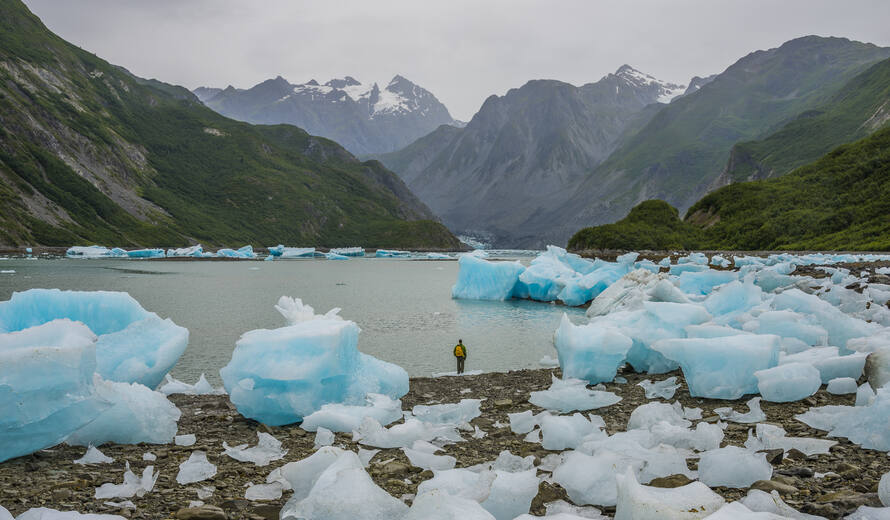
Melting of Glaciers
82
Introduction
The melting of glaciers is a significant and concerning phenomenon that is largely attributed to global warming and climate change. Glaciers are large masses of ice that form over long periods of time from the accumulation and compaction of snow. They play a crucial role in regulating Earth's climate and providing freshwater to various regions. Several factors contribute to glacier melting:

- Rising Temperatures: The primary driver of glacier melting is the increase in global temperatures. As the Earth's climate warms, temperatures at high altitudes and latitudes also rise, causing glaciers to melt.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, leading to a warming effect known as the greenhouse effect, which accelerates the melting of glaciers.
- Albedo Effect: Glaciers have a high albedo, meaning they reflect a significant portion of incoming solar radiation. As glaciers melt, they expose darker surfaces like rocks and soil, which have lower albedo. This results in more absorption of sunlight and further warming, creating a feedback loop that accelerates melting.
- Ocean Warming: Warmer ocean temperatures can also contribute to glacier melting, particularly for glaciers that terminate in the ocean. Warmer water can erode the glacier's base, leading to increased melting and calving.

