The Global Refugee Crisis: Challenges and Potential Solutions
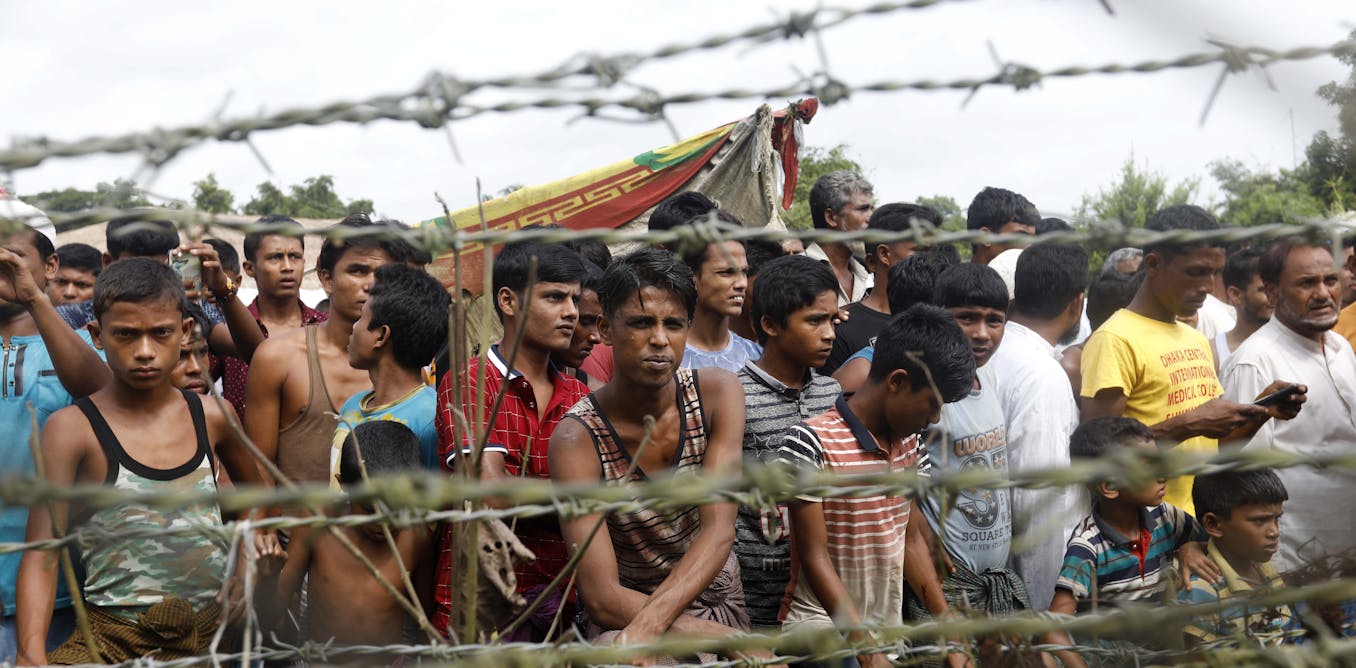 The global refugee crisis is one of the most pressing humanitarian issues of our time. Millions of people are displaced from their homes due to conflict, persecution, and natural disasters, seeking refuge and safety in foreign lands.
The global refugee crisis is one of the most pressing humanitarian issues of our time. Millions of people are displaced from their homes due to conflict, persecution, and natural disasters, seeking refuge and safety in foreign lands.
The scale of this crisis presents numerous challenges, but it also offers opportunities for innovative and compassionate solutions.
This article explores the complexities of the global refugee crisis, the challenges faced by refugees and host countries, and potential strategies to address these issues effectively.
Understanding the Crisis: Scope and Causes
The Scope of Displacement
As of recent estimates, there are over 26 million refugees worldwide, with millions more internally displaced or seeking asylum. This unprecedented level of displacement is driven by a range of factors, including armed conflicts, political instability, economic hardships, and environmental changes.
The crisis is particularly acute in regions like the Middle East, Africa, and Central America, where conflict and persecution are prevalent.
Root Causes of Displacement
- Conflict and Violence: Wars, civil conflicts, and persecution based on ethnicity, religion, or political beliefs are major drivers of displacement. Countries like Syria, Afghanistan, and South Sudan have seen significant outflows of refugees due to ongoing violence and instability.
