TURKISH ECONOMY
Turkey is one of the world's emerging market economies. Its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) has experienced growth over the years, driven by a combination of domestic consumption, investments, and exports. However, economic growth has been subject to fluctuations.
2. Key Economic Sectors:
- Services: The services sector, including finance, tourism, and telecommunications, plays a significant role in Turkey's economy.
- Industry: Manufacturing, textiles, automotive, and machinery are crucial components of the industrial sector.
- Agriculture: Although the agricultural sector's contribution to GDP has decreased, it remains an important part of the economy, providing employment in rural areas.
3. Inflation and Monetary Policy:
Turkey has faced challenges related to inflation. The Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey has implemented various monetary policies to control inflation and stabilize the economy.
4. External Trade:
Turkey is strategically positioned, serving as a bridge between Europe and Asia. The country engages in significant international trade, with key export sectors including automotive, textiles, machinery, and agricultural products.
5. Tourism:
Tourism is a vital source of revenue for Turkey. The country attracts millions of tourists each year, drawn to its rich historical and cultural sites, as well as its natural beauty.
6. Fiscal Policies:
The government has implemented fiscal policies to support economic growth and stability. These policies include initiatives to attract foreign investment and enhance the business environment.
7. Infrastructure Development:
Turkey has invested in infrastructure projects to improve transportation, energy, and telecommunications. Projects like the Istanbul Airport and high-speed rail networks demonstrate a commitment to modernizing infrastructure.
8. Challenges:
Turkey faces economic challenges, including external debt, a current account deficit, and geopolitical factors. Managing these challenges is essential for sustaining economic stability.
10. Future Outlook:
The outlook for Turkey's economy depends on factors such as political stability, global economic conditions, and the success of ongoing economic reforms. A young and growing population provides potential for future economic development.
For the most current and detailed information on Turkey's economy, I recommend checking recent reports from reliable sources such as the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey, the Turkish Statistical Institute, and international financial organizations.
2. Key Economic Sectors:
- Agriculture: While the share of agriculture in the overall GDP has decreased, it still plays a crucial role in providing employment, especially in rural areas.
- Industry: Turkey has a robust industrial sector, with a focus on manufacturing, textiles, automotive, and machinery. The country is known for its strong export-oriented industries.
- Services: The services sector, including tourism, finance, and telecommunications, has experienced substantial growth and contributes significantly to the GDP.
As of my last knowledge update in January 2022, Turkey's economy encompasses various key sectors that contribute significantly to its GDP and employment. These sectors are diverse, reflecting Turkey's status as a bridge between Europe and Asia. Here are some of the key economic sectors in Turkey:
Services Sector:
- Finance and Banking: The financial and banking sector is a crucial component of Turkey's services industry, contributing to economic growth and stability.
- Tourism: Turkey is a popular tourist destination, attracting millions of visitors annually to explore its historical sites, natural beauty, and cultural attractions.
- Telecommunications: The telecommunications sector has experienced rapid growth, with increased mobile and internet penetration.
Industrial Sector:
- Manufacturing: Turkey has a well-developed manufacturing sector, including automotive, textiles, and machinery. The automotive industry, in particular, has been a major contributor to exports.
- Construction: The construction sector has been booming, with infrastructure projects, real estate development, and urbanization driving growth.
Agriculture:
- Although the share of agriculture in the overall GDP has decreased, it remains a significant sector, especially in rural areas. Turkey produces a variety of agricultural products, including fruits, vegetables, and grains.
Energy:
- Turkey has been investing in its energy sector, including renewable energy sources, to meet growing demand and reduce dependency on imports. The country has significant potential in wind and solar energy.
Technology and Innovation:
- The technology sector has been gaining prominence, with a focus on information technology, software development, and innovation. Istanbul has emerged as a hub for technology startups.
Textiles and Apparel:
- Turkey is a major player in the global textiles and apparel industry. The country is known for its textile manufacturing and exports a variety of textile products.
Mining and Minerals:
- Turkey has rich natural resources, and the mining sector contributes to the economy through the extraction of minerals such as coal, copper, and boron.
