The Secret Lives of Whales
Whales, the majestic giants of the ocean, have fascinated humans for centuries. Their sheer size, intelligence, and the mystery surrounding their behaviors and migrations continue to intrigue researchers and the general public alike.
Despite significant scientific advancements, many aspects of whale behavior and migration remain elusive.
This article explores some of the lesser-known aspects of these enigmatic creatures, unveiling the secrets of their lives beneath the waves.
The Intricacies of Whale Migration
 Whale migration is one of nature's most incredible phenomena, involving journeys that span thousands of miles. These migrations are primarily driven by the need to access optimal feeding and breeding grounds.
Whale migration is one of nature's most incredible phenomena, involving journeys that span thousands of miles. These migrations are primarily driven by the need to access optimal feeding and breeding grounds.
Long-Distance Travelers
Humpback whales are renowned for their extensive migratory patterns, traveling up to 5,000 miles from their summer feeding grounds in the cold, nutrient-rich waters of the Arctic and Antarctic to tropical breeding grounds. In the North Pacific, humpback whales migrate from Alaska to Hawaii, covering 3,000 miles in as little as 28 days.
This incredible journey is driven by the need to breed in warmer waters, which are safer for their newborn calves (SD Whale Watch) (NOAA Fisheries).
Uncharted Routes
Some whale species, like the North Pacific right whale, have migration routes that remain largely unknown.
With an estimated population of fewer than 50 individuals, the North Pacific right whale is one of the rarest and most mysterious whale populations.
Recent sightings have provided crucial insights, but their calving grounds and complete migratory paths are still a mystery (NOAA Fisheries) (NOAA Fisheries).
Migration Strategies
Whales utilize a variety of migration strategies to maximize their energy efficiency. For instance, humpback whales have been observed using specific migratory corridors and exhibiting behaviors that minimize energy expenditure while maximizing feeding opportunities along the way.
This strategic migration is essential for their survival, as it allows them to exploit different ecological niches throughout the year (BioMed Central) (SpringerLink).
Social Structures and Communication
 Whales are highly social creatures with complex communication systems and social structures that are critical to their survival and reproduction.
Whales are highly social creatures with complex communication systems and social structures that are critical to their survival and reproduction.
Vocalizations and Songs
Humpback whales are famous for their complex songs, which can last up to 20 minutes and be heard across vast distances underwater.  These songs are thought to play a role in mating, as males sing to attract females and establish dominance.
These songs are thought to play a role in mating, as males sing to attract females and establish dominance.
Each population of humpback whales has its own distinct song, which evolves over time, adding an element of cultural transmission (NOAA Fisheries).
Social Bonds and Group Dynamics
Social structures vary significantly among different whale species. Southern right whales, for instance, exhibit strong mother-calf bonds, with mothers providing extensive care and protection to their young.
These bonds are crucial during the early stages of a calf's life, ensuring they receive the necessary nourishment and safety from predators (SpringerLink).
Cooperative Behaviors
Whales also engage in cooperative behaviors that enhance their survival. For example, baleen whales like humpbacks often feed in groups, employing techniques such as bubble-net feeding, where they create bubbles to herd and concentrate fish before engulfing them.
This cooperative hunting strategy not only improves feeding efficiency but also reinforces social bonds within the group (SpringerLink).
Mysteries of Whale Behavior
Despite extensive research, many aspects of whale behavior remain shrouded in mystery, offering intriguing areas for future exploration.
Suckling and Maternal Care
Humpback whale suckling behavior provides a fascinating glimpse into maternal care strategies.
Recent studies have highlighted the extended period during which calves rely on their mothers for nutrition and protection, a critical phase that influences their survival and development.
Understanding these behaviors is key to ensuring the protection of critical breeding and nursery habitats (BioMed Central).
