Why air brake system is safe for heavy duty vehicles?
Introduction
An air braking system, also known as an air brake system, is a type of braking system commonly used in heavy vehicles such as trucks, buses, and trains. It relies on compressed air to activate and control the braking mechanisms. The system is designed to provide efficient and reliable braking performance, especially for large and heavy vehicles that require significant stopping power.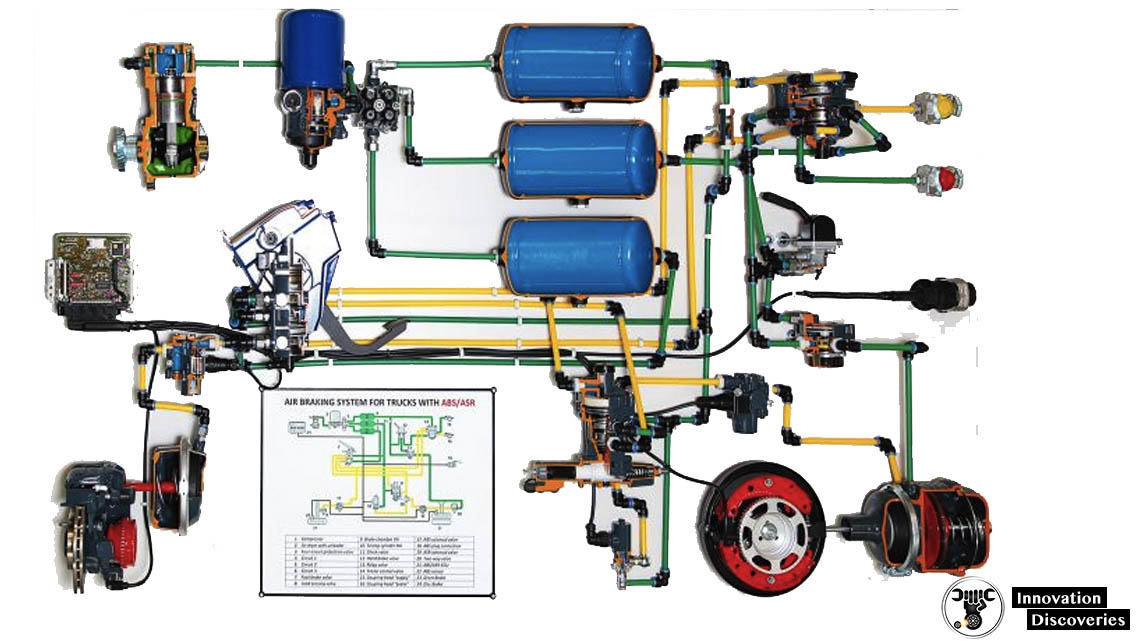
Components of an Air Braking System:
- Air Compressor: The air compressor is responsible for compressing atmospheric air and supplying it to the air storage tanks. It is typically driven by the engine and ensures a constant supply of compressed air.
- Air Storage Tanks: Compressed air from the compressor is stored in air storage tanks. These tanks provide a reservoir of pressurized air that can be used for various functions within the braking system.
- Brake Pedal: The brake pedal is the primary input device for the driver. When the brake pedal is pressed, it sends a signal to the brake control valve to release compressed air and apply the brakes.
- Brake Control Valve: The brake control valve is a critical component that regulates the flow of compressed air to the different brake chambers. It receives signals from the brake pedal and distributes the air pressure accordingly.
- Brake Chambers: Brake chambers, also known as brake actuators, are responsible for converting the compressed air into mechanical force to activate the brakes. They contain diaphragms or pistons that move when pressurized air is applied, ultimately causing the brake shoes or pads to engage with the wheels.
- Brake Shoes/Pads: Brake shoes or pads are the frictional components that come into contact with the wheels to create the braking force. In drum brake systems, the brake shoes are pressed against the inside of the brake drum, while in disc brake systems, the brake pads squeeze the rotating brake discs.
- Brake Drums/Discs: Brake drums and discs are the rotating components of the wheel assembly that work in conjunction with the brake shoes or pads. They provide the surface against which the frictional force is applied to slow down or stop the vehicle.
- Air Lines and Hoses: Air lines and hoses connect the various components of the air braking system, allowing the flow of compressed air between them. These lines and hoses need to be properly maintained to ensure the integrity of the system.

Working Principle:
When the driver presses the brake pedal, it sends a signal to the brake control valve, which releases compressed air from the air storage tanks. The released air flows through the air lines and hoses to the brake chambers. In the brake chambers, the diaphragms or pistons move, applying mechanical force to the brake shoes or pads.
In drum brake systems, the brake shoes press against the inside of the brake drum, causing friction that slows down or stops the rotation of the wheels. In disc brake systems, the brake pads squeeze the rotating brake discs, generating the necessary friction to decelerate the vehicle.
