Crypto Safety: Hot Cold & Exchange
Looking at the various types of wallets you’ll encounter on your crypto journey.
If you aren’t a medium member, you can read with no paywall via substack
Cryptocurrency can be risky due to market volatility and lack of regulation. Use reputable platforms, avoid emotional trading, and only invest what you can afford to lose. Be cautious and remember, not your keys, not your crypto.
When you’re starting your crypto journey, there’s a lot to take on board around things like security and where and how to store your crypto. If you’re pretty new to the world of Web 3 then you might find navigating this advice to be difficult and even a little intimidating.
Today, we’ll break down some of these myths and help explain some of the different types of wallets you might see as well as some of the pros and cons around each type. We’ll also look at how you might back up and protect some of these wallets. Let’s get started!
What Is A Wallet?
An essential part of your crypto journey a wallet is used for storing your cryptocurrency and processing transactions on the blockchain. While your wallet is able to store your tokens, you’ll also find your wallet can hold other things as well. This can include Non-Fungible Tokens (NFT) and even Domain Names (SNS/ENS) which allow you to use an identifier for transactions instead of a complex wallet number, making it much easier to transact on the blockchain.
When you’re using your wallet, you’ll need to get used to a few relevant terms. There’s the “seed phrase”, which should be properly stored for recovery purposes. There’s a “public key” which is your external wallet address as well as a “private key” which must be carefully secured.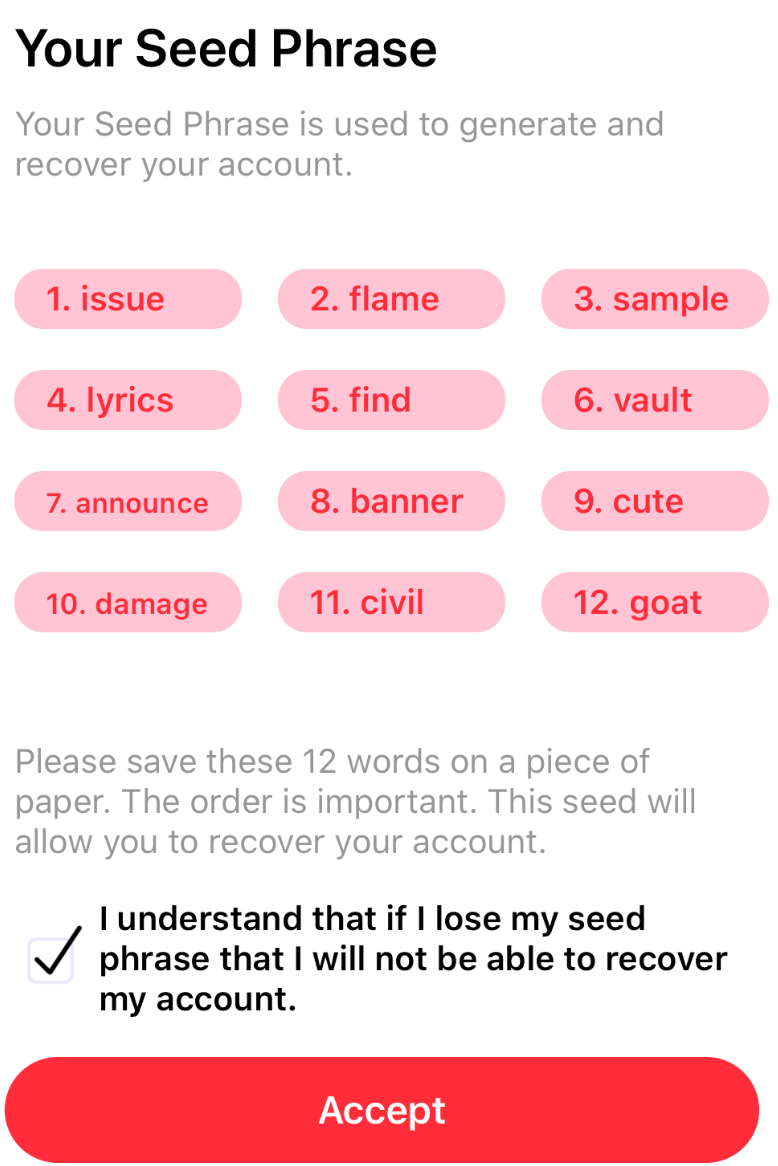 Knowing and protecting your seed phrase is extremely important. Source: Wikipedia
Knowing and protecting your seed phrase is extremely important. Source: Wikipedia
You’ll also “Sign” transactions using your wallet, allowing you to move funds across the blockchain and sometimes you’ll sign a fee-free transaction to a website that allows you to log in to access a particular Web3 service.
Crypto scams will often target a users wallet so being aware of what types of scams you may encounter will help you become more confident as you start to navigate the blockchain.
