Enhancing User Satisfaction in Public Housing: A Comprehensive Approach
Introduction:
Housing is a fundamental human need, essential for shelter, security, and well-being. Public housing initiatives play a crucial role in providing affordable and accessible housing for low-income individuals and families. However, the effectiveness of public housing programs ultimately hinges on user satisfaction – the extent to which residents are content with their living conditions and amenities. This article explores the concept of user satisfaction in public housing, delving into its theoretical framework, the importance of periodic assessment, and innovative approaches to measuring satisfaction, such as Mohit's Relative Satisfaction Index formula.
Background on Housing and Public Housing:
Housing is a complex socio-economic phenomenon influenced by factors such as income, demographics, urbanization, and government policies. Public housing refers to housing projects initiated and managed by government agencies or non-profit organizations to provide affordable housing options for low-income households. Public housing developments often aim to address housing shortages, urban sprawl, and homelessness, promoting social inclusion and community development.
Understanding Housing Satisfaction:
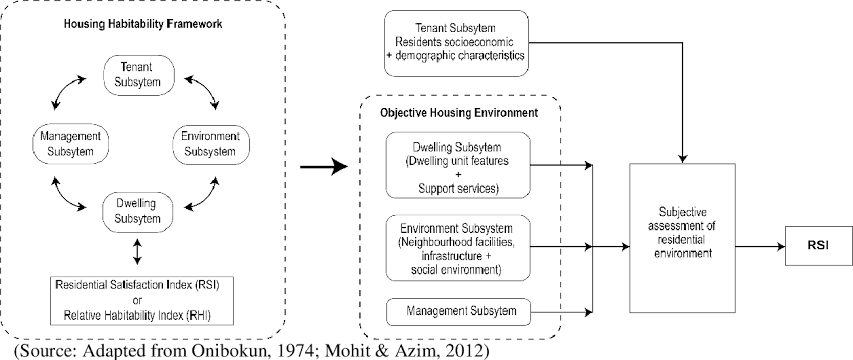
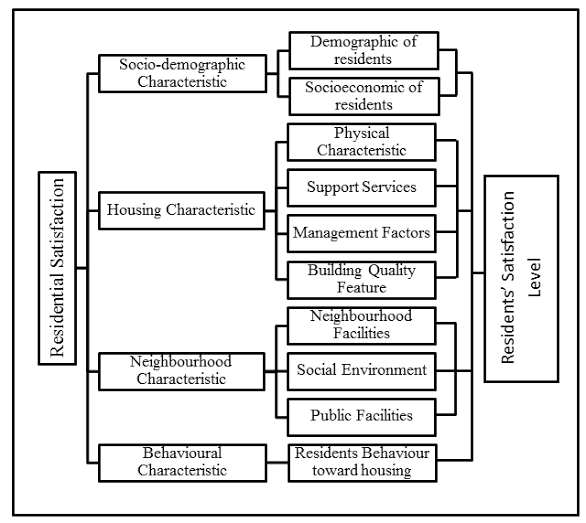
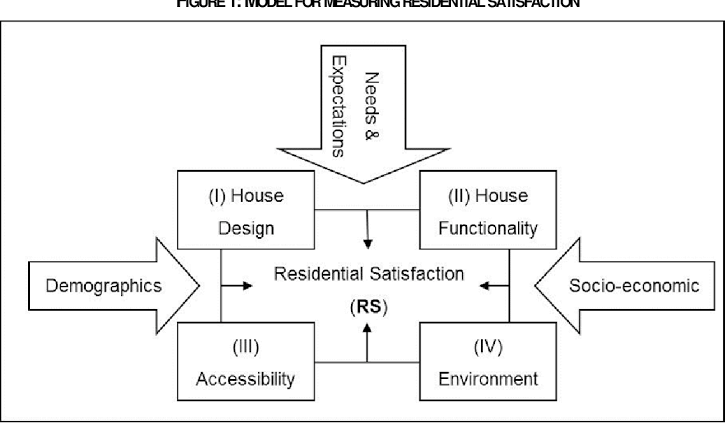
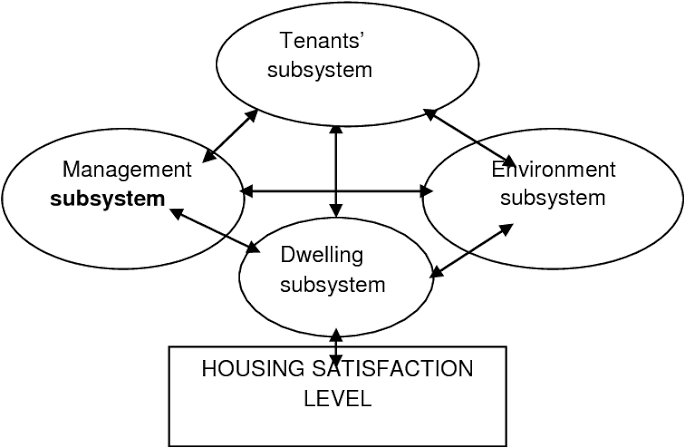
Housing satisfaction refers to the subjective evaluation of housing conditions and amenities by residents. It encompasses various dimensions, including physical quality, safety, affordability, accessibility, and social environment. Satisfaction levels can vary among residents based on individual preferences, needs, and experiences. Factors such as housing design, location, maintenance, and neighborhood amenities influence overall satisfaction levels.