Transportation and Logistics:
- Given its strategic location, Turkey plays a vital role in transportation and logistics. The country has invested in improving its transportation infrastructure, including roads, railways, and airports.
Automotive Industry:
- The automotive sector is a key driver of industrial growth and exports. Turkish automotive manufacturers produce a wide range of vehicles and components.
It's important to note that economic conditions can change, and the prominence of specific sectors may evolve over time. For the most up-to-date and detailed information on Turkey's key economic sectors, it's recommended to refer to reports from official sources such as the Turkish Statistical Institute and industry-specific organizations.
3. Trade and Export:
Turkey is a major player in international trade, with a focus on both European and Middle Eastern markets. Key exports include automotive products, textiles, machinery, and agricultural goods.
1. Key Export Products:
- Automotive Industry: Turkey is a significant exporter of automotive products, including vehicles, spare parts, and accessories.
- Textiles and Apparel: The textile and clothing industry is a major contributor to Turkey's exports, with a wide range of textile products and ready-made garments.
- Machinery and Equipment: Turkey exports machinery, equipment, and appliances, contributing to its industrial export base.
- Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals: Chemical products, including petrochemicals, and pharmaceuticals are part of Turkey's export portfolio.
- Agricultural Products: Turkey exports various agricultural products such as fresh fruits, vegetables, nuts, and processed food items.
2. Trade Partners:
- European Union (EU): The EU is a crucial trading partner for Turkey. The Customs Union with the EU facilitates the flow of industrial goods and certain agricultural products.
- Middle East: Turkey has strong economic ties with Middle Eastern countries, engaging in trade partnerships with nations in the Gulf region.
- North America and Asia: Turkey also conducts trade with North American and Asian countries, contributing to its global economic connections.
3. Customs Union with the European Union:
- Turkey has a Customs Union agreement with the European Union, promoting free trade in industrial goods and certain agricultural products. However, it does not include services or the free movement of labor.
4. Trade Balance:
- Turkey has historically experienced a trade deficit, where the value of imports exceeds the value of exports. Efforts have been made to address this imbalance through policies aimed at boosting exports and reducing dependence on imports.
5. Export Promotion:
- The Turkish government actively promotes exports through various incentives and support programs for businesses. Export credit programs and initiatives to explore new markets are part of the strategies to enhance export competitiveness.
6. Geopolitical Factors:
- Geopolitical considerations, including regional stability and diplomatic relations, can impact Turkey's trade dynamics. Political developments in the region may influence trade relationships.
7. Customs and Regulations:
- Turkey has specific customs regulations and procedures that businesses must follow for importing and exporting goods. Adherence to these regulations is crucial for smooth trade operations.
https://www.ttcexport.com/products?gclid=EAIaIQobChMI65jZ6bPmgwMVaIpoCR1F8wddEAAYASAAEgLxJfD_BwE
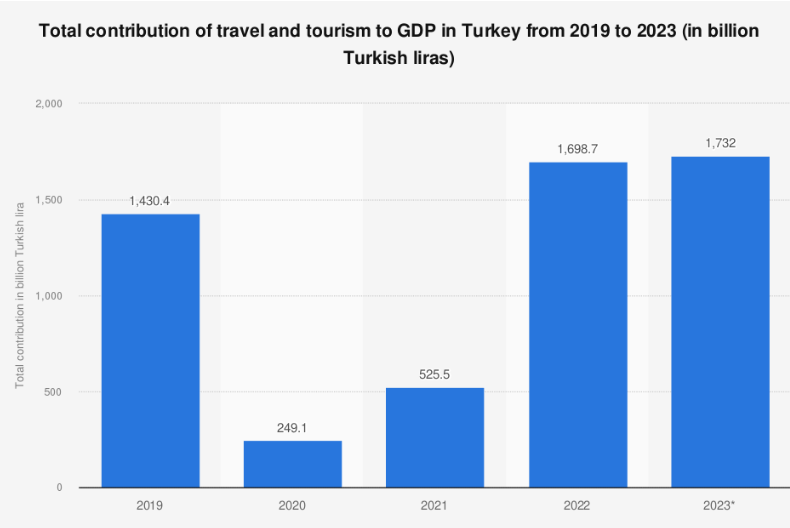
4. Tourism:
The tourism industry is a vital component of Turkey's economy, attracting millions of visitors annually. Popular destinations such as Istanbul, Cappadocia, and the Mediterranean coast contribute significantly to the country's revenue.
