Layer 2 Networks: The Future of Blockchain Scalability
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we think about data security and transactions. However, one of the biggest challenges facing blockchains is scalability. The original blockchain, Bitcoin, can only process about 7 transactions per second. This is not enough to handle the volume of transactions that would be required for widespread adoption.
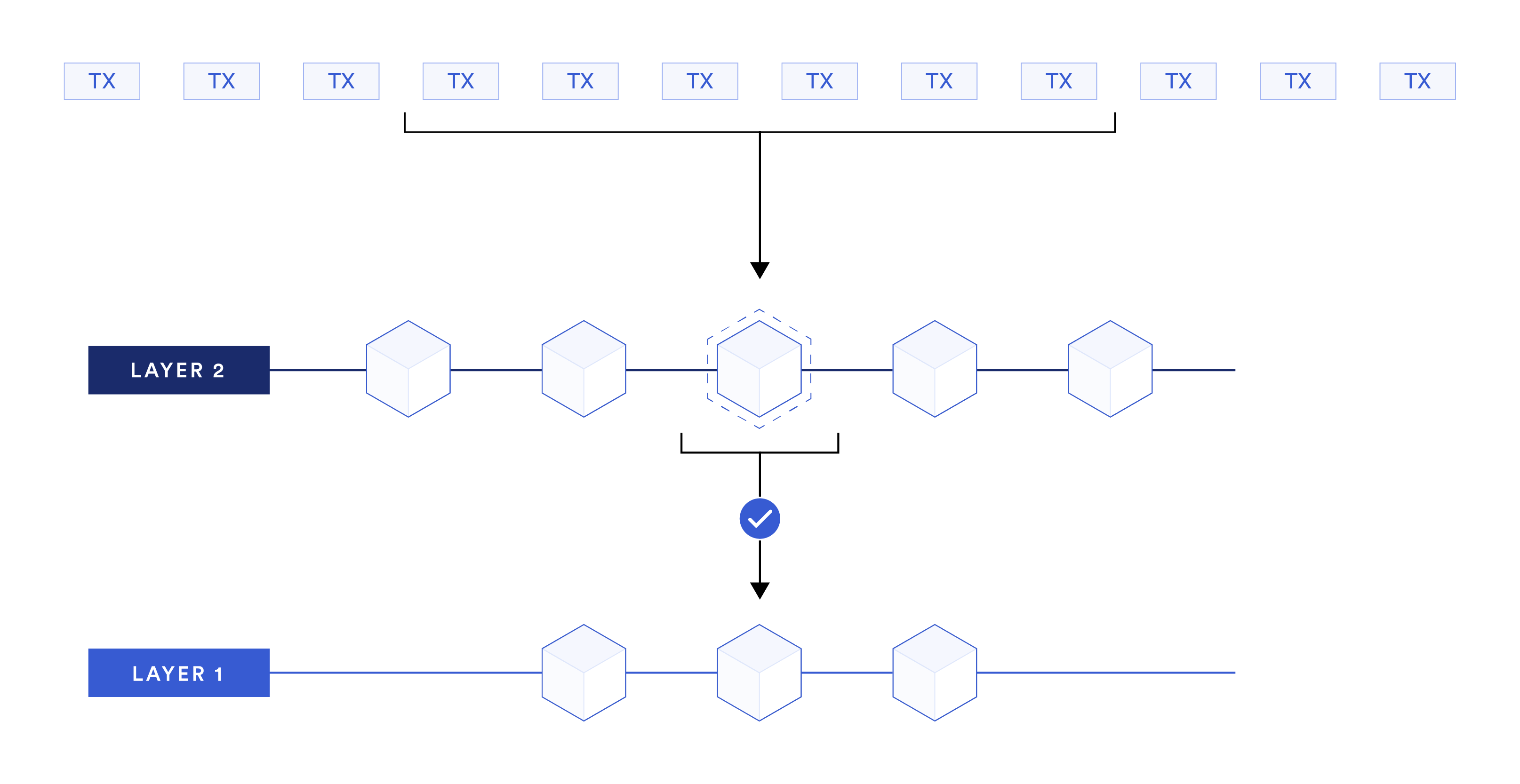
Layer 2 networks are a way to address the scalability problem of blockchains. They are essentially sidechains that run alongside the main blockchain. This allows them to process transactions much faster and more cheaply than the main chain.
