Supra IntraLayer
Plug-and-Play Microservices for a Cross-Chain Economy
Built to scale for the most demanding use cases and backed by peer-reviewed research, Supra is setting a new gold standard for efficiency, security, and user experience by synthesizing a vertical stack of Web3 modules within a shared security environment.
Table of Contents
- The Next Generation Blockchain is an IntraLayer
- Supra's Chained Moonshot Consensus
- DORA the Supra Oracle Network
- Supra Distributed Verifiable Random Function
- Supra HyperNova: Cross-Chain Relay Protocol
- HyperLoop: Robust Pairwise Bridge
- Optimal Harmony Between Modular and Monolithic
The Next Generation Blockchain is an IntraLayer
After years of research and development, the time has come to unveil what is really under Supra’s hood and kick the tires around, so to speak. Indeed, Supra’s advancements in research on distributed systems and secure computation are paving the way for improved user experiences in DeFi across a number of use cases.
Each product or microservice offered by Supra was carefully engineered from first principles. The aim is to optimize for both security and efficiency while maintaining L1 security guarantees when interoperating with external networks.
The secret sauce of the Supra ecosystem lies in how the products and microservices are natively integrated, sharing the same best-in-class security guarantees from the L1 consensus on up the stack. This translates to a more efficient network, better end-user experiences, and better gas efficiency. In other words, the whole suite of decentralized services is optimized for performance — the novel consensus mechanism, the oracle price feeds, verifiable random functions, and secure cross-chain bridges.
As one, they are superior tools for projects of all kinds to leverage. When considered together, they present a turning-point for the Web3 user and developer experience as liquidity is no longer bound by a single chain but consolidated via a new kind of Layer 1, an all-in-one IntraLayer featuring first-class native microservices which had previously required third parties, an arduous process, and additional security risks.
From a liquidity perspective, Supras IntraLayer consolidates what was once a myriad of complicated steps into a streamlined user experience, making DeFi into the unified and coherent experience that is necessary to scale the industry for enterprise use cases. Fragmented liquidity in the form of assets on different chains will soon be a thing of the past. Here is an overview of the IntraLayer, at least what can be revealed for now.
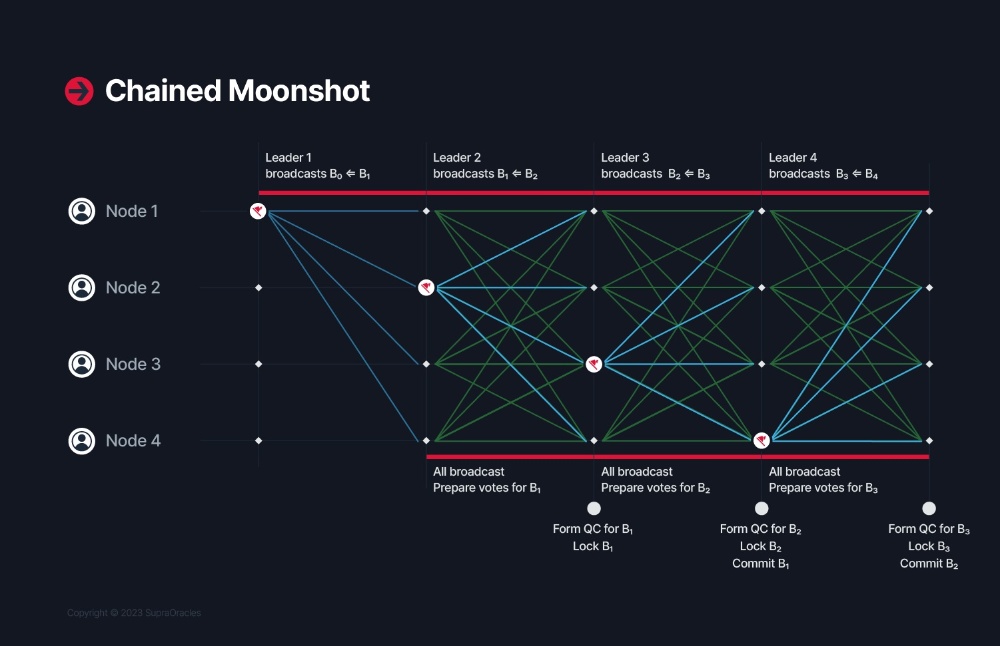
Supra’s Chained Moonshot Consensus
As for the L1 of Supra itself, the network’s mechanism significantly surpasses the capabilities of its predecessors Tendermint (Cosmos), Hotstuff (Libra), & Jolteon (Aptos) when it comes to block finalization throughput and latency. Anti-collusion and anti-frontrunning redundancies have also been carefully implemented to protect against external attacks, adaptive adversaries, or Byzantine nodes from conspiring to benefit from asymmetrical knowledge.