Tourism is a significant and vibrant sector in Turkey, contributing substantially to the country's economy. Turkey is known for its rich historical and cultural heritage, stunning landscapes, and diverse attractions.
1. Historical and Cultural Attractions:
- Turkey boasts a wealth of historical and cultural sites, including ancient ruins, medieval castles, and Ottoman architecture. Iconic landmarks such as the Hagia Sophia and Topkapi Palace in Istanbul, the ancient city of Ephesus, and the fairy-tale landscapes of Cappadocia draw millions of tourists.
2. Coastal and Natural Attractions:
- The Turkish Riviera, also known as the Turquoise Coast, is famous for its beautiful beaches, clear waters, and luxury resorts. Popular destinations include Antalya, Bodrum, and Marmaris. Additionally, the country's diverse landscapes, including mountains, hot springs, and natural wonders, attract nature lovers.
3. Unique Cultural Experiences:
- Turkish cuisine, known for its diverse flavors and influences, is a major attraction for food enthusiasts. Traditional Turkish baths, markets (bazaars), and vibrant local festivals provide unique cultural experiences for tourists.
4. Medical and Wellness Tourism:
- Turkey has become a popular destination for medical tourism, offering high-quality healthcare services at competitive prices. Wellness tourism, including spa and thermal tourism, has also seen growth.
5. Cruise Tourism:
- Turkey's strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia makes it an attractive destination for cruise tourism. Cruise ships often dock at ports like Istanbul, Kusadasi, and Bodrum.
6. Government Initiatives:
- The Turkish government has implemented various initiatives to promote tourism, including marketing campaigns, infrastructure development, and efforts to enhance the overall tourist experience. The "Tourism Strategy 2023" aims to increase the number of visitors and revenue.
7. Impact on Economy:
- Tourism significantly contributes to Turkey's GDP and employment. The sector generates foreign exchange earnings, supports small businesses, and contributes to regional development.
8. Challenges:
- The tourism sector is susceptible to external factors such as geopolitical tensions, economic uncertainties, and health crises. The COVID-19 pandemic, for example, had a significant impact on global tourism, including Turkey.
9. Future Prospects:
- Despite challenges, Turkey remains optimistic about the future of its tourism industry. Ongoing efforts to diversify tourism offerings, improve infrastructure, and implement sustainable practices aim to ensure long-term growth.
It's important to note that the status of the tourism industry can change, and developments may have occurred since my last update in January 2022. For the latest and most accurate information, it is recommended to refer to recent tourism reports, government announcements, and industry analyses.
https://www.reportlinker.com/market-report/Tourism/6226/Tourism?term=tourism%20reports&matchtype=b&loc_interest=&loc_physical=1012782&utm_group=standard&utm_term=tourism%20reports&utm_campaign=ppc&utm_source=google_ads&utm_medium=paid_ads&utm_content=transactionnel-1&gad_source=1&gclid=EAIaIQobChMIn5H0y7TmgwMV8oZoCR1m5A4EEAAYASAAEgJCPfD_BwE
5. Challenges:
Despite its economic strengths, Turkey faces challenges such as inflation, a current account deficit, and fluctuations in the currency. Political and geopolitical factors can also impact economic stability.
Economic conditions can evolve, so it's essential to consider more recent sources for the latest information. Here are some of the challenges that Turkey has been contending with:
- Inflation and Monetary Policy:
- Turkey has struggled with high inflation rates, which can erode the purchasing power of its currency, the Turkish lira. Managing inflation and implementing effective monetary policies to stabilize the currency are ongoing challenges.
Currency Volatility:
- The Turkish lira has experienced significant volatility, leading to concerns about exchange rate stability. Currency fluctuations can affect trade balances, inflation, and overall economic confidence.
Current Account Deficit:
- Turkey has historically had a current account deficit, meaning that its imports exceed its exports. This imbalance can put pressure on the country's external finances and make it dependent on foreign capital.