Wallet Types
The first thing to understand is that there is no one-size-fits-all for crypto wallets. Each come with their own strengths and weakness and you’ll find useful use cases for each one. You’ll also find that some wallets are not “cross-chain” compatible and require their own chain-specific wallet to function. This means a Bitcoin wallet will be different to a Solana wallet, so you’ll need to ensure you’re able to identify what you need before you get involved.
All these points aside though, typically you’ll find 3 wallet types commonly used.
Hot Wallets:
A hot wallet is a type of wallet that is connected to the internet, allowing for immediate access to funds. It’s often used for frequent transactions or trading due to its convenience. Hot wallets are typically less secure than cold wallets (offline storage) because they are constantly connected to the internet, making them vulnerable to hacking or malware attacks.
Despite this risk, hot wallets are popular among users who need quick access to their funds for active trading or spending. They provide flexibility and accessibility but require careful security measures to mitigate the associated risks effectively. Browser-based wallets are considered to be hot wallets.
Cold Wallets:
A cold wallet is a wallet that stores digital assets offline, disconnected from the internet. This isolation from online networks enhances security significantly, as it minimizes the risk of unauthorized access, hacking, or theft.
Cold wallets are typically used for long-term storage of cryptocurrencies, as they offer a high level of protection against cyber threats. Common forms of cold wallets include hardware wallets (physical devices that store private keys offline) and paper wallets (physical documents containing private keys).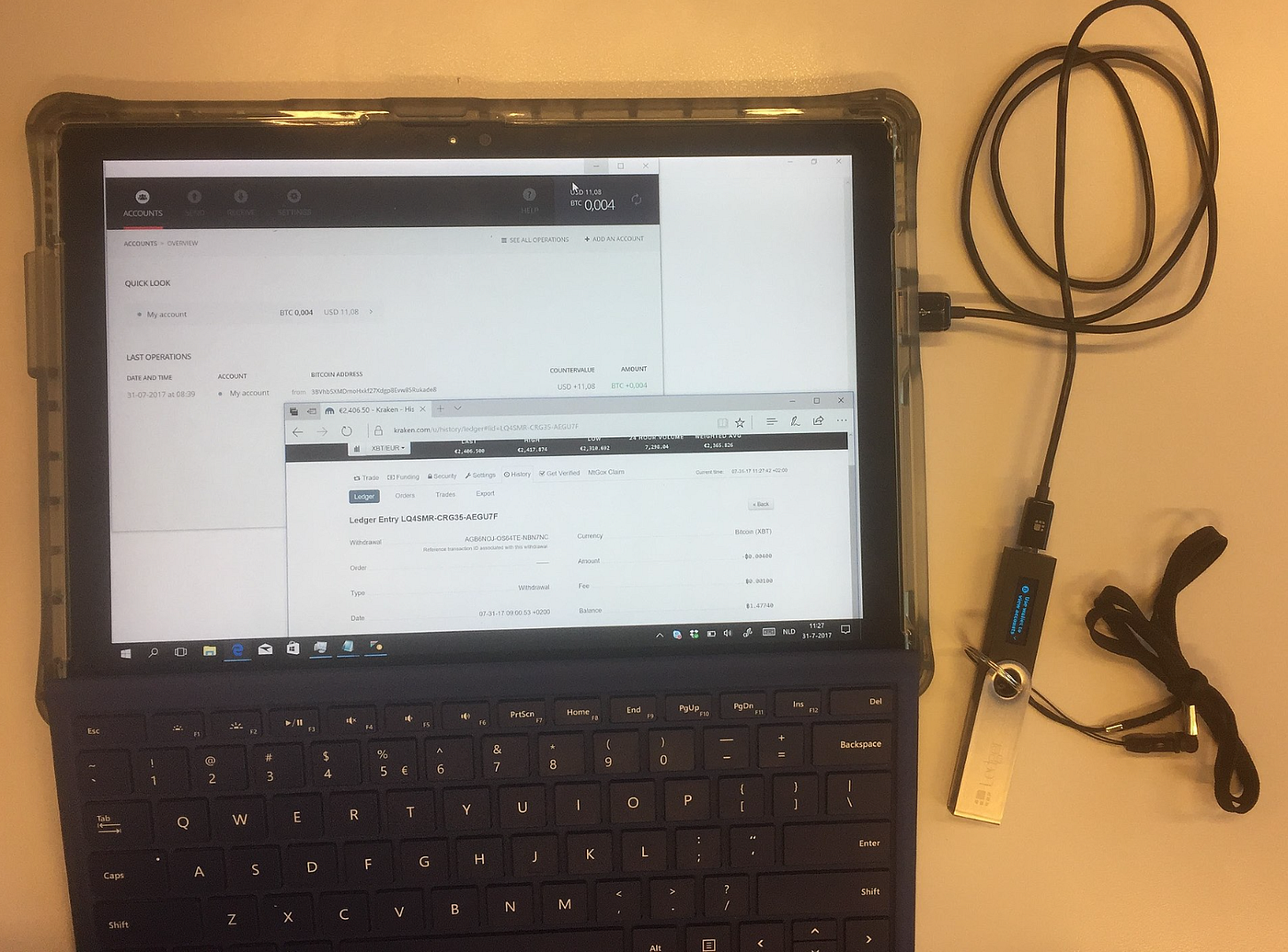 Cold Wallets are a great long-term option. Source: Wikipedia
Cold Wallets are a great long-term option. Source: Wikipedia
While cold wallets provide robust security, they require extra steps, such as manual transactions for access, making them less suitable for frequent trading or transactions compared to hot wallets.