Legacy projects still running these older consensus mechanisms are simply less capable of keeping up with this fast-paced industry. However, Chained Moonshot offers the basis for a truly remarkable ecosystem of lightning-fast transactions and near-instant finality in only two blocks. This is thanks in part to a novel Two-Phase Commit design featuring Quorum Certificate chaining and block proposal pipelining.
This basically means that the consensus process uses asynchronous but overlapping blocks for better efficiency and network availability. What’s more, this breakthrough has already been formally verified by Microsoft’s Ivy, the gold standard when it comes to demonstrating the security guarantees of distributed systems.
In a world of high stakes global value transfers, formal verification is necessary in order for enterprise organizations to run their businesses on public rails at scale. This is the foundation for the next technological leap forward for the smart contract economy and provides the kind of secure yet seamless user experience for which we all yearn.
DORA the Supra Oracle Network
The Supra IntraLayer also includes native oracle price feeds, cryptographically verifying and reporting on over 300 price pairs to roughly 50 different L1 and L2 destinations, and the list is growing on a weekly basis. Using a bespoke Tribes and Clans model, the Supra oracle network, DORA, creates a division of labor to validate data which fosters efficient and secure block finalization.
Likewise, oracle nodes, Tribes, Clans, and the commodity on which they fetch and report data are shuffled periodically to perpetuate the security of the network across time. These additional layers of randomness are generated by Supra’s VRF algos to safeguard against static adversaries, Byzantine behavior, frontrunning bots, and other collusion techniques before they ever get the chance to manifest.
DORA not only gathers and verifies data but also detects irregularities, filtering out unreliable inputs to provide accurate information to contracts.
This plays a crucial role in the tokenization of assets like real estate, stocks or government bonds, meaning they are turned into digital tokens for on-chain trading. That means increased access to financial products and services for people around the world who are lacking, not to mention increased efficiency, liquidity, and cost-effective ways to transact with peers.
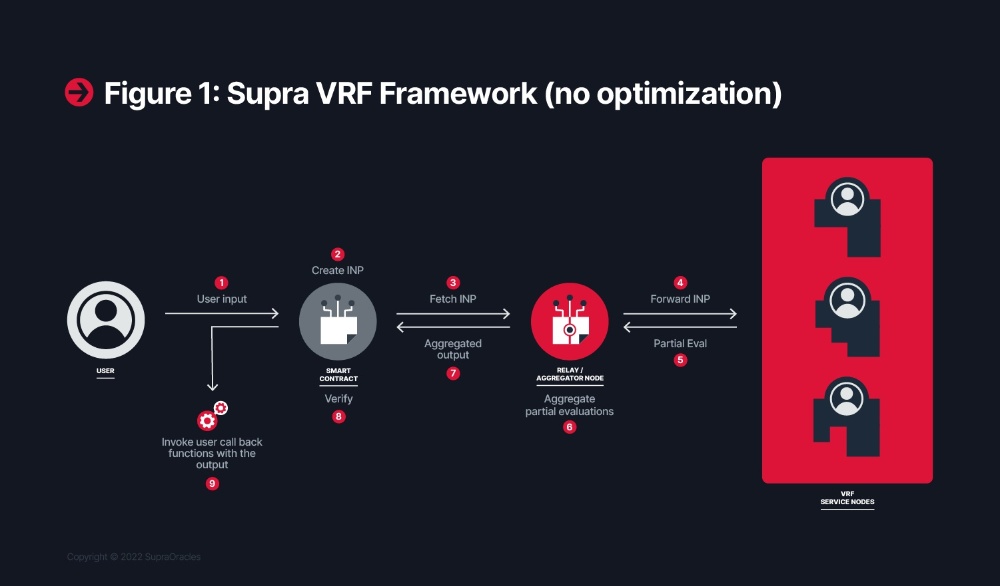
Supra Distributed Verifiable Random Function
As for Supra’s dVRF, this deterministic algorithm leverages cryptographic primitives to generate random outputs based on a secret key and an input. As such, the dVRF’s random outputs are unpredictable to participants beforehand, yet the fidelity and fairness of outputs is easily verified on-chain afterwards.
This is useful for gaming applications, lotteries, and generative art. Say a developer wants to randomly generate a collection of loot boxes with a variety of contents based on rarity scores — Supra’s dVRF is on the job. Here’s how it works when users open their loot boxes.
First, dVRF clans “listen” for random number generation requests, take inputs and construct partial keys to generate tamper-proof randomness along with an on-chain proof of its fidelity. For instance, a DeFi user comes along and opens a loot box within a dApp, initiating an RNG request and “spending” their loot box.
The optimized version allows for multiple concurrent requests and a more gas-efficient batching of RNG requests.
This request is done by distributed sets of nodes to maintain the unpredictability and integrity of the whole experience. These VRF nodes produce partial signatures, akin to the scattered pieces of a puzzle, which prevents tampering or unfairly anticipating outputs beforehand.
