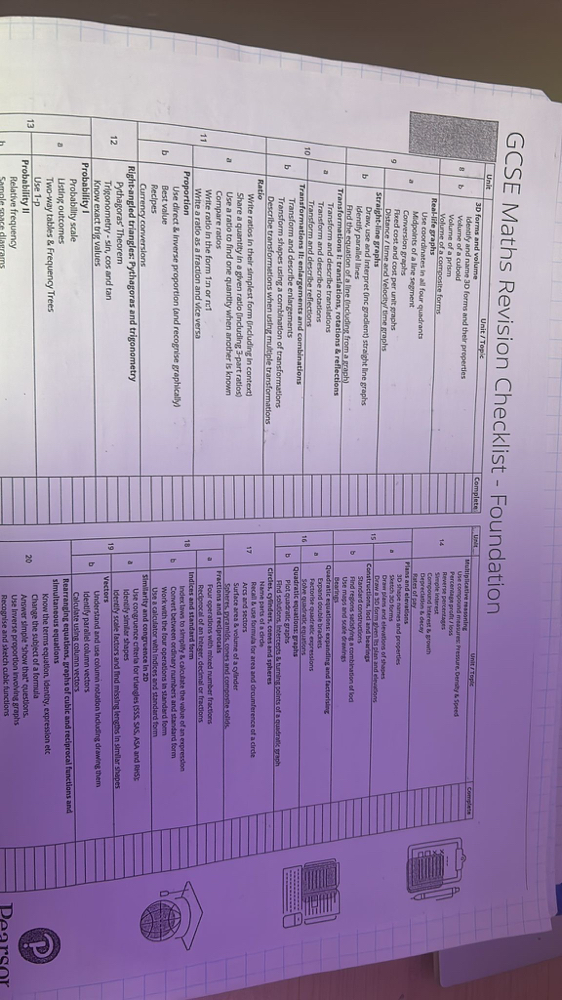
The Rise of Autonomous Vehicles and Their Impact on Transportation
Introduction
The advent of autonomous vehicles represents a revolutionary shift in transportation, promising safer roads, increased efficiency, and reduced congestion. As technology continues to advance, the deployment of self-driving cars, trucks, and buses is becoming increasingly feasible. This article explores the rise of autonomous vehicles and their profound impact on transportation systems worldwide.
Understanding Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles, also known as self-driving or driverless vehicles, represent a groundbreaking advancement in transportation technology. At their core, these vehicles rely on a sophisticated combination of hardware and software to perceive their environment, interpret data, and make driving decisions without human intervention. Here's an in-depth explanation of the key components and concepts involved in understanding autonomous vehicles:
1. Sensors:
Autonomous vehicles are equipped with an array of sensors that provide them with a comprehensive view of their surroundings. These sensors include:
- Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging): Lidar sensors emit laser pulses and measure the time it takes for the light to bounce back, creating a 3D map of the vehicle's environment. This technology is particularly adept at detecting objects and obstacles with high precision.
- Cameras: Cameras capture visual information, allowing the vehicle to recognize and identify objects such as pedestrians, vehicles, road signs, and traffic signals. Advanced image processing algorithms analyze camera data to understand the vehicle's surroundings.
- Radar: Radar sensors use radio waves to detect the distance, speed, and direction of objects in the vehicle's vicinity. Radar is especially useful in adverse weather conditions or situations where visibility is limited.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: Ultrasonic sensors emit high-frequency sound waves to detect nearby objects, providing close-range awareness for parking and maneuvering.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
The heart of autonomous vehicle technology lies in its artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities. These systems process data from sensors in real-time, enabling the vehicle to perceive its environment and make decisions autonomously. AI algorithms continuously learn from experience, allowing autonomous vehicles to improve their driving behavior over time.
- Perception: AI algorithms analyze sensor data to identify objects, predict their behavior, and classify potential hazards. This includes recognizing pedestrians, cyclists, other vehicles, road markings, and obstacles in the vehicle's path.
- Decision-making: Once the vehicle has perceived its surroundings, AI algorithms must decide how to navigate safely and efficiently. This involves planning a trajectory, adjusting speed, and anticipating changes in traffic conditions. Decision-making algorithms prioritize safety while also considering factors such as traffic laws, road conditions, and the vehicle's intended destination.