Exchange Wallets:
An exchange wallet is provided by cryptocurrency exchanges to facilitate the trading and storage of digital assets. These wallets are integrated into the exchange platform, allowing users to buy, sell, and exchange various cryptocurrencies directly within the exchange environment.
Exchange wallets offer convenience and accessibility, as users can manage their funds and execute transactions seamlessly through the exchange’s interface. However, they also come with inherent security risks, as they are centralized and controlled by the exchange. Instances of hacking or security breaches targeting exchange wallets have occurred in the past, resulting in the loss of funds for users.
So, while exchange wallets are convenient for active trading and liquidity purposes, there are better ways of achieving long-term storage safely.
Backing Up
To gain peace of mind while you’re dealing with blockchain assets, you’ll want to ensure that you’re able to understand the process behind backing up your wallet including how to recover it after an incident or transfer.
This is where the “seed phrase” we mentioned earlier will come into play. By restoring a wallet and entering this seed phrase you’ll be able to view your assets on a different machine or wallet system. However, it’s important to understand that anyone with this phrase will also be able to recover your wallet. So, when you’re backing up your wallets it’s wise to take a few precautions while doing so to help protect the integrity of your funds. Paper Bitcoin Wallet. Source: Wikipedia
Paper Bitcoin Wallet. Source: Wikipedia
Some good practices are using encrypted storage and/or using offline storage. However, you’ll also find some more die-hard crypto fans will sometimes use metal imprinting or even simple paper wallets to help track their assets. Like anything in life, you should make these decisions based on your own personal circumstances. For now, we should understand that we should never reveal our seed phrase, especially if someone has asked for it.
Signing Your Wallet
While signing your wallet will eventually become part of the process of exploring the blockchain, understanding what happens when this occurs is also an important part of the crypto journey as well. When you “Sign” a transaction with your wallet, you’re effectively giving approval to transfer funds and pay for gas while doing so. If you’re using a genuine site you’ll find no issue in this. Should you connect to a malicious site though, you’ll find that in signing the malicious transaction you’re compromising the integrity of your wallet at the same time.
This happens because for the process to occur we’ll need to obtain a cryptographic signature which requires both the public and private sections of our wallet keys. Malicious sites are able to use this to their advantage.