Elusive Feeding Strategies
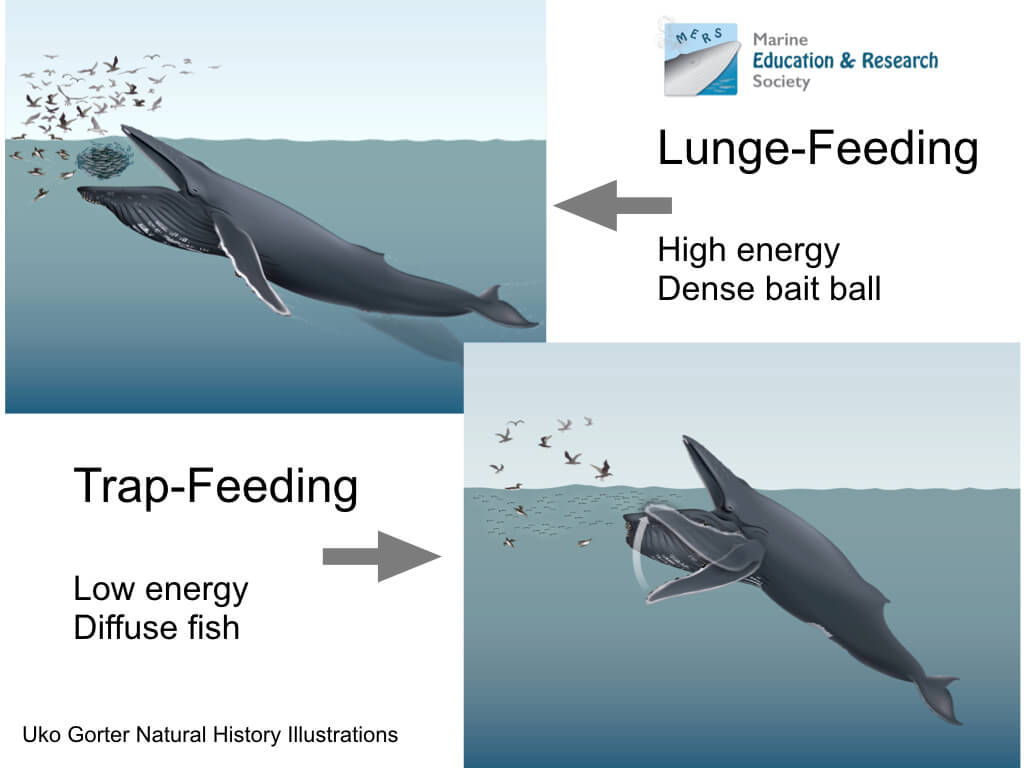 Whales employ a variety of feeding strategies, some of which are still being uncovered. For example, a previously unknown feeding strategy involving coordinated lunging and rapid directional changes has been observed in humpback whales.
Whales employ a variety of feeding strategies, some of which are still being uncovered. For example, a previously unknown feeding strategy involving coordinated lunging and rapid directional changes has been observed in humpback whales.
These complex behaviors highlight the adaptability and intelligence of these ocean giants as they exploit different prey types and environmental conditions (SpringerLink) (SD Whale Watch).
Mysterious Vocalizations
While much is known about whale songs, other vocalizations remain less understood. North Pacific right whales, for instance, produce "gunshot" calls whose exact purpose is still debated among scientists.
These loud, sharp sounds could play a role in communication, navigation, or social interactions, offering an intriguing area for further research (NOAA Fisheries) (NOAA Fisheries).
Conservation and Future Research
The study of whale behavior and migration is not only fascinating but also crucial for their conservation. Understanding these aspects can inform better protection measures and ensure the survival of these majestic creatures.
Threats to Whale Populations
Whales face numerous threats, including entanglement in fishing gear, vessel strikes, and ocean noise pollution.
These threats can disrupt their migratory patterns, communication, and breeding behaviors, making conservation efforts all the more critical.
Organizations like NOAA Fisheries are actively working to mitigate these threats through various conservation and management programs (NOAA Fisheries) (NOAA Fisheries).
The Role of Technology
Advancements in technology, such as satellite telemetry and acoustic monitoring, have revolutionized the study of whales.
These tools allow researchers to track whale movements in real time, uncovering migratory routes, feeding grounds, and social interactions.
Continued innovation in these areas will be essential for deepening our understanding of whale behavior and enhancing conservation efforts (BioMed Central) (NOAA Fisheries).
Community and Global Efforts
Conservation is a global effort that requires collaboration across borders. International agreements, such as those enforced by the International Whaling Commission, play a crucial role in protecting whale populations worldwide.
Additionally, public awareness and community involvement are vital for supporting conservation initiatives and promoting sustainable practices that safeguard whale habitats (NOAA Fisheries) (NOAA Fisheries).
Conclusion
The secret lives of whales, filled with complex behaviors and vast migrations, continue to captivate and inspire. As we uncover more about these magnificent creatures, it becomes clear that protecting them is not only a scientific imperative but also a moral one. By advancing our knowledge and fostering a global commitment to conservation, we can ensure that future generations will continue to marvel at the mysteries of the largest ocean dwellers.
References
- "First description of migratory behavior of humpback whales," Animal Biotelemetry.
- Recent Sightings of Highly Endangered Eastern North Pacific
- "Baleen Whale Migration