What Is Phishing and How Does It Work?
How Phishing Works
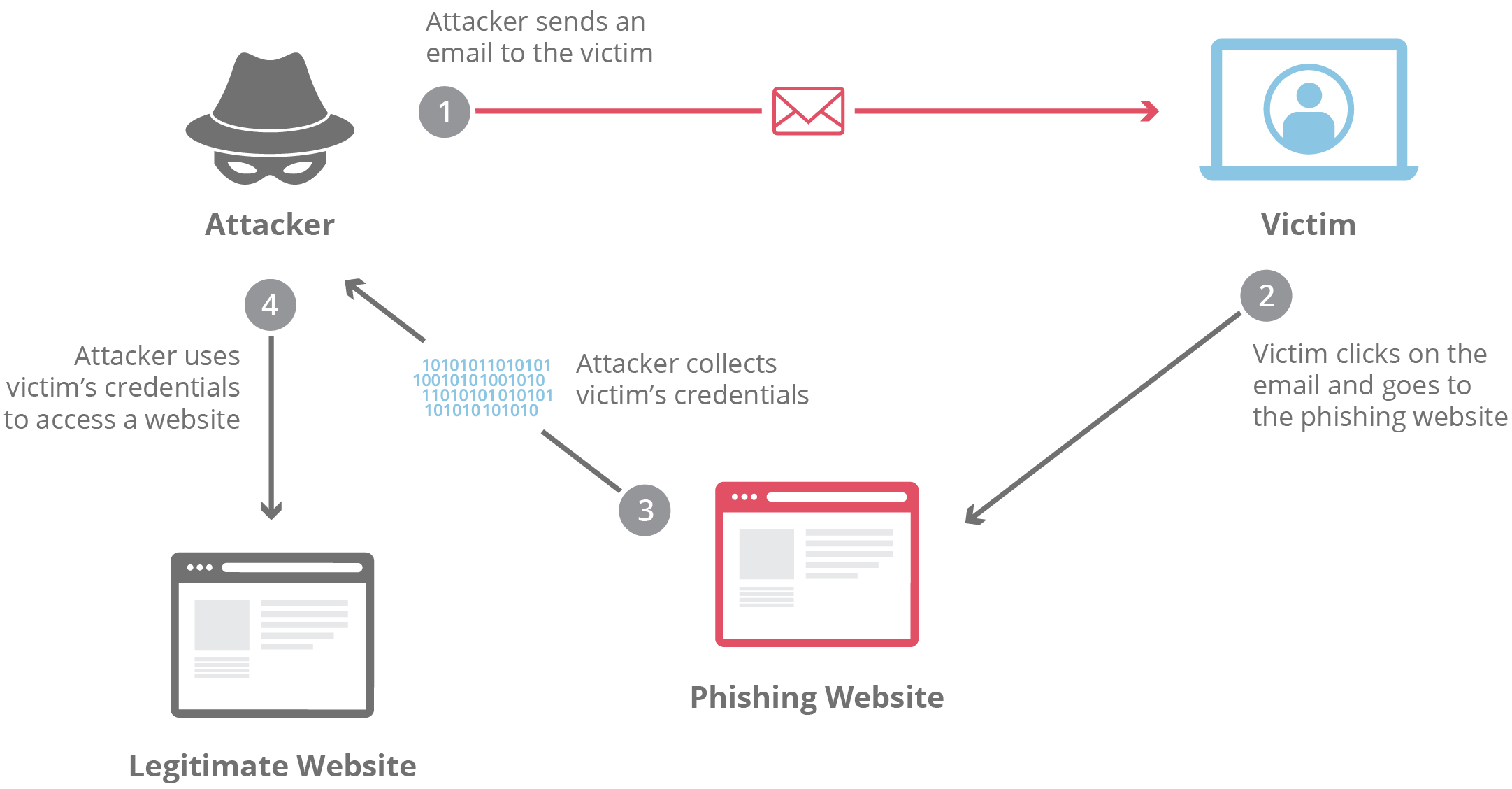
- The Bait: You'll get an email, text message, or social media message that looks like it's from a real source. It might be your bank, a streaming service, or even someone you know.
- The Sense of Urgency: The message will often create a sense of urgency. It might say things like:"Your account has been compromised!"
- "You've won a prize!"
- "There's a problem with your payment!"
- The Fake Link or Attachment: The message will have a link or an attachment. If you click the link, it'll take you to a fake website that looks almost identical to the real thing. If you open the attachment, it might download malware onto your computer.
- The Trap: Once you're on the fake website or have malware on your device, the scammers will try to get you to enter your personal information. This could be your login details, credit card info, etc.
- The Payoff (For the Scammer): Once they have your info, they can:Steal your money
- Open accounts in your name
- Sell your info to other criminals
Recognizing Phishing Attempts
Common Red Flags of Phishing Attempts
- Urgent or Threatening Language: Phishers often try to scare you into acting quickly. Look out for phrases like:
- "Your account will be closed if you don't act now!"
- "You've been hacked! Click here to reset your password."
- "Urgent security alert!"
- Too-Good-To-Be-True Offers: Be wary of unexpected prizes, free gifts, or unbelievable deals. These are designed to make you click without thinking.
- Requests for Personal Information: Legitimate companies will NEVER ask for sensitive information like the following through email, text, or pop-up messages:
- Passwords
- Social Security numbers
- Credit card numbers
- Bank account details
- Sloppy Grammar and Spelling: Phishing emails are often riddled with typos and grammatical errors. Reputable companies carefully proofread their communications.
- Suspicious Links or Attachments:
- Links: Hover over links (without clicking) to see the actual web address. Does it match the company's real website? Look for subtle misspellings or extra characters.
- Attachments: Never open attachments from unknown senders. They could contain malware.
- Generic Greetings: Phishers often use generic greetings like "Dear Customer" instead of your actual name.
How to Prevent Phishing Attacks