Theory of Housing Satisfaction:
The Theory of Housing Satisfaction posits that satisfaction with housing is influenced by residents' perceptions of housing attributes and their expectations. According to this theory, residents compare their housing situation with their ideal or expected standards, leading to satisfaction or dissatisfaction. Key determinants of housing satisfaction include housing quality, affordability, neighborhood characteristics, and social interactions. The theory emphasizes the importance of understanding residents' perceptions and needs to enhance satisfaction levels.
Importance of Periodic Assessment:
Periodic assessment of housing satisfaction is essential for identifying areas of improvement and ensuring the effectiveness of public housing programs. By regularly surveying residents and gathering feedback, housing authorities can identify strengths and weaknesses in housing developments, address maintenance issues, and prioritize resources for necessary upgrades. Periodic assessments also empower residents by giving them a voice in decision-making processes and fostering a sense of ownership and community pride.
Measuring Housing Satisfaction:
Mohit's Relative Satisfaction Index formula is a valuable tool for quantifying housing satisfaction ratings and comparing satisfaction levels across different housing developments. This formula calculates satisfaction scores based on residents' ratings of various housing attributes, such as cleanliness, security, amenities, and maintenance. By aggregating individual satisfaction ratings into a single index, housing authorities can assess overall satisfaction levels and identify areas requiring intervention.
Illustrative Example:
Consider a public housing estate comprising multiple residential blocks. To assess housing satisfaction, housing authorities administer surveys to residents, asking them to rate various aspects of their housing experience using a scale of 1 to 5. Residents rate factors such as cleanliness, safety, maintenance, amenities, and neighborhood environment. Using Mohit's Relative Satisfaction Index formula, authorities calculate satisfaction scores for each attribute and aggregate them to obtain an overall satisfaction index for the estate. This index serves as a benchmark for evaluating satisfaction levels and guiding decision-making processes.
Conclusion:
Enhancing user satisfaction in public housing is paramount for promoting livability, well-being, and social cohesion in communities. By understanding the theory of housing satisfaction and implementing periodic assessments, housing authorities can identify areas for improvement, address residents' needs, and enhance the quality of public housing developments. Innovative tools such as Mohit's Relative Satisfaction Index formula offer valuable insights into residents' satisfaction levels and support data-driven decision-making for future housing initiatives. Through collaborative efforts between housing authorities, residents, and stakeholders, public housing can evolve into vibrant, inclusive, and sustainable communities that meet the diverse needs of all residents.
References
1. Mohit, M. A., Ibrahim, M., & Rashid, Y. R. (2014). "Development of Relative Satisfaction Index (RSI) for Evaluating Housing Satisfaction: A Case Study of PPR Low-Cost Housing in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia." *Habitat International,* 43, 14-23.
2. Gilderbloom, J. I., & Markham, J. P. (1995). "A Theoretical Foundation for the Measurement of Housing Satisfaction." *Journal of Urban Affairs,* 17(1), 1-23.
3. van Kamp, I., Leidelmeijer, K., Marsman, G., & de Hollander, A. (2003). "Urban Environmental Quality and Human Well-being: Towards a Conceptual Framework and Demarcation of Concepts; A Literature Study." *Landscape and Urban Planning,* 65(1-2), 5-18.
4. Ahituv, A., & Lerman, Y. (2013). "The Relation Between Housing Characteristics and Satisfaction: A New Look at Hierarchy." *Journal of Housing Economics,* 22(2), 101-111.
5. Sridhar, M. K. (2017). "Public Housing in India: A Study of Satisfaction and Quality." *Asian Journal of Research in Social Sciences and Humanities,* 7(10), 35-50.



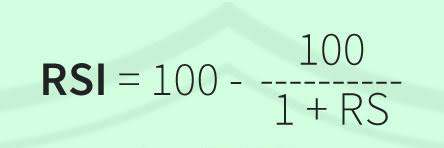












































![[FAILED] Engage2Earn: Shayne is helping koalas!](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/08e2e573-f490-4ef4-93b6-f2285814da59/1)








