basically a liquidity pool takes two tokens and pairs them to create a market. We have token A and token B. At the creation of the pool exactly 50% of value of token A and 50% of value of token B need to be added as liquidity to the pool. If after the pool creation, somebody swaps A to get B, we will see more tokens A in the pool than tokens B. However, the value of each token remains the same. In other words, token B will have gained value and token A will have lost value. This is not that easy to explain with words. So let's take this illustration: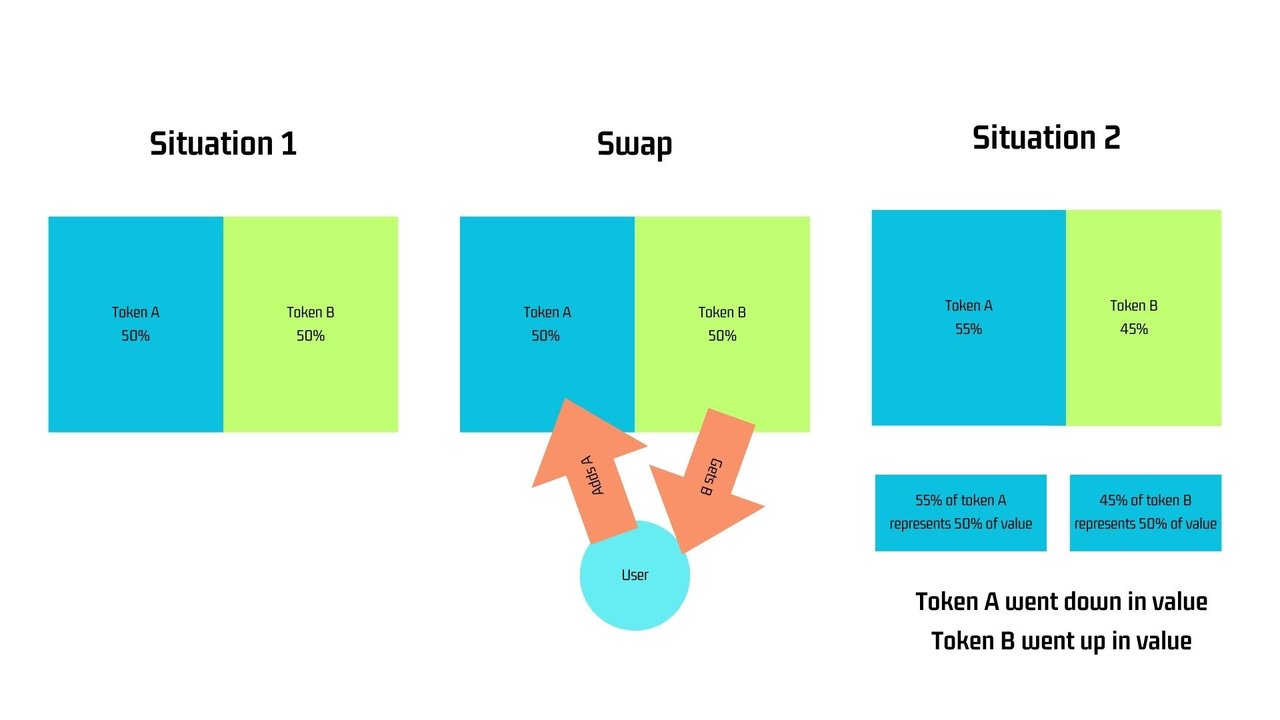 After the swap we have more token A than before and less token B. Both tokens are still worth 50% of the value however. There are more tokens A for the same value and therefore the value of A went down. There are less tokens B for the same value and therefore the value of B went up.
After the swap we have more token A than before and less token B. Both tokens are still worth 50% of the value however. There are more tokens A for the same value and therefore the value of A went down. There are less tokens B for the same value and therefore the value of B went up.
With each transaction, things are recalculated and that's how at any time a liquidity pool can give a price to a token in respect to its paired token. This is actually such a big step forward from the traditional order book market where you could sell your title only if there was a buyer for the title. In addition to that, the price to buy and sell are the same. There is no spread other than the fee that for each pool is predefined. With traditional order books, you had to pay the spread and in addition to that fees that were added by the broker also called courtage.
The variables of liquidity pools
To understand liquidity pools better, it's important to look at what differentiates them. Of course we first to have to look at the tokens that are combined. You can have two stable coins paired. One stable coin and one volatile coin or two volatile coins. The look for the perfect pair of tokens is the most important factor when using liquidity pools.
Size of the liquidity
An important factor is how much liquidity is in a pool. When you want to swap tokens, it is very important to have a high liquidity. The more the better. With little liquidity, your swap can provoke a big change of price, also called slippage. If for example you have a pool with 10$ SOL and 10$ USDC, when you want to swap 5$ you will change the price dramatically and you will get a very bad change. If you have a pool with 100'000 $ of each token, your swap will have a minimal impact on the price and your exchange will be very close to market prices.
However, if you want to provide liquidity it is also important that there is not too much liquidity involved. The more liquidity, the more the fees will be spread among the liquidity providers.
Fees
Another important aspect are the fees that are deducted from each swap. These fees normally go in majority to the liquidity providers. For the person who swaps, little fees are an advantage but for somebody providing liquidity maybe a bit higher fees wouldn't be bad. What we should keep in mind is that very high fees will reduce the quantity of transactions. People will want to pay as little as possible for transacting and if the fees are too high, there will be less transactions and therefore few fees for liquidity providers.
The blockchain
It really matters where your liquidity pool is located. When providing liquidity or swapping tokens, you will need to pay network fees and there are big differences between the blockchains. Etherum is known for its high fees. Other chains like SUI or Solana have much lower fees. For swapping and providing liquidity its best to opt for chains with low fees.
The transaction volume
The quantity of transactions matters mainly if you want to provide liquidity. The more transactions, the more fees you will generate. When you need to chose, always go for the pool with more transactions.
The return
On the different platforms, you often get an indication of the return that you can expect in pools. This is often calculated on a historic basis over the last days and it can't be taken as guarantee for further returns. It's important to understand that on some platforms you get ab indication on the return per 24h and on others on a yearly return.
Concentrated vs normal liquidity pools
Most modern platforms offer nowadays the concept of concentrated liquidity pools. In the next post, I will explain the difference between a normal and a concentrated liquidity pool.