External Debt:
- Turkey's high external debt levels, including corporate and public debt, have been a concern. Servicing and repaying this debt can become challenging, especially during periods of currency depreciation.
Political and Geopolitical Risks:
- Political uncertainties and geopolitical tensions in the region can impact investor confidence and economic stability. Relations with neighboring countries and broader geopolitical developments are factors that influence Turkey's economic environment.
Structural Reforms:
- Implementing structural reforms to enhance the business environment, improve the rule of law, and increase transparency is an ongoing challenge. Such reforms are crucial for attracting foreign investment and fostering sustainable economic growth.
Unemployment and Labor Market Issues:
- Unemployment rates and labor market challenges, including informal employment, remain areas of concern. Creating sufficient job opportunities, especially for the youth, is crucial for social and economic stability.
Global Economic Conditions:
- Turkey's economy is susceptible to global economic trends, trade dynamics, and external shocks. Changes in international markets and economic conditions can have a direct impact on Turkey's export-oriented sectors.
Tourism Vulnerability:
- The tourism sector, a significant contributor to Turkey's economy, is vulnerable to external shocks, including geopolitical events and health crises. The COVID-19 pandemic, for example, had a substantial impact on global tourism.
Environmental and Sustainability Challenges:
- Addressing environmental challenges and promoting sustainable practices are becoming increasingly important. Balancing economic development with environmental sustainability is a complex task.
Social Disparities:
- There are disparities in income distribution and regional development, with some regions benefiting more from economic growth than others. Addressing social inequalities is crucial for long-term stability and inclusivity.
Addressing these challenges requires a coordinated effort from policymakers, economic institutions, and various stakeholders. Economic reforms, sound fiscal and monetary policies, and efforts to enhance the business environment are essential components of a strategy to overcome these challenges and foster sustainable economic development.
https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/turkey/overview
6. Government Policies:
Here are some key aspects of Turkey's government policies related to the economy:
Economic Reforms:
- The Turkish government has initiated economic reform programs aimed at improving the overall economic structure, increasing competitiveness, and attracting foreign investment. These reforms encompass various sectors, including finance, industry, and trade.
Inflation and Monetary Policy:
- The Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey plays a crucial role in implementing monetary policies to control inflation and stabilize the currency. Interest rate decisions and other monetary tools are utilized to manage economic challenges.
Fiscal Policies:
- Fiscal policies, including government spending and taxation, are designed to support economic growth while maintaining fiscal discipline. The government aims to strike a balance between stimulating economic activity and ensuring fiscal sustainability.
Investment Incentives:
- Turkey offers various incentives to attract both domestic and foreign investments. These incentives may include tax breaks, subsidies, and other financial support measures to encourage businesses and industries.
Infrastructure Development:
- The government has prioritized infrastructure development projects, including transportation, energy, and telecommunications. These projects aim to enhance connectivity, improve logistics, and support overall economic development.
Export Promotion:
- The government actively promotes exports through initiatives such as trade agreements, export credit programs, and market diversification strategies. Efforts are made to boost the competitiveness of Turkish products in international markets.
Customs and Trade Facilitation:
- Policies related to customs procedures and trade facilitation are designed to streamline import and export processes, reducing bureaucratic hurdles and improving the ease of doing business.
Financial System Stability:
- The government works to ensure the stability of the financial system, collaborating with the banking sector and regulatory authorities. Policies are in place to address any systemic risks and maintain financial stability.
Tourism Promotion:
- Given the importance of tourism to the Turkish economy, the government implements policies to promote the sector. This includes marketing campaigns, infrastructure improvements, and measures to enhance the overall tourist experience.
Social Programs:
- The government may implement social programs to address unemployment, income inequality, and other social challenges. These programs aim to provide support to vulnerable populations and promote social stability.
Technology and Innovation:
- Policies to foster technology and innovation are increasingly important. Supporting the growth of the technology sector, encouraging research and development, and promoting a culture of innovation are key components.