So, when signing transactions it’s good practice to confirm you’re using the intended website and not a copy, as well as exploring what exactly happens when you’re signing the transaction. Thankfully many wallets provide “simulations” that will help to identify scam transactions before they happen, however, we should pick up the habit of checking our transactions manually as well.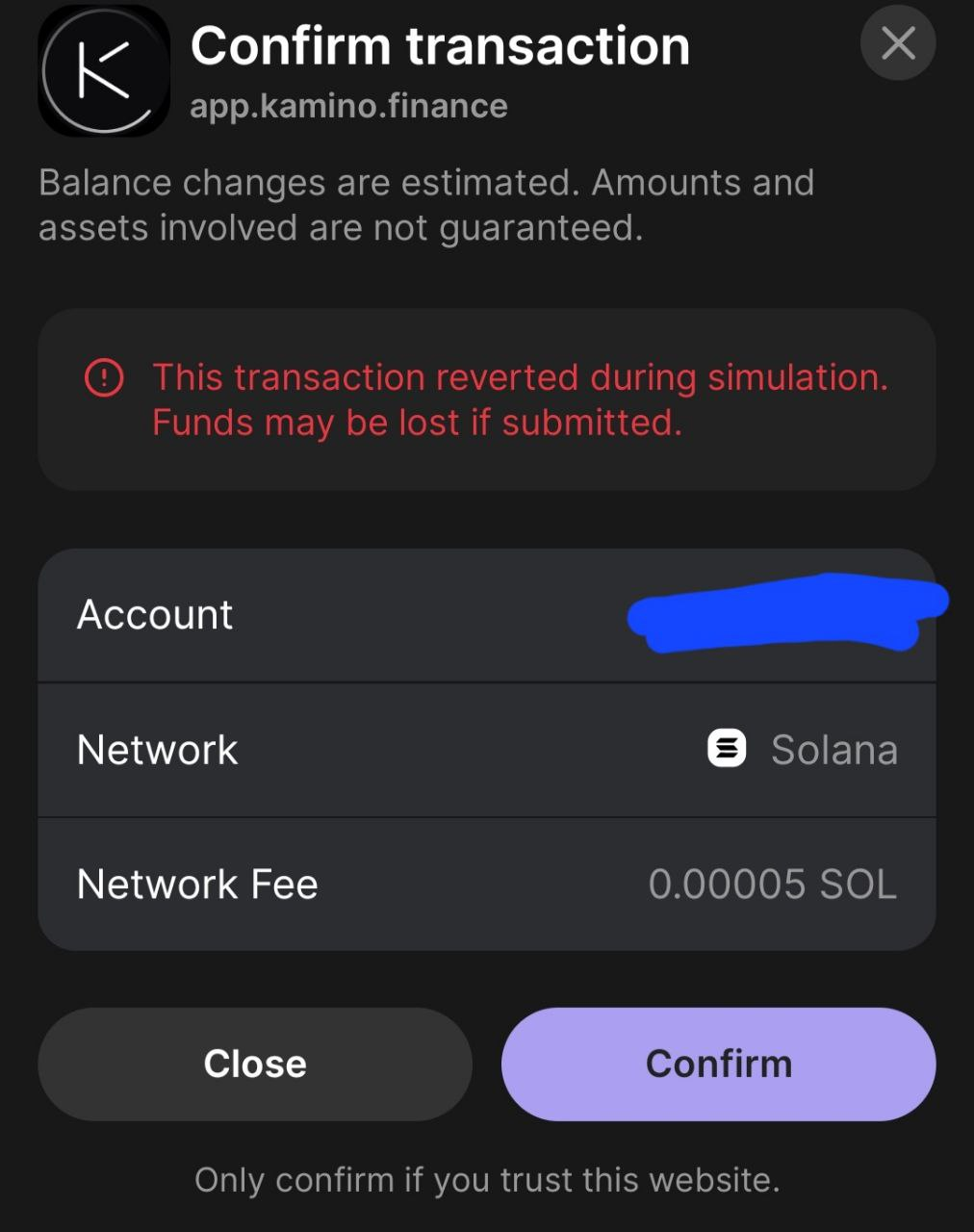
Revoking Authority
One of the last things we’ll need to remember is the concept of “revoking” authority permissions to sites we’ve approved previously. While you won’t need to do this too often, it’s a good habit to do this every so often to tidy up your footprint as you’re navigating on-chain. Thankfully, we can use some specific tools for this, and one of the best tools is Revoke.Cash.
Revoke.cash will allow you to see active permission in your wallet and give you the means to revoke those that are no longer needed, quickly and easily. While it won’t prevent all incidents, understanding how to give and revoke permissions is still a large part of your new crypto journey.
In Closing
So there you have it! You’ve now learnt about different wallet types, including how to secure them, private and public keys and how to check and revoke permissions. In our next Getting Started article we’ll look at the process of sending and receiving different types of cryptocurrency using your wallet as well as exploring the fundamentals behind cryptocurrency bridges and providing liquidity.
Would you like to read about a specific topic, or see a particular type of tutorial? If so, drop a request in the comments. We’d love to hear from you!
Medium has recently made some algorithm changes to improve the discoverability of articles like this one. These changes are designed to ensure that high-quality content reaches a wider audience, and your engagement plays a crucial role in making that happen.
If you found this article insightful, informative, or entertaining, we kindly encourage you to show your support. Clapping for this article not only lets the author know that their work is appreciated but also helps boost its visibility to others who might benefit from it.
🌟 Enjoyed this article? Support our work and join the community! 🌟
💙 Support me on Ko-fi: Investigator515
📢 Join our OSINT Telegram channel for exclusive updates or
📢 Follow our crypto Telegram for the latest giveaways
🐦 Follow us on Twitter and
🟦 We’re now on Bluesky!
🔗 Articles we think you’ll like:
- Software Defined Radio & Radio Hacking Pt 1
- OSINT Investigators Guide to Self Care & Resilience
✉️ Want more content like this? Sign up for email updates

























![[LIVE] Engage2Earn: auspol follower rush](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/c1a761de-5ce9-4e9b-b5b3-dc009e60bfa8/1)













![[ℕ𝕖𝕧𝕖𝕣] 𝕊𝕖𝕝𝕝 𝕐𝕠𝕦𝕣 𝔹𝕚𝕥𝕔𝕠𝕚𝕟 - And Now What.... Pray To The God Of Hopium?](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/79e7827b-c644-4853-b048-a9601a8a8da7/1)


















