Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
Restriction Mapping of Plasmid DNA Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Typing Demonstrates Substantial Diversity among Pneumocystis jirovecii Isolates(1)
AIM: Our aim is to learn the RFLP technique and its usage purposes.
INTRODUCTION: Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) is a type of polymorphism that results from variation in the DNA sequence recognized by restriction enzymes.(2) The RFLP probes are frequently used in genome mapping and in variation analysis (genotyping, forensics, paternity tests, hereditary disease diagnostics, etc.).(3) Restriction endonucleases are enzymes that cut lengthy DNA into short pieces. Each restriction endonuclease targets different nucleotide sequences in a DNA strand and therefore cuts at different sites.(4)
MATERIALS: -Patient specimens -Purification Kit -Dra1, HindIII, or Xba1 restriction enzymes - 1.2% TBE agarose gel
METHOD: Restriction enzyme treatment. PCR products were purified using QuickStep 2 PCR Purification Kit , according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The purified products were digested with Dra1, HindIII, or Xba1 restriction enzymes for 5–6 h at 37°C. The digested products were analyzed on a 1.2% TBE agarose gel and were visualized by SYBR green staining (Molecular Probes). After transfer to a Nytran membrane, the blot was hybridized with a digoxigenin-labeled DNA probe. The PCR probe (spanning 1.3 Kb) was an equal mixture of 4 products obtained by PCR amplification of lung samples from 4 P. jirovecii–infected individuals. The hybridization signal was detected by chemiluminescence with use of alkaline phosphatase–conjugated antidigoxigenin antibody and CDPstar. The results were recorded with a Luminescent Imager.
DISCUSSION: A strength of RFLP analysis is that, rather than examining a single or very limited number of nucleotide polymorphisms, as is the case with many available typing methods, it interrogates the entire msg repertoire of the Pneumocystis genome, which is estimated to include 50–100 genes, with 40% of each msg of 3200 nucleotides being evaluated in the RFLP analysis. Because there are multiple msg copies per genome and there is a high level of sequence conservation in short stretches across msg genes, it is likely that recombination in Pneumocystis can lead to rearrangements and establishment of unique msg repertoires, as we and others have previously shown. One potential disadvantage of RFLP analysis is that it is unable to distinguish the contributions of individual isolates to the banding pattern in patients infected with >1 isolate. If only one of multiple strains is transmitted to a new host, however, the RFLP bands should be easily distinguishable as a subset of those in the first host. In addition, the reproducibility of RFLP analysis was lost in samples with <1000 msg copies. This likely represents a sampling bias in a specimen with a low organism load that resulted in uneven distribution of msg variants in different aliquots.
RESULT:
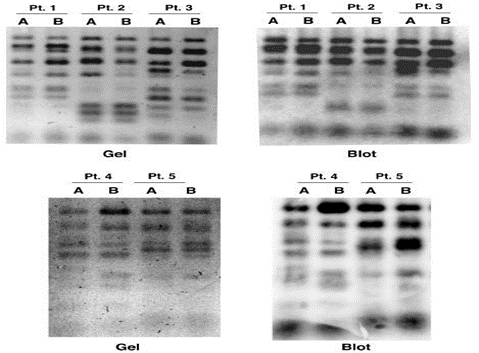
Figure 1 Stability of the restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) banding pattern in samples obtained over time. Representative gels (left) and corresponding blots (right) show the RFLP pattern of 2 samples (A and B) collected from 5 individuals at different times.
Figure 2 Similarity analysis of restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) patterns. The percent similarity scale is shown above the dendrogram and is indicated by the numbers at the individual nodes. The samples grouped with the same color are from the same country: orange, Italy; green, the Netherlands; blue, the United States. Bronchoalveolar lavage samples that were collected from the same patient are indicated by a red box around the number. The green box indicates a sputum pair collected from the same patient.
REFERENCES:
1. https://academic.oup.com/jid/article/200/10/1616/881526?login=true
2. https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Restriction-Fragment-Length-
Polymorphism#:~:text=Restriction%20fragment%20length%20polymorphism%20(RFLP)%20is%20a %20type%20of%20polymorphism,as%20markers%20on%20genetic%20maps.
3. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/probe/docs/techrflp/
4. https://www.news-medical.net/life-sciences/Restriction-Fragment-LengthPolymorphism-(RFLP)-Technique.aspx