To release the brakes and allow the vehicle to move, the driver releases the brake pedal. This action allows the brake control valve to close, cutting off the flow of compressed air to the brake chambers. The compressed air is then directed back to the air storage tanks for future use.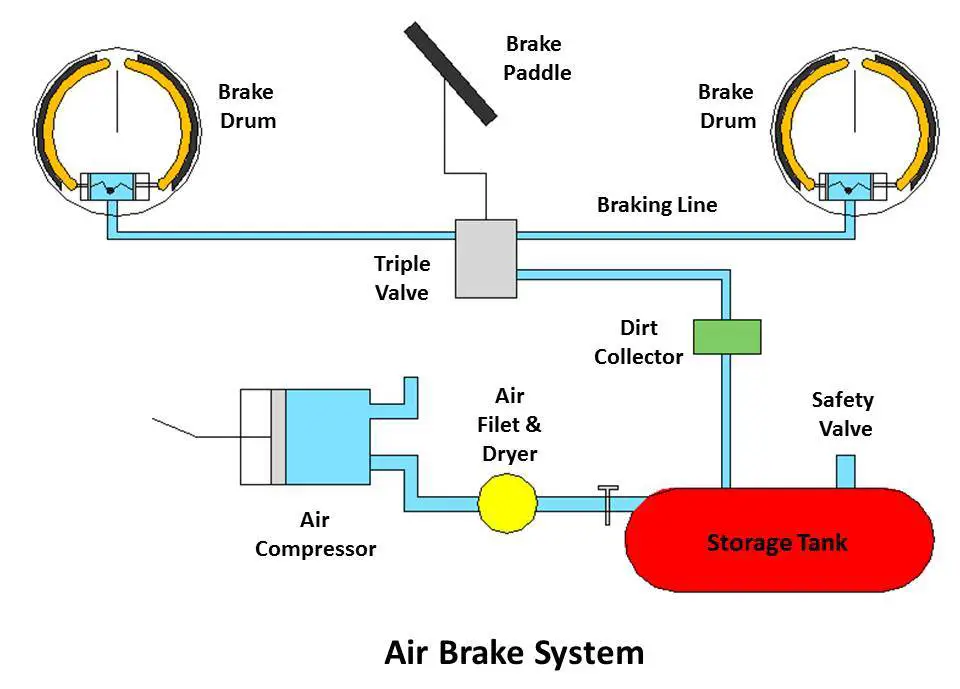
Advantages of Air Braking Systems:
- Reliable Performance: Air brakes offer consistent and reliable braking performance, particularly in heavy vehicles that require substantial stopping power.
- Heat Dissipation: Air brakes are capable of dissipating heat effectively, making them suitable for applications that involve frequent braking and high thermal loads.
- Fail-Safe Operation: Air brakes are designed to be fail-safe, meaning that if there is a loss of air pressure, the brakes automatically engage rather than disengage. This enhances safety by ensuring that the vehicle comes to a stop even in the event of a system failure.
Safety Concern
The air braking system is considered safe for several reasons. Let's explore some of the key aspects that contribute to its safety:
- Reliability: Air brakes are known for their high reliability. They have been extensively used in heavy-duty vehicles such as trucks, buses, and trains for many years, demonstrating their effectiveness in various demanding applications. The system's design and components are engineered to withstand heavy loads and provide consistent and reliable braking performance.
- Redundancy and Fail-Safe Operation: Air brake systems incorporate redundancy and fail-safe mechanisms to enhance safety. In the event of a failure or loss of air pressure, the brakes automatically engage rather than disengage. This ensures that the vehicle comes to a stop even if there is a system failure, providing an added layer of safety.
- Heat Dissipation: Air brakes are capable of effectively dissipating heat, which is critical for ensuring consistent braking performance. When brakes are applied, friction is generated, leading to heat buildup. Air brakes are designed to manage this heat by allowing air to flow over the braking components, preventing overheating and maintaining optimal braking efficiency.
- Progressive Braking: Air brake systems offer progressive braking, meaning that the amount of braking force applied can be adjusted based on the input from the driver. This feature allows for smooth and controlled deceleration, preventing sudden jolts or lock-ups of the wheels, which could lead to loss of control.
- Driver Feedback and Monitoring: Modern air brake systems often include advanced features such as the Driver Display Unit (DDU) or electronic dashboards that provide real-time information to the driver. This feedback includes air pressure readings, brake status, and system warnings. By having access to this information, drivers can monitor the braking system's performance and respond promptly to any issues, enhancing overall safety.
- Compliance with Regulations: Air brake systems are subject to rigorous standards and regulations, ensuring their safety and performance. Organizations such as the Department of Transportation (DOT) in the United States and similar regulatory bodies worldwide enforce standards that manufacturers must adhere to when designing and manufacturing air brake systems. These regulations aim to ensure the reliability and safety of the braking systems used in commercial vehicles.
- Proper Maintenance and Inspection: To maintain the safety of an air brake system, regular maintenance and inspections are crucial. Vehicle operators and maintenance personnel should follow recommended maintenance schedules, check for leaks or damaged components, and conduct periodic inspections to ensure that the system is functioning correctly. By following these practices, potential issues can be identified and addressed before they compromise the system's safety.
In conclusion, the air braking system's reliability, fail-safe operation, heat dissipation capabilities, progressive braking, driver feedback, compliance with regulations, and proper maintenance contribute to its reputation as a safe braking system. These features have made it the preferred choice for heavy vehicles, offering consistent and effective braking performance while prioritizing driver and road safety.





























