Artificial Intelligence and Statistics: The Future of Data Science
In today's rapidly evolving world, data science is becoming increasingly complex. In this evolution, artificial intelligence (AI) and statistics are transforming the world of data science and shaping its future. In this article, we will focus on the combination of AI and statistical disciplines, exploring this dynamic change and its potential impacts on the future. Data is merely the raw material of knowledge." Statistics is the most powerful tool we have in harnessing information for meaningful purposes
Examples of the Application of Statistics:
Economics and Finance:
- Analysis of economic indicators.
- Valuation of stock prices and financial assets.
- Prediction of inflation and unemployment rates.
Health Sciences:
- Epidemiological studies and models of disease spread.
- Data analysis in clinical trials for pharmaceuticals.
- Evaluation of healthcare service quality.
Education:
- Assessment of student achievements.
- Analysis of the effects of educational policies.
- Evaluation of teaching methods.
Marketing and Advertising:
- Analysis of consumer behaviors.
- Market segmentation and determination of target audience.
- Measurement of the effectiveness of advertising campaigns.
Environmental Sciences:
- Creation of climate change models.
- Analysis of sustainable use of natural resources.
- Assessment of pollution levels.
Social Sciences:
- Analysis of surveys and survey results.
- Examination of social trends and demographic characteristics.
- Evaluation of crime statistics.
Computer Sciences:
- Data mining and big data analysis.
- Evaluation of algorithm performance.
- Network security and risk analysis.
Industrial Engineering:
- Improvement and optimization of production processes.
- Quality control and product standardization.
- Occupational safety and risk management.
Why Do We Learn Statistics?
Statistics is a crucial tool in various fields, and the following fundamental reasons help explain why it is learned:
- Understanding and Interpreting Data: Statistics assists in understanding, organizing, and interpreting collected data. It provides a way to add meaning to information and uncover the story behind the data.
- Empowering Decision-Making Processes: Statistics strengthens decision-making processes by grounding them in data. Decisions supported by accurate analyses tend to be more effective and informed.
- Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: Statistics plays a foundational role in fields such as machine learning and artificial intelligence. The creation, training, and evaluation of models are based on statistical principles.
- Social and Economic Analyses: Statistics forms the basis for various analyses in social sciences and economics. In these fields, statistical data helps understand trends, patterns, and relationships.
- Application in Health and Medicine: Statistics is crucial in a range of health and medical fields, from clinical trials to epidemiology. It is used for analyzing disease spread patterns and evaluating treatment effectiveness.
- Marketing and Business: Statistics is used in creating marketing strategies and making demand forecasts in the business world. It is important for understanding consumer behavior and conducting competitive analyses.
- Quality Control and Engineering: The use of statistical methods in quality control and engineering projects improves processes and enhances product quality in manufacturing.
Inference
- In the streets of Istanbul, how many homeless people are living? How often do married individuals engage in arguments? These questions may seem quite different from each other; however, both can be answered using basic statistical tools. Statistics is used to make predictions in larger-scale issues where we don't have complete information. In essence, we use statistics to make inferences about the 'unknown world' based on the data from the 'known world.'
- For example, a political survey is a form of sampling. A research organization tries to create a household sample representing a large population segment to learn about their political views or opinions about a candidate. This is, of course, much more cost-effective and faster than contacting all voters in a city or country. A properly selected sample of 1,000 people, methodologically determined, will yield the same result as evaluating every household in Turkey.
What is correlation and what does it do?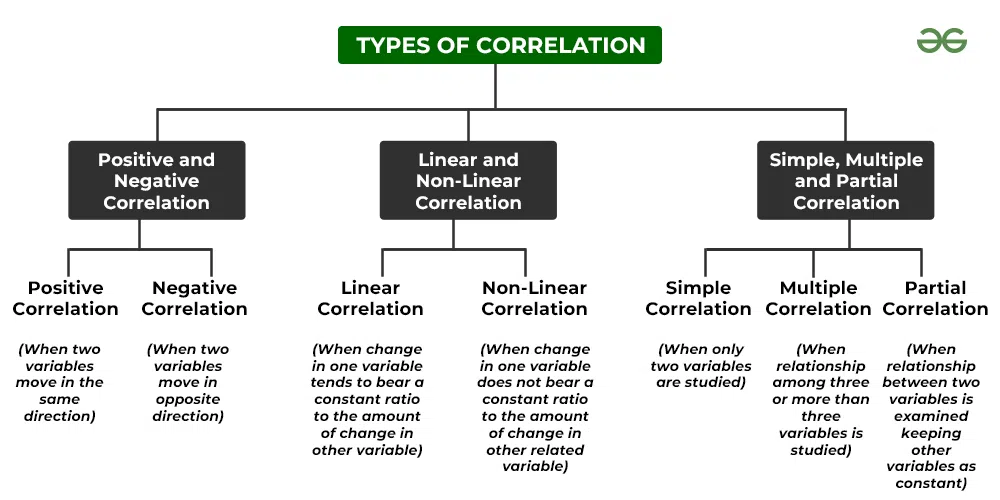 Correlation is a statistical concept that measures the relationship between two variables. This relationship indicates the degree of linear association between variables. Correlation typically takes a value between -1 and 1:
Correlation is a statistical concept that measures the relationship between two variables. This relationship indicates the degree of linear association between variables. Correlation typically takes a value between -1 and 1:
- 1: Perfect negative correlation
- 0: No correlation (no relationship between variables)
- 1: Perfect positive correlation
The correlation coefficient, which expresses correlation, is often denoted by the letter "r." It measures both the direction (negative or positive) and the strength of the relationship between variables.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Correlation_coefficient-56a792873df78cf77297414e.png)
Correlation is utilized in various fields:
- Statistics and Science: Used to understand the relationship between two variables. For example, a scientist may examine the correlation between climate change and sea level rise.