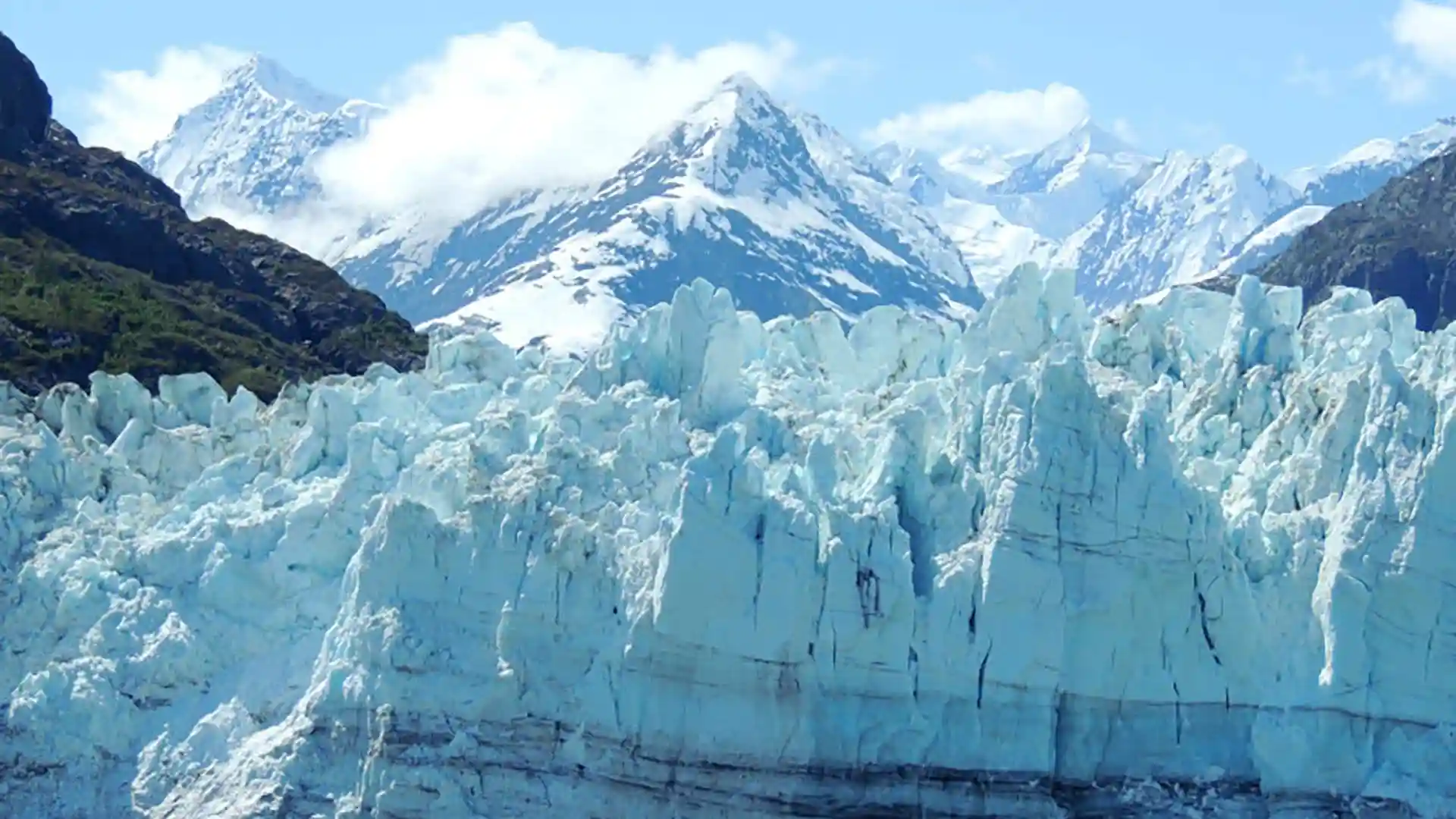
The consequences of glacier melting are far-reaching and include:
- Rising Sea Levels: Meltwater from glaciers contributes to rising sea levels, posing a threat to coastal areas and low-lying islands.
- Water Supply Changes: Glaciers act as natural reservoirs, storing freshwater. The melting of glaciers can alter water availability in downstream areas, affecting ecosystems and human communities that depend on glacier-fed rivers.
- Impact on Ecosystems: Glacier melt can affect the habitats of various plant and animal species, particularly those adapted to cold environments. Changes in water temperature and flow can disrupt ecosystems.
- Extreme Weather Events: Changes in glacier dynamics can contribute to the occurrence of extreme weather events, such as floods and landslides.
Efforts to address glacier melting involve mitigating climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, adopting sustainable practices, and implementing policies that promote environmental conservation. Additionally, scientists monitor glaciers to better understand their behavior and contribute to more accurate predictions of future changes.
What if all glaciers were melt?