It's crucial to consider that the effectiveness of these policies and their impact on the economy can vary. Moreover, economic conditions and policy priorities may change over time. For the latest and most accurate information on Turkey's government policies related to the economy, it is recommended to consult official government publications, statements, and economic analyses.
7. Infrastructure Development:
Turkey has invested heavily in infrastructure projects, including transportation and energy. Mega projects like the Istanbul Airport and the ongoing construction of high-speed rail networks demonstrate the commitment to modernizing the country's infrastructure.
Infrastructure projects cover various sectors, including transportation, energy, and telecommunications. Here are some key aspects of Turkey's infrastructure development:
Transportation:
- Roads and Highways: Turkey has invested significantly in expanding and modernizing its road network. Highways, bridges, and tunnels have been constructed to improve connectivity between cities and regions.
- Railways: The development of high-speed rail networks has been a priority, connecting major cities and improving the efficiency of passenger and freight transportation.
- Airports: Turkey has undertaken major airport projects, with the construction of new airports and the expansion of existing ones. The Istanbul Airport, one of the world's largest, is a notable example.
Energy:
- Renewable Energy: Turkey has been investing in renewable energy projects, including wind and solar power. The goal is to increase the share of renewable energy in the country's overall energy mix.
- Natural Gas Pipelines: The development of natural gas pipelines, both domestic and international, has been a focus to ensure a stable and diversified energy supply.
Telecommunications:
- Fiber Optic Networks: The expansion of fiber optic networks aims to improve high-speed internet connectivity across the country, supporting digital transformation and innovation.
- 5G Technology: Turkey has been working on implementing 5G technology to enhance telecommunications infrastructure and support the growth of the digital economy.
Urban Development:
- Smart Cities: Some cities in Turkey are adopting smart city initiatives, incorporating technology and data to improve urban services, transportation, and overall quality of life.
- Housing Projects: The government has undertaken housing projects to address urbanization challenges, providing affordable housing options and improving living conditions.
Water Management:
- Dams and Irrigation Projects: Infrastructure projects related to water management, including the construction of dams and irrigation systems, aim to support agricultural development and water resource management.
Mega Projects:
- Canal Istanbul: A major infrastructure project, Canal Istanbul aims to create an artificial shipping channel parallel to the Bosporus, relieving maritime traffic and providing strategic advantages.
- Istanbul Finance Center (IFC): The IFC is envisioned as a financial hub, bringing together financial institutions, businesses, and services in a designated area in Istanbul.
Tourism Infrastructure:
- Cruise Ports: Infrastructure projects related to tourism include the development and expansion of cruise ports to accommodate the growing cruise tourism industry.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs):
- Turkey has utilized PPP models for some infrastructure projects, attracting private sector investment and expertise to contribute to project financing and management.
Infrastructure development plays a crucial role in supporting economic activities, improving living standards, and attracting investments. It is important to check more recent sources for the latest updates on Turkey's infrastructure projects, as new developments may have occurred since my last update.
8. Financial System:
Turkey has a well-developed financial system, with a mix of public and private banks. The Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey plays a crucial role in monetary policy and maintaining financial stability.
The financial sector plays a crucial role in supporting economic activities, facilitating investments, and contributing to overall economic stability. Here are some key aspects of Turkey's financial system:
Banking Sector:
- Central Bank: The Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey (CBRT) is the country's central banking authority. It is responsible for implementing monetary policy, controlling inflation, and maintaining financial stability.
- Commercial Banks: Turkey has a diverse array of commercial banks, both public and private. These banks provide a wide range of financial services, including deposit accounts, loans, and investment products.
Capital Markets:
- Stock Exchange: Borsa Istanbul is the main stock exchange in Turkey, where publicly traded companies list their shares. It plays a crucial role in providing a platform for equity financing and investment opportunities.
- Bond Market: Turkey's bond market allows the government and corporations to raise funds through the issuance of bonds. It provides an avenue for investors to participate in fixed-income securities.
Insurance and Pension Funds:
- Insurance Sector: Turkey has a developed insurance sector that offers various types of insurance products, including life insurance, property insurance, and health insurance.
- Pension Funds: The pension system in Turkey involves both public and private pension funds, contributing to long-term savings and retirement planning.