- Environmental Factors: Climate change and natural disasters, such as floods, droughts, and hurricanes, force people to leave their homes. Environmental refugees, often overlooked in policy discussions, are increasing in number as climate change accelerates.
- Economic and Social Factors: In some cases, economic collapse and extreme poverty push people to seek better opportunities elsewhere. This is often intertwined with political repression and lack of basic rights, compelling individuals to flee their countries.
Challenges Faced by Refugees and Host Countries
Humanitarian and Security Concerns
Refugees face numerous challenges, including unsafe travel conditions, lack of access to basic necessities, and exposure to exploitation and violence. Upon arrival in host countries, they often encounter barriers such as discrimination, legal obstacles, and limited access to education and healthcare.
- Protection and Safety: Many refugees live in precarious conditions, either in camps or urban settings, where they are vulnerable to violence, exploitation, and human trafficking. Ensuring their safety and protecting their rights is a critical challenge for host countries and international organizations.
- Legal and Social Integration: Refugees often struggle with legal status issues, hindering their ability to work, access education, and integrate into society. This can lead to marginalization and social tensions, especially in countries with limited resources to support large influxes of people.
Economic and Social Strain on Host Countries
Host countries, especially those with limited resources, face significant economic and social challenges in accommodating refugees. This includes the cost of providing shelter, healthcare, and education, as well as the strain on local labor markets and social services.
- Economic Burden: The sudden influx of refugees can strain public resources and infrastructure, particularly in developing countries already facing economic difficulties. This can lead to competition for jobs and services, potentially fueling resentment among local populations.
- Social Cohesion and Integration: Integrating refugees into local communities is a complex process that requires cultural sensitivity, adequate support systems, and policies that promote social cohesion. Failure to address these issues can lead to social tensions and xenophobia.
Potential Solutions: Towards a Comprehensive Approach
International Cooperation and Responsibility Sharing
Addressing the global refugee crisis requires a coordinated international response that includes both immediate humanitarian aid and long-term solutions. Key to this is the principle of responsibility sharing, where countries work together to support refugees and host nations.
- Humanitarian Aid and Development Assistance: Providing immediate aid to refugees, such as food, shelter, and healthcare, is crucial. However, there is also a need for long-term development assistance to improve living conditions in host countries and address the root causes of displacement in origin countries.
- Resettlement and Safe Pathways: Increasing resettlement quotas and providing safe and legal pathways for refugees to relocate can alleviate pressure on host countries and offer refugees a chance for a better life. This requires a commitment from wealthier nations to take in more refugees and support integration efforts.
Legal and Policy Frameworks
Strengthening international legal frameworks and national policies is essential for protecting the rights of refugees and ensuring fair treatment. This includes adhering to international treaties, such as the 1951 Refugee Convention, and developing national policies that facilitate integration and access to services.
- Refugee Rights and Protections: Ensuring that refugees have access to legal protection, including the right to seek asylum and protection against refoulement (forced return), is a fundamental aspect of international law that needs to be upheld.
- Integration Policies: Effective integration policies, including language training, employment programs, and social services, can help refugees rebuild their lives and contribute to their new communities. Education and employment are particularly important for enabling refugees to become self-sufficient and integrate into society.
Innovative Solutions and Community Engagement
Innovative approaches and active community engagement are critical for addressing the complex challenges of the refugee crisis. This includes leveraging technology, fostering public-private partnerships, and involving local communities in support efforts.
- Technology and Innovation: Technology can play a pivotal role in improving refugee support services, from mobile apps that provide legal information to online platforms for job matching. Innovations in education and healthcare delivery can also enhance access to essential services for refugees.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in refugee support efforts can foster social cohesion and mutual understanding. This includes initiatives that promote cultural exchange, community-based support networks, and volunteer programs.
Conclusion
The global refugee crisis is a multifaceted challenge that requires a comprehensive and compassionate response. While the challenges are significant, there are also opportunities to create meaningful change through international cooperation, legal reforms, and innovative solutions. By addressing the root causes of displacement, supporting host countries, and ensuring the protection and integration of refugees, the international community can work towards a future where all individuals have the opportunity to live in safety and dignity.
Sources
World Bank: The Economic and Social Impact of Refugees
The Guardian: How Climate Change is Driving a New Global Refugee Crisis
UNESCO: Education and the Refugee Crisis