- Localization and Mapping: Autonomous vehicles rely on precise localization and mapping techniques to understand their position relative to their surroundings. High-definition maps, combined with GPS and inertial sensors, enable the vehicle to navigate accurately and stay on course.
3. Control Systems:
Autonomous vehicles are equipped with advanced control systems that translate decision-making outputs from AI algorithms into physical actions. These control systems manage acceleration, braking, steering, and other vehicle dynamics in response to changing road conditions and traffic scenarios.
- Drive-By-Wire Technology: Many autonomous vehicles utilize drive-by-wire systems, where electronic signals replace traditional mechanical linkages between the steering wheel, brakes, and throttle. This allows for precise control and coordination of vehicle movements.
- Redundancy and Fail-safes: To ensure safety, autonomous vehicles incorporate redundant systems and fail-safe mechanisms. If a sensor or component malfunctions, backup systems can compensate or safely bring the vehicle to a stop.
4. Levels of Autonomy:
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has defined six levels of vehicle autonomy, ranging from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation). Understanding these levels is crucial for assessing the capabilities and limitations of autonomous vehicles.
- Level 0: No automation; the driver is responsible for all aspects of driving.
- Level 1: Driver assistance features such as adaptive cruise control or lane-keeping assistance, but the driver remains in control.
- Level 2: Partial automation; the vehicle can control both steering and acceleration/deceleration under certain conditions, but the driver must remain engaged and supervise the driving task.
- Level 3: Conditional automation; the vehicle can perform all driving tasks under certain conditions, but the driver must be ready to intervene when prompted.
- Level 4: High automation; the vehicle can operate without human intervention in specific environments or scenarios, although a human driver may still have the option to take control if needed.
- Level 5: Full automation; the vehicle can perform all driving tasks under all conditions without human intervention.
Development and Adoption
The development of autonomous vehicle technology has been driven by both traditional automotive manufacturers and tech companies, such as Tesla, Waymo, and Uber. Significant investments in research and development have accelerated progress, leading to successful pilot programs and limited deployments in select cities.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the potential benefits of autonomous vehicles are vast, several challenges must be addressed before widespread adoption can occur. Safety concerns, regulatory hurdles, ethical dilemmas, and cybersecurity risks pose significant obstacles to overcome. Additionally, questions regarding liability in the event of accidents and the impact on employment in industries reliant on driving jobs remain unresolved.
However, the opportunities presented by autonomous vehicles are equally compelling. These include enhanced safety through the reduction of human error, increased mobility for individuals unable to drive, and improved efficiency in transportation networks. Furthermore, autonomous vehicles have the potential to revolutionize the concept of car ownership, with the rise of shared, on-demand mobility services.
Impact on Transportation
The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles is expected to reshape transportation systems in profound ways. Below are some of the key areas where their impact will be felt:
1. Safety
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to significantly reduce traffic accidents and fatalities caused by human error. By eliminating factors such as distracted driving, speeding, and drunk driving, self-driving cars can make roads safer for all users.
2. Efficiency
Autonomous vehicles can optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion through advanced routing algorithms and coordination with other vehicles. By communicating with each other and infrastructure systems, self-driving cars can minimize delays and improve overall travel times.
3. Accessibility
For individuals with disabilities or those who are unable to drive due to age or other factors, autonomous vehicles offer newfound independence and mobility. These individuals can access transportation services more easily and participate more fully in society.
4. Urban Planning
The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles may necessitate changes to urban planning and infrastructure. Cities may need to reconsider parking requirements, road design, and public transportation systems to accommodate the unique needs of self-driving cars.
5. Environmental Impact
While autonomous vehicles have the potential to reduce emissions through more efficient driving patterns and the adoption of electric powertrains, their overall environmental impact remains uncertain. Factors such as increased vehicle miles traveled and changes in consumer behavior could offset any potential gains.
Conclusion
The rise of autonomous vehicles represents a transformative moment in the history of transportation. While significant challenges remain, the potential benefits of self-driving technology are too compelling to ignore. By addressing safety concerns, regulatory issues, and societal implications, we can unlock the full potential of autonomous vehicles and create a safer, more efficient, and more accessible transportation future for all.