Next, VRF clans aggregate these partial signatures to collaboratively form a threshold signature. This aggregated signature is then securely written onto the destination blockchain, providing a history of provenance and public verifiability. The generated random number is inextricably linked to the potential prizes available, meaning a number corresponds to the contents of the opened loot box.
Every step, from the initial request for RNG to the delivery of the loot box contents, is transparently recorded on the blockchain. This transparency not only ensures the integrity of the process but also allows users and observers to validate outcomes, lending credibility to chance events which use random sampling and RNG.
Supra HyperNova: Cross-Chain Relay Protocol
In a multi-chain, decentralized smart contract economy, speed is more than an advantage—it’s essential to conducting business. Natively, dApps run smart contracts that are compatible with their own blockchain ecosystems and consensus mechanisms, and therefore transferring those assets to a different chain has been tedious, costly, and even risky to move.
HyperNova addresses this pain point by providing cross-chain liquidity without the single-point-of-failure risks accompanying traditional bridge setups. Instead of performing a complicated escrow service, Supra’s HyperLoop fetches block finalization from source chains and then relays the settled transactions to destination chains with additional proof of authenticity by the Supra blockchain.
HyperNova relay nodes therefore successfully leverage the source chain’s L1 security guarantees, with an additional validation being processed on the Supra chain. This contrasts starkly with the usual multisig escrow protocols for bridges which introduce single points of failure and other additional risks.
HyperLoop: Robust Pairwise Bridge
Similar to HyperNova in that it facilitates cross-chain liquidity, Hyperloop is a pairwise bridge protocol that connects two blockchains, enabling information and asset transfers between them. There are three main actors in – a network of bridge nodes to form consensus on new blocks, a set of whistle-blower nodes to oversee operations, and AuditDAO for settling disputes.
HyperLoop’s bridge nodes run clients of both the source and destination chains to follow the events on them. The whistle-blower nodes also run both clients and constantly monitor the actions of the bridge nodes to detect anomalies.
These whistleblower nodes raise objections upon the detection of double-spending or Byzantine behavior and report them to AuditDAO. Of course, bridge nodes are required to stake a predetermined amount of tokens, and whistle-blower nodes are also required to stake assets in escrow when raising objections. This prevents spamming of the network or malicious use of the whistleblower functionality.
Upon having an objection successfully rendered legitimate, the staked assets of the Byzantine bridge nodes would be slashed and a portion would be paid as a reward to the corresponding whistle-blower nodes, another portion to AuditDAO, and the protocol’s insurance fund. Whistle-blower nodes are also rewarded for their efforts as an oversight committee. In contrast, the bond posted by objecting whistleblowers would be withheld if they were determined to be falsely reported.
Optimal Harmony Between Modular and Monolithic
Exploring Supra’s vertically-integrated stack of native services reveals that it is both modular and monolithic. That is to say that it is both plug-and-play interoperable with other chains, yet vertically-integrated, high-performing, and reliable as demonstrated by Microsoft’s Ivy Formal Verification.
To recap, devs can leverage Supra’s Moonshot for the strongest L1 security guarantees and enjoy near-instant settlements. Add a native stack of microservices which are also interoperable with other chains and you have a new level of composability. Additionally, Move smart contracts allow for the sort of security and flexibility that has never been seen before.
Native, anti-fragile oracles make cross-chain interoperability a breeze without single-point-of-failure risks. With Supra’s dVRF, dApps have access to a simple yet elegant method to provide on-chain randomness for chance events, demonstrating that they were conducted in unbiased and tamper-proof ways.
Supra’s HyperNova and HyperLoop Bridgeless Relay services secure cross-chain swaps while enjoying the same L1 security guarantees on the source and destination chains. That is to say that users of the Supra Liquidity Network will enjoy unmatched levels of optionality and liquidity.
Supra’s IntraLayer is the most performant and scalable network of its kind in the world. As such, builders in the ecosystem are poised to scale their work along with the industry, and well beyond. After all, Supra has big dreams, and is driven by an ethos of decentralization and fairness coupled with a passion for providing the best experience possible for end-users and builders alike.
Read Next
- What are Oracles?
- Verifiable Random Functions: Fair Play in a Decentralized World
- Restaking: Adding Token Utility



























![[LIVE] Engage2Earn: auspol follower rush](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/c1a761de-5ce9-4e9b-b5b3-dc009e60bfa8/1)







![[ℕ𝕖𝕧𝕖𝕣] 𝕊𝕖𝕝𝕝 𝕐𝕠𝕦𝕣 𝔹𝕚𝕥𝕔𝕠𝕚𝕟 - And Now What.... Pray To The God Of Hopium?](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/79e7827b-c644-4853-b048-a9601a8a8da7/1)
