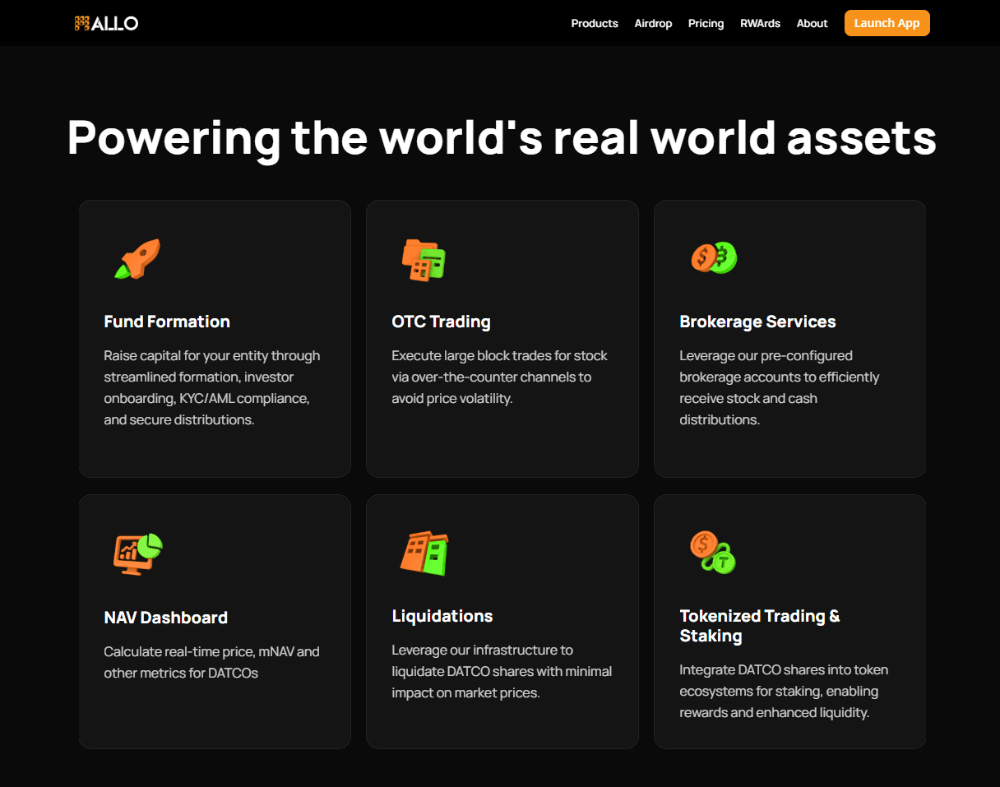
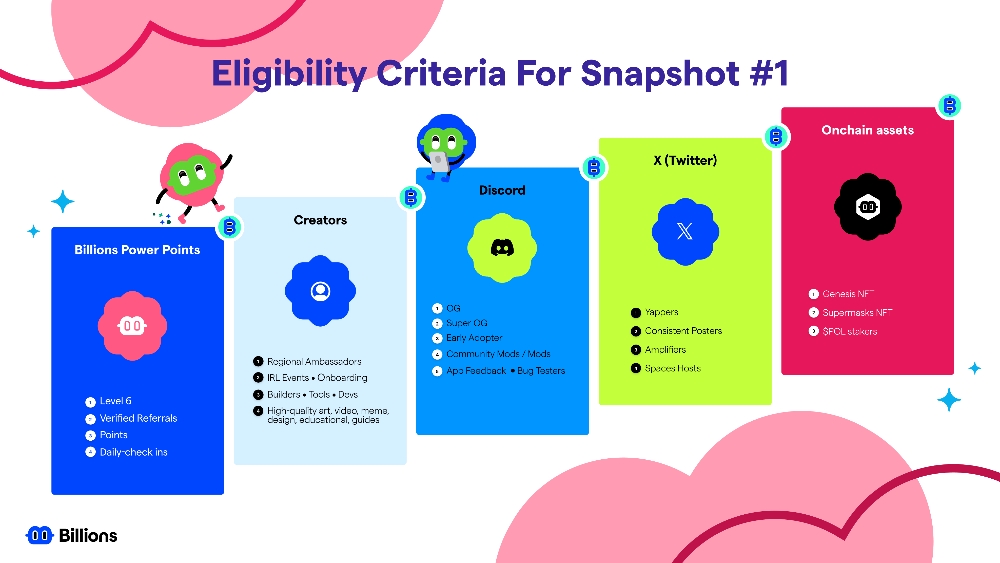
Understanding Proof-of-Stake: A Secure and Efficient Way to Power Blockchains
31
What is Proof-of-Stake (PoS)?
Proof-of-stake is a consensus mechanism used in blockchains to validate transactions and secure the network. Unlike proof-of-work (PoW) which relies on miners solving complex puzzles, PoS relies on validators who have a stake in the cryptocurrency itself.
Here's how PoS works:
- Staking:
- Validators "stake" their cryptocurrency holdings. This essentially locks up their coins for a period of time.
- Selection Process:
- The selection of validators to validate new blocks is often based on the amount of cryptocurrency they have staked. The more coins staked, the higher the chance of being chosen. This contrasts with PoW where miners with more computing power have an advantage.
- Block Validation:
- The chosen validators get to validate new transactions and add them to the blockchain. They are rewarded with new cryptocurrency for their service.
- Security:
- Since validators have their own coins staked, there's a strong disincentive to act maliciously. If they try to approve invalid transactions, their stake could be slashed (reduced). This ensures they act in the best interest of the network.
Benefits of Proof-of-Stake:
- Energy Efficient:
- One of the biggest advantages of PoS is that it's significantly more energy-efficient than PoW. This is because there's no need for massive amounts of computational power to solve puzzles.
- Faster Transactions:
- PoS blockchains can often process transactions faster than PoW blockchains. This is because there's no need for miners to compete to solve puzzles.
- Improved Security:
- The economic stake that validators have in the network can potentially make PoS blockchains more secure than PoW blockchains. Dishonest validators risk losing their stake, which discourages malicious activity.
Variations of PoS:
- Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS):
- In DPoS, users vote to elect a set of delegates who act as validators. This can improve scalability but introduces a layer of centralization.
Is Proof-of-Stake perfect?
While PoS offers several advantages, it's still under development. Some potential drawbacks include:
- Security Concerns:
- PoS systems are still relatively new, and there's a chance they might have undiscovered vulnerabilities.
- Centralization Risks:
- Some variations of PoS, like DPoS, can introduce centralization if a small number of delegates control the network.
Overall, proof-of-stake is a promising alternative to proof-of-work. It offers increased scalability, lower energy consumption, and potentially more secure networks.