- Economics: Used to understand the relationship between two economic variables. For instance, evaluating the correlation between the unemployment rate and economic growth.
- Finance: Utilized to measure the relationship between stock prices, assess investment portfolios, and understand risk.
- Health Sciences: Employed to assess the relationship between the effectiveness of a specific treatment and a patient's condition.
- Education: Used to evaluate the relationship between student achievements and teaching methods.
Correlation is a powerful tool for understanding the relationship between variables and making predictions. However, it does not imply causation. In other words, even if there is a correlation between two variables, it doesn't necessarily mean that one causes the other. Therefore, caution and consideration of other factors are crucial when conducting correlation analysis. How does Spotify know what kind of music I like?
How does Spotify know what kind of music I like?
Spotify and similar music platforms employ various methods to understand users' music preferences and provide personalized recommendations. Here are some methods that Spotify uses to understand your music preferences:
Listening History Analysis: Spotify analyzes users' listening history, recording which songs, artists, or genres they have listened to and for how long. This data is used to understand users' musical preferences.
Likes and Adding to Favorites: Songs liked by users and those added to favorites help the platform better understand the music users enjoy.
Playlists and Custom Lists: User-created playlists and custom lists provide Spotify with additional information about users' music preferences. For instance, a "Workout Playlist" or "Chill Songs" list may reflect the music style a user prefers in specific situations.
Music Discovery and Recommendation Algorithm: Spotify utilizes recommendation algorithms based on users' listening history. By suggesting songs enjoyed by other users with similar music tastes, Spotify helps users discover new music.
Emotional Analysis: Some music platforms subject users' listening habits to emotional analysis. For example, the types of music a user listens to during stressful moments or the songs they prefer when feeling happy can be understood through emotional analysis.
The combination of these methods allows Spotify to better understand users' musical preferences and offer more personalized music recommendations. However, various policies and options regarding user privacy and data protection are provided, so users should be cautious and adjust privacy settings according to their preferences.
The Power Collaboration of Artificial Intelligence and Statistics
Artificial intelligence stands out with its ability to analyze large datasets through complex algorithms and learning models. When combined with statistical methods, this allows us to better understand patterns in datasets and achieve more reliable results. This collaboration strengthens the foundation of data science by enhancing the accuracy of predictions.
Future Trends: Data Science and Advanced Analytics
When artificial intelligence techniques such as machine learning and deep learning are integrated with statistical modeling, prediction capabilities increase, and improvements are made in decision-making algorithms. This enables more effective and informed decision-making in sectors such as finance, healthcare, marketing, and many others.
Shift in Data Science Education: Artificial Intelligence and Statistics
The education of future data science professionals should adopt an approach that encompasses the integration of traditional statistics and artificial intelligence topics. This will not only help students understand basic statistical methods but also empower them with the ability to apply artificial intelligence algorithms.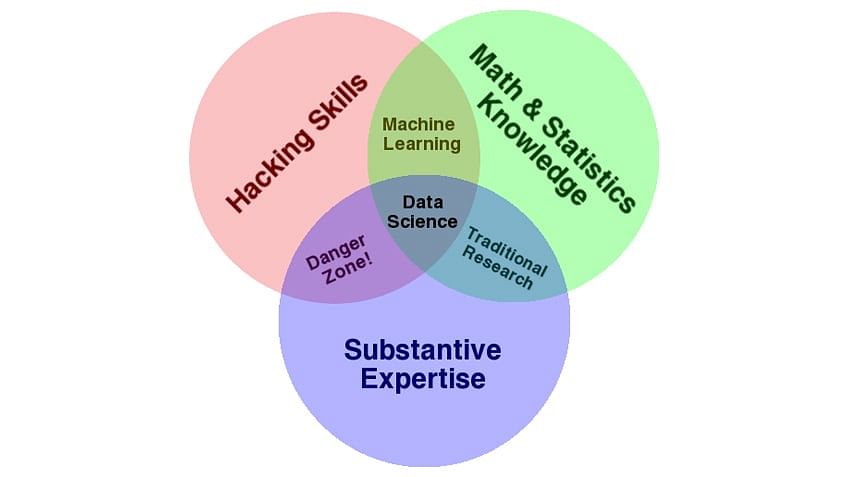
Ethics and Reliability: The Relationship Between Artificial Intelligence and Statistics
Artificial intelligence and statistics play a significant role in ethical and reliability issues in data science applications. In this article, we will explore how these two disciplines can be combined with ethical principles and how data reliability can be increased.
Conclusion: The Future of Data Science
The combination explored under the title "Artificial Intelligence and Statistics: The Future of Data Science" represents a significant paradigm shift in the field of data science. The strong relationship between artificial intelligence and statistics heralds an era where data science will become even more crucial in the future.