Why are Layer 2 Networks Necessary?
There are several reasons why layer 2 networks are necessary for the future of blockchain technology.
- Scalability: As mentioned above, layer 2 networks can help to improve the scalability of blockchains. This is essential for widespread adoption, as it will allow blockchains to handle the volume of transactions that would be required for mass usage.
- Speed: Layer 2 networks can also help to improve the speed of transactions on blockchains. This is important for users who want to be able to make quick and easy payments.
- Cost: Layer 2 networks can also help to reduce the cost of transactions on blockchains. This is important for businesses and individuals who want to save money on their transactions.
- Security: Layer 2 networks are still secure, as they are backed by the main blockchain. This means that users can be confident that their funds are safe even if the layer 2 network is hacked.
Types of Layer 2 Networks
There are several different types of layer 2 networks. Some of the most popular include:
- State channels: State channels are a way to bundle multiple transactions together and process them off-chain. This can significantly reduce the load on the main blockchain, and it can also improve the speed and cost of transactions.
- Rollups: Rollups are a way to compress transactions and store them on the main blockchain. This can also improve the scalability of blockchains, and it can also make it easier to audit transactions.
- Sidechains: Sidechains are completely separate blockchains that are linked to the main blockchain. This allows them to process transactions more quickly and cheaply, and it also gives them more flexibility.
Conclusion
Layer 2 networks are an essential part of the future of blockchain technology. They can help to improve the scalability, speed, cost, and security of blockchains. As blockchain technology continues to grow, layer 2 networks will become increasingly important.
In addition to the benefits mentioned above, layer 2 networks can also offer other advantages, such as:
- Privacy: Layer 2 networks can be used to improve the privacy of transactions. This is because they can process transactions off-chain, which means that they do not need to be recorded on the public blockchain.