Regulatory Framework:
- Banking Regulation and Supervision Agency (BRSA): The BRSA is responsible for regulating and supervising the banking sector to ensure financial stability and consumer protection.
- Capital Markets Board (CMB): The CMB oversees and regulates capital markets activities, including the stock exchange and other securities markets.
Financial Inclusion:
- Turkey has made efforts to promote financial inclusion, ensuring that a broader segment of the population has access to financial services. This includes initiatives to increase banking penetration and the use of digital financial services.
Digitalization and Fintech:
- The financial sector in Turkey has embraced digitalization, with the adoption of online banking, mobile payments, and other fintech solutions. This trend contributes to increased efficiency and accessibility of financial services.
Foreign Exchange Market:
- Given Turkey's status as an emerging market, the foreign exchange market is crucial. The Turkish lira is the official currency, and the exchange rate is influenced by various factors, including economic conditions and external developments.
Interest Rates and Monetary Policy:
- The Central Bank sets and adjusts interest rates as part of its monetary policy tools to control inflation and stabilize the economy. Interest rates play a significant role in shaping borrowing and lending activities.
It's important to note that economic conditions and financial landscapes can change. For the latest and most accurate information on Turkey's financial system, it is recommended to refer to official reports from the Central Bank, regulatory authorities, and other financial institutions.
https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/pub/ubeyad/issue/57695/822869
9. Future Prospects:
Despite challenges, Turkey's economic outlook is optimistic, with a young and dynamic population, strategic geographic location, and ongoing efforts to diversify the economy. Continued reforms and a focus on innovation could further enhance its global economic standing.
This overview provides a snapshot of Turkey's economy, highlighting its strengths, challenges, and the various factors that shape its economic landscape.
9. Future Prospects:
Despite challenges, Turkey's economic outlook is optimistic, with a young and dynamic population, strategic geographic location, and ongoing efforts to diversify the economy. Continued reforms and a focus on innovation could further enhance its global economic standing.
Diversification and Innovation:
- Future prospects may be influenced by efforts to diversify the economy and promote innovation. Encouraging technological advancements, research and development, and fostering a culture of innovation could contribute to sustained economic growth.
Export-Led Growth:
- Turkey's continued emphasis on export-oriented industries, such as automotive, textiles, and machinery, could play a pivotal role in future economic performance. Strengthening ties with existing trading partners and exploring new markets may be key strategies.
Investment Climate:
- The attractiveness of Turkey to both domestic and foreign investors will impact its economic prospects. A favorable investment climate, driven by policies that enhance business confidence, reduce bureaucratic hurdles, and ensure regulatory predictability, may stimulate economic activities.
Infrastructure Development:
- Ongoing infrastructure projects, including those related to transportation, energy, and telecommunications, could enhance connectivity, improve logistics, and contribute to economic development. Large-scale initiatives like Canal Istanbul and the Istanbul Finance Center may shape the economic landscape.
Tourism Recovery:
- The recovery of the global tourism industry, coupled with effective promotion and management of tourism assets, could significantly contribute to economic growth. Addressing challenges, such as geopolitical tensions and pandemics, will be crucial for the tourism sector.
Financial Stability:
- Maintaining financial stability, controlling inflation, and managing external balances will be important for sustaining economic growth. Effective monetary and fiscal policies, coupled with prudent financial sector regulation, can contribute to stability.
Global Economic Conditions:
- Turkey's economic prospects are interconnected with global economic trends. Changes in international markets, trade dynamics, and geopolitical developments can impact the country's economic performance.
Political and Geopolitical Factors:


















![[LIVE] Engage2Earn: Sam Rae for Hawke boost](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/6b43c624-bd70-48c8-b0bc-7bc27c86e0ee/1)

![[ℕ𝕖𝕧𝕖𝕣] 𝕊𝕖𝕝𝕝 𝕐𝕠𝕦𝕣 𝔹𝕚𝕥𝕔𝕠𝕚𝕟 - And Now What.... Pray To The God Of Hopium?](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/79e7827b-c644-4853-b048-a9601a8a8da7/1)







