Understanding Blockchain. A Simple Explanation.
Understanding Blockchain.
A Simple Explanation.

Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary innovation with the potential to transform various industries, from finance to supply chain management. Despite its complexity, the underlying principles of blockchain can be explained in simple terms. In this document, we'll provide a straightforward explanation of what blockchain is and how it works.
What is Blockchain?
At its core, a blockchain is a digital ledger that records transactions in a decentralized and immutable manner. Imagine a digital spreadsheet or database that stores information in a series of blocks, with each block containing a list of transactions. These blocks are linked together in a chronological and linear fashion, forming a chain of blocks – hence the name "blockchain."
How Does Blockchain Work?
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases that are centralized and controlled by a single entity, a blockchain operates on a decentralized network of computers, called nodes. Each node maintains a copy of the blockchain, ensuring transparency, redundancy, and resilience against tampering or censorship.
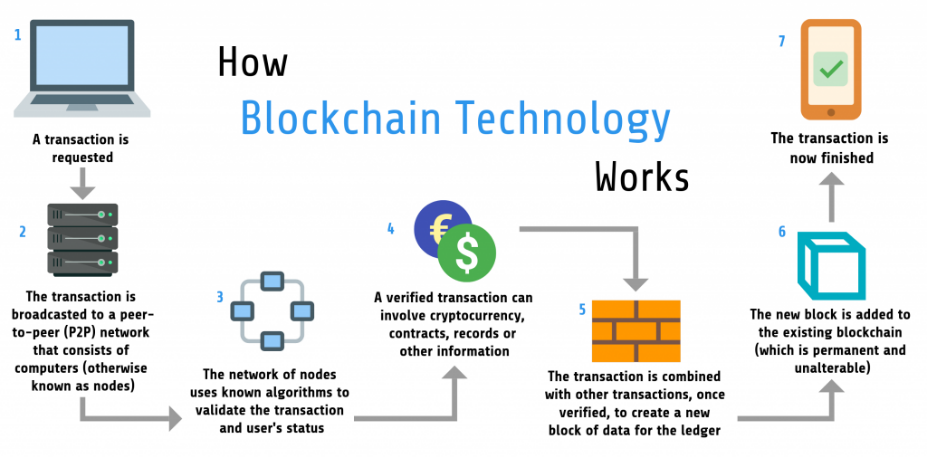
- Transactions: When a transaction occurs, it is broadcasted to the network and verified by multiple nodes through a process known as consensus. Once validated, the transaction is grouped together with other transactions to form a block.
- Block Formation: Each block in the blockchain contains a unique identifier, called a hash, which is generated using cryptographic algorithms. The hash of each block also includes the hash of the previous block in the chain, creating a chronological and immutable record of transactions.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), ensure that all nodes in the network agree on the validity of transactions and the order in which they are added to the blockchain. These mechanisms prevent double-spending and maintain the integrity of the blockchain.
- Immutability: Once a block is added to the blockchain, it becomes virtually impossible to alter or delete the transactions recorded within it. Any attempt to tamper with the blockchain would require the collusion of a majority of nodes in the network, making it highly secure and resistant to fraud.
Applications of Blockchain:
Blockchain technology has a wide range of applications beyond cryptocurrency, including:
- Financial Transactions: Blockchain enables secure and transparent peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can track the provenance and movement of goods throughout the supply chain, ensuring transparency and traceability.
- Smart Contracts: Blockchain-based smart contracts automate and enforce the execution of contractual agreements, reducing the need for intermediaries and streamlining business processes.
In summary, blockchain is a decentralized and immutable digital ledger that records transactions in a transparent and secure manner. By leveraging cryptographic techniques and consensus mechanisms, blockchain technology enables trustless transactions and opens up a world of possibilities for innovation and disruption across various industries.



