- Interoperability: Layer 2 networks can also help to improve the interoperability of blockchains. This is because they can be used to connect different blockchains together.
Overall, layer 2 networks are a powerful tool that can be used to improve the performance and functionality of blockchains. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, layer 2 networks are likely to play an increasingly important role.
Examples of layer 2 networks:
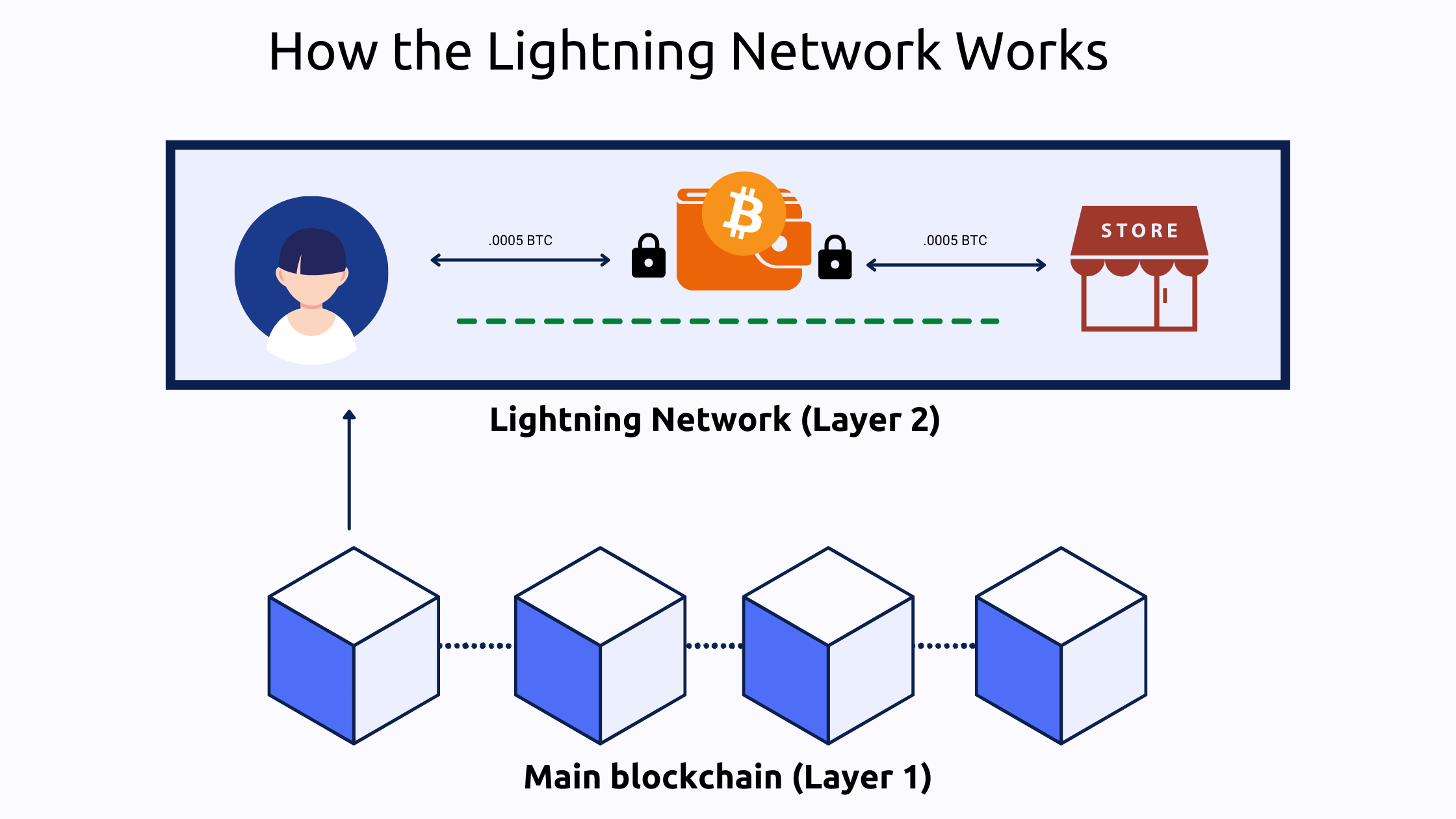
- Lightning Network: The Lightning Network is a layer 2 network for Bitcoin that allows for fast and cheap payments. It works by creating payment channels between users, which allows them to send payments to each other without having to broadcast every transaction to the main blockchain.
- Optimistic Rollups: Optimistic rollups are a type of layer 2 network for Ethereum that uses fraud proofs to ensure the validity of transactions. This allows them to process transactions much faster and more cheaply than the main Ethereum network.

- zkRollups: zkRollups are a type of layer 2 network for Ethereum that uses zero-knowledge proofs to verify the validity of transactions. This is even more secure than optimistic rollups, but it also comes with a slight performance penalty.
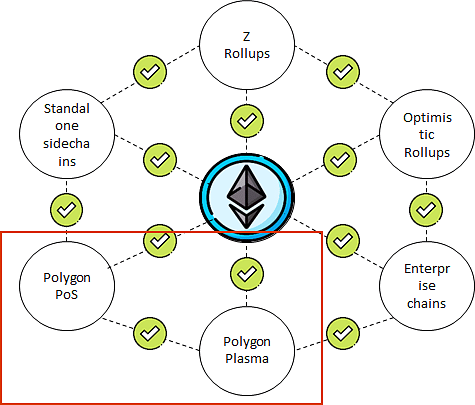
- Polygon: Polygon is a layer 2 network for Ethereum that uses a variety of different scaling techniques, including sidechains, rollups, and plasma. This allows it to offer a wide range of scalability and security options for developers.
- Arbitrum: Arbitrum is a layer 2 network for Ethereum that uses optimistic rollups to improve scalability. It is designed to be as compatible with Ethereum as possible, so that developers can easily port their applications to Arbitrum.

These are just a few examples of the many layer 2 networks that are currently being developed. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more layer 2 networks emerge in the future.





































![𝐐𝐮𝐢𝐜𝐤 𝐚𝐥𝐩𝐡𝐚: [𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑚𝑦 𝑎𝑡 𝑇𝐺𝐸] – 𝐉𝐔𝐒𝐓 𝐃𝐎 𝐈𝐓 𝐍𝐎𝐖!!!!](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/30a2649d-ce6e-4d5d-8666-7a0e754fc4e6/1)