Technical Defenses
- Anti-Phishing Software: Install reputable security software that includes anti-phishing filters and real-time website reputation checks. This software can help block fake websites and warn you about suspicious links.
- Firewall: A firewall can be your first line of defense, blocking unauthorized access attempts to your network or device.
- Spam Filters: Use email spam filters to catch many phishing emails before they reach your inbox. Make sure these are updated regularly
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA on your accounts whenever possible. This adds an extra layer of security, typically requiring a code sent to your phone or generated by an authenticator app in addition to your regular password.
Personal Best Practices
- Be Skeptical: Approach all unsolicited emails, texts, and social media messages with a healthy dose of skepticism. Don't be easily swayed by urgency or too-good-to-be-true offers.
- Inspect Links and Sender Addresses:
- Hover over links to see the true destination before clicking. Look for subtle misspellings or unusual domains.
- Check the sender's email address closely. Does it match the usual company email format?
- Never Give Out Sensitive Information: No legitimate company will ask for your passwords, PINs, credit card details, or Social Security number via email or text.
- Type URLs Directly: Instead of clicking links, go directly to websites by typing the address into your browser. This reduces the risk of landing on fake look-alike sites.
- Keep Software Updated: Install security updates for your operating system, web browser, and other software promptly. These updates often patch vulnerabilities that phishers exploit.
Types of Phishing

Core Types
- Email Phishing: The most classic and widespread form. These mimic emails from familiar companies (banks, streaming services, etc.), asking you to click links or download attachments.
- Spear Phishing: A more targeted version of email phishing, tailored to specific individuals or organizations. This often involves research to make the scam appear even more convincing.
- Whaling: Similar to spear phishing, but whaling attacks specifically target high-level executives and those with access to sensitive company data.
- Smishing: Phishing attacks carried out through text messages (SMS). Often appear as alerts or notifications with malicious links.
- Vishing: Phishing using phone calls. Scammers will impersonate customer support or banks, aiming to trick you into giving up personal information.
Variations and Techniques
- Clone Phishing: The attacker takes a legitimate email you've already received but replaces links/attachments with malicious ones. It's harder to spot because the layout is familiar.
- HTTPS Phishing: Scammers use secure websites (the "HTTPS" in the address) to gain a false sense of legitimacy. Don't assume a site is always safe just because it has the lock icon.
- Angler Phishing: These target you via social media. Scammers might create fake customer service accounts or impersonate a friend to direct you to phishing sites.
- Pop-up Phishing: Malicious pop-up windows appear on legitimate sites, often with urgent warnings or offers, designed to get you to click without thinking.
I hope this information has been helpful on your trading journey. If you have any further questions or need more specific advice, feel free to ask!
Check Out My Latest Blogs:
1- Don't Get Hooked:Crypto Phishing Scams (Great)
2- Demystifying the Portal to Web3: Your Guide to Web3 Wallets (Great)
3- A beginner-friendly guide to sidechains: Everything you need to know about it (Brilliant)
4- How to Grow Your Savings (Brilliant)
5- Trump's CBDC Blockade (Brilliant)
6- Tips to Secure Your Cryptocurrency Holdings (Brilliant)
7- Demystifying NFT Loans: Risks, Rewards, and How They Work (Brilliant)
8- What Is a Hardware Wallet and Why You Should Use It (Brilliant)
9- Trading Psychology: How to Trade Without Emotions (Brilliant)
10- Five Risk Management Strategies (Brilliant)
11- Pyramid and Ponzi Schemes (Brilliant)









![[LIVE] Engage2Earn: Sam Rae for Hawke boost](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/6b43c624-bd70-48c8-b0bc-7bc27c86e0ee/1)























![[ℕ𝕖𝕧𝕖𝕣] 𝕊𝕖𝕝𝕝 𝕐𝕠𝕦𝕣 𝔹𝕚𝕥𝕔𝕠𝕚𝕟 - And Now What.... Pray To The God Of Hopium?](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/79e7827b-c644-4853-b048-a9601a8a8da7/1)






