What is a sidechain in cryptocurrency?
A sidechain is a separate blockchain that is linked to a main blockchain, also known as the parent chain. It is used to offload some of the load from the main blockchain, such as processing transactions or storing data. Sidechains can also be used to experiment with new features or applications without affecting the main blockchain.
How do sidechains work?
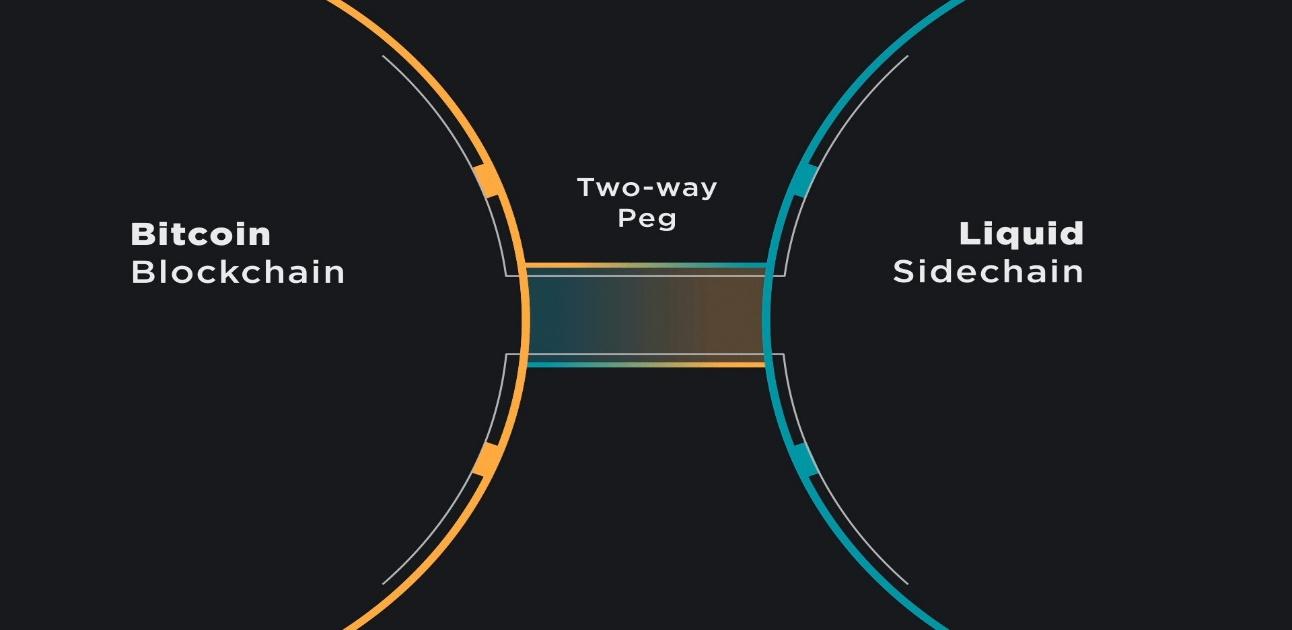
Sidechains are connected to the main blockchain using a two-way peg. This means that tokens can be transferred back and forth between the two chains. There are two main types of sidechains: federated sidechains and pegged sidechains.
- Federated sidechains are controlled by a group of nodes that are trusted by the main blockchain. This makes them more centralized than pegged sidechains, but they can be faster and more efficient.

- Pegged sidechains use a more decentralized mechanism to secure the bridge between the two chains. This makes them slower and less efficient than federated sidechains, but they are more secure.
What are the benefits of sidechains?
Sidechains offer a number of benefits over the main blockchain, including:
- Scalability: Sidechains can be used to offload some of the load from the main blockchain, which can improve its scalability.
- Experimentation: Sidechains can be used to experiment with new features or applications without affecting the main blockchain.
- Security: Sidechains can be used to improve the security of the main blockchain by isolating certain risks.
What are the drawbacks of sidechains?
Sidechains also have some drawbacks, including:
- Complexity: Sidechains can be complex to set up and manage.
- Risk: Sidechains are still relatively new, so there is some risk associated with using them.
- Interoperability: Sidechains can be difficult to connect to each other.
Sidechains are a promising technology that can be used to improve the scalability, security, and flexibility of blockchains. However, they are still a relatively new technology, and there are some challenges that need to be addressed before they can be widely adopted.
Here are some examples of sidechains:
- Liquid Network: The Liquid Network is a sidechain for Bitcoin that is designed to improve its scalability and speed.

- Rootstock (RSK): RSK is a sidechain for Bitcoin that is designed to support smart contracts.

- Cosmos Hub: The Cosmos Hub is a general-purpose sidechain that can be used to connect different blockchains.

- Multichain: Multichain is a platform that allows users to create and manage sidechains.
The future of sidechains
Sidechains are a promising technology that has the potential to play a major role in the future of blockchain. As the blockchain industry continues to grow, sidechains will be used to address the scalability, security, and flexibility challenges that are facing blockchains today.
Sidechains and L2 solutions
Sidechains and Layer 2 solutions are both scalability solutions for blockchains. However, they have different approaches and offer different trade-offs.
Sidechains are separate blockchains that are linked to a main blockchain, also known as the parent chain. They are used to offload some of the load from the main blockchain, such as processing transactions or storing data. Sidechains can also be used to experiment with new features or applications without affecting the main blockchain.
Layer 2 solutions are built on top of the main blockchain and do not have their own blockchain. They use a variety of techniques to improve scalability, such as batching transactions, off-chain computation, and state channels. Layer 2 solutions are typically more efficient than sidechains, but they are also more complex and less secure.
In general, sidechains are considered to be less secure than Layer 2 solutions because they have their own blockchain and consensus mechanism. However, sidechains can be more flexible and easier to use than Layer 2 solutions.
The best approach for scalability will depend on the specific needs of the blockchain. If security is the top priority, then a sidechain may be a better choice. If scalability is the top priority, then a Layer 2 solution may be a better choice.
Here is a table summarizing the key differences between sidechains and Layer 2 solutions: