The Consequences of Poor Health Management
Introduction:
Poor health management is a pervasive issue that affects individuals, communities, and societies at large. It encompasses a range of behaviors, practices, and systems that contribute to the deterioration of one's well-being. This article explores the various aspects of poor health management, its consequences, and the importance of adopting proactive approaches to foster a healthier society.
1. Lack of Preventive Measures:
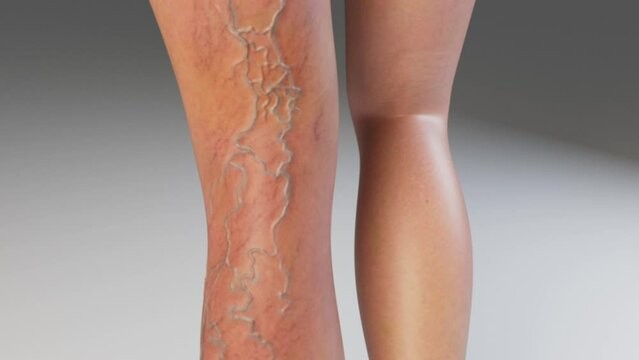
One of the key contributors to poor health management is the neglect of preventive measures. Individuals often fail to prioritize regular health check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings, leading to the late detection of potential health issues. This oversight can result in the progression of diseases to more advanced stages, making treatment more challenging and costly.
2. Unhealthy Lifestyle Choices:
The modern lifestyle is characterized by sedentary habits, poor dietary choices, and high stress levels. These factors contribute significantly to poor health management. Lack of physical activity, consumption of processed foods, and chronic stress can lead to obesity, cardiovascular diseases, and mental health issues. Addressing these lifestyle factors is crucial in mitigating the negative impact on overall health.
3. Inadequate Access to Healthcare:
Limited access to healthcare services is a significant barrier to effective health management, especially in economically disadvantaged communities. In many parts of the world, individuals face challenges such as lack of healthcare infrastructure, shortage of medical professionals, and financial constraints preventing timely medical attention. This disparity exacerbates health issues and perpetuates a cycle of poor health management.
4. Ignoring Mental Health:
Another aspect often overlooked in health management is mental well-being. Failure to address mental health issues can lead to a range of consequences, including decreased productivity, strained relationships, and increased susceptibility to physical illnesses. A holistic approach to health management should encompass both physical and mental aspects to promote overall well-being.
5. Escalating Healthcare Costs:
Poor health management not only takes a toll on individual well-being but also contributes to escalating healthcare costs for societies. Treating advanced stages of diseases, managing chronic conditions, and addressing preventable health issues place a significant burden on healthcare systems. Proactive health management can help reduce these costs by preventing the progression of diseases and minimizing the need for extensive medical interventions.
Conclusion:
Addressing poor health management requires a comprehensive and collaborative effort from individuals, communities, and policymakers. Emphasizing preventive measures, promoting healthy lifestyle choices, improving access to healthcare, and recognizing the importance of mental health are essential steps toward building a society that values and prioritizes well-being. By understanding the consequences of poor health management, we can work together to create a healthier and more resilient future for all.