If all glaciers were to melt, it would have profound and wide-ranging consequences for both natural systems and human societies. While the complete melting of all glaciers is an extreme scenario that may take a considerable amount of time, the ongoing trend of glacier retreat is a cause for concern. Here are some possible scenarios if all glaciers were to melt:
Rising Sea Levels: The most immediate and significant impact would be a substantial rise in sea levels. Glaciers store a significant amount of freshwater, and their melting contributes to the volume of water in oceans. This could lead to coastal flooding, threatening low-lying areas and island nations. Disruption of Water Supply: Glaciers act as natural reservoirs, supplying freshwater to many rivers and lakes. The disappearance of glaciers would affect the seasonal availability of water, leading to disruptions in water supply for communities that rely on glacier-fed rivers. Ecosystem Changes: Glacier-fed ecosystems are adapted to cold and unique conditions. The disappearance of glaciers would alter water temperatures, flows, and sediment transport, affecting aquatic ecosystems and the species that depend on them. Increased Risk of Natural Disasters: Glacial melt contributes to the formation of glacial lakes, and sudden releases of water from these lakes can lead to glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs). The absence of glaciers would eliminate this risk, but it could increase the likelihood of other natural disasters such as landslides and rockfalls. Loss of Unique Landscapes: Glaciers shape distinctive landscapes, including valleys, fjords, and moraines. The disappearance of glaciers would result in the loss of these unique landforms, impacting both the visual aesthetics of the environment and the tourism industry that relies on such features. Impact on Weather Patterns: The presence of glaciers influences local weather patterns by regulating temperatures and influencing precipitation. The loss of glaciers could lead to changes in regional climate patterns, potentially affecting weather conditions and agricultural practices. Global Climate Feedbacks: The melting of glaciers contributes to the overall feedback loop of climate change. As glaciers disappear, darker surfaces like rock and soil are exposed, absorbing more sunlight and contributing to further warming. This positive feedback loop could accelerate global climate change.
It's important to note that the complete melting of all glaciers is an extreme scenario that would likely take an extended period. However, ongoing glacier melt, which is already occurring in many parts of the world, poses significant challenges and underscores the importance of addressing climate change to mitigate its impacts on glaciers and associated ecosystems. Efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to changing environmental conditions are crucial in addressing the potential consequences of glacier loss.

What can we do to decrease melting of glaciers?
To decrease the melting of glaciers and address the broader issue of climate change, it is essential to take collective and sustained actions at various levels—individual, community, national, and global. Here are some strategies to help mitigate glacier melting:
Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Transition to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. Increase energy efficiency in industries, transportation, and buildings. Implement and support policies that regulate and reduce emissions from various sectors. Promote Sustainable Practices: Encourage sustainable land use and forestry practices to preserve natural carbon sinks. Support sustainable agriculture to reduce deforestation and land-use change. Advocate for responsible tourism in glacier regions to minimize environmental impact. Conserve Water Resources: Implement water conservation measures to reduce overall water consumption. Develop and promote technologies for efficient water use in agriculture and industry. Adopt water management practices that take into account the impact of glacier melt on river systems. Protect Glacial Environments: Establish and enforce protected areas around glaciers to preserve their ecosystems. Implement measures to prevent pollution, such as restricting waste disposal and industrial activities in glacier regions. Raise Awareness and Education: Increase public awareness about the causes and consequences of glacier melting and climate change. Support educational initiatives to promote environmental literacy and sustainable practices. International Cooperation: Participate in global efforts to address climate change, such as international climate agreements. Collaborate with other nations to share knowledge, technologies, and best practices for mitigating climate change impacts. Invest in Research and Monitoring: Support scientific research to better understand glacier dynamics and their response to climate change. Establish monitoring systems to track glacier changes and provide early warnings for potential hazards like glacial lake outburst floods. Adaptation Strategies: Develop and implement strategies to adapt to the impacts of glacier melt, particularly in vulnerable regions. Invest in infrastructure improvements to withstand changing water patterns, such as more intense floods or altered river flows. Support Sustainable Policies: Advocate for and support policies that promote sustainable development, conservation, and climate resilience at the local, national, and international levels.
It's important to recognize that addressing glacier melting requires a comprehensive and global effort. Individuals, communities, businesses, and governments all play crucial roles in combating climate change and preserving glacier ecosystems. By making conscious choices and supporting policies that prioritize environmental sustainability, we can contribute to the protection of glaciers and the overall health of our planet.