Title: The Rise and Future of Blockchain Technology
Introduction
In recent years, blockchain, a revolutionary technology in the digital world, has had a significant impact on various industries. By providing a decentralized, secure, and transparent structure, blockchain enables diverse applications in sectors such as finance, healthcare, energy, logistics, and more. This article will delve into the fundamental principles, advantages, and future potential of blockchain technology.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger formed by a series of interconnected blocks. Each block contains information from the previous block, creating a chain, making any alteration in one block affect the entire system. This characteristic enhances the reliability of blockchain, as altering or manipulating data becomes challenging. Key Principles of Blockchain
Key Principles of Blockchain
- Decentralization: Blockchain operates as a system where data is shared and stored across numerous computers on a network, eliminating centralized access points.
- Encryption: Blockchain employs complex encryption algorithms to enhance security, ensuring data integrity and preventing unauthorized access.
- Absence of Central Authority: Instead of relying on a central authority, blockchain is a self-governing system where each user has equal rights as part of the network.
Advantages of Blockchain
- Reliability and Transparency: Blockchain offers a trustworthy system without the need for a central authority, and it shares a transparent transaction history among all participants.
- Fast and Cost-Effective Transactions: Its decentralized nature enables fast and cost-effective transactions, deviating from the slow and costly processes of traditional systems.
- Data Security: Encryption algorithms guarantee the security of data, limiting access to authorized entities within the system.
Impact of Blockchain on Industries
- Finance: Blockchain particularly revolutionizes payments and transfers in the financial sector by providing more reliable, rapid, and cost-effective transactions.
- Healthcare: By ensuring secure and shareable electronic health records, blockchain improves data management in the healthcare sector.
- Energy: Optimizing energy trade and distribution, blockchain enhances efficiency in the energy sector.
 Potential Developments in the Future
Potential Developments in the Future
- Widespread Adoption of Smart Contracts: With the increasing prevalence of blockchain, the use of smart contracts—programmable contracts executed automatically—is expected to rise.
- Industry 4.0 and Internet of Things (IoT): Blockchain can support Industry 4.0 by securely integrating industrial processes and IoT devices.
- Digital Identity and Security: Strengthening digital identity management, blockchain has the potential to enhance online security.
Challenges and Ongoing Developments
Despite its immense potential, blockchain technology is not without challenges. Scalability remains a significant hurdle as the network expands, and finding solutions to accommodate a larger number of transactions without compromising speed and efficiency is crucial. Additionally, achieving regulatory compliance is essential for blockchain to integrate seamlessly into existing legal frameworks.
Ongoing developments in blockchain technology aim to address these challenges. Scaling solutions such as sharding and layer-two protocols are being explored to increase transaction throughput. Collaboration between the blockchain community and regulatory bodies is intensifying to establish frameworks that ensure compliance without stifling innovation.
Potential Applications and Emerging Trends
As blockchain matures, new applications and trends are emerging. One notable trend is the exploration of blockchain in supply chain management. By providing an immutable and transparent record of the supply chain, blockchain can enhance traceability, reduce fraud, and improve overall efficiency.
Another promising area is decentralized finance (DeFi), where blockchain enables financial services without traditional intermediaries. This includes lending, borrowing, and trading of digital assets, offering users more control over their finances.
Global Adoption and Cross-Industry Collaboration
Blockchain's global adoption is gaining momentum as countries recognize its transformative potential. Governments are exploring the use of blockchain in public services, voting systems, and record-keeping to enhance transparency and reduce fraud. Cross-industry collaborations are also increasing, with companies realizing the benefits of shared blockchain networks for secure data exchange.
While blockchain provides enhanced security, it is not immune to risks. The concept of "51% attacks," where a single entity gains control of the majority of a blockchain network's mining power, poses a threat. Ongoing research focuses on mitigating such risks and ensuring the continued robustness of blockchain networks.
Ethical considerations surrounding data privacy and the environmental impact of blockchain mining are also areas of concern. Striking a balance between innovation and ethical practices is essential for the sustainable development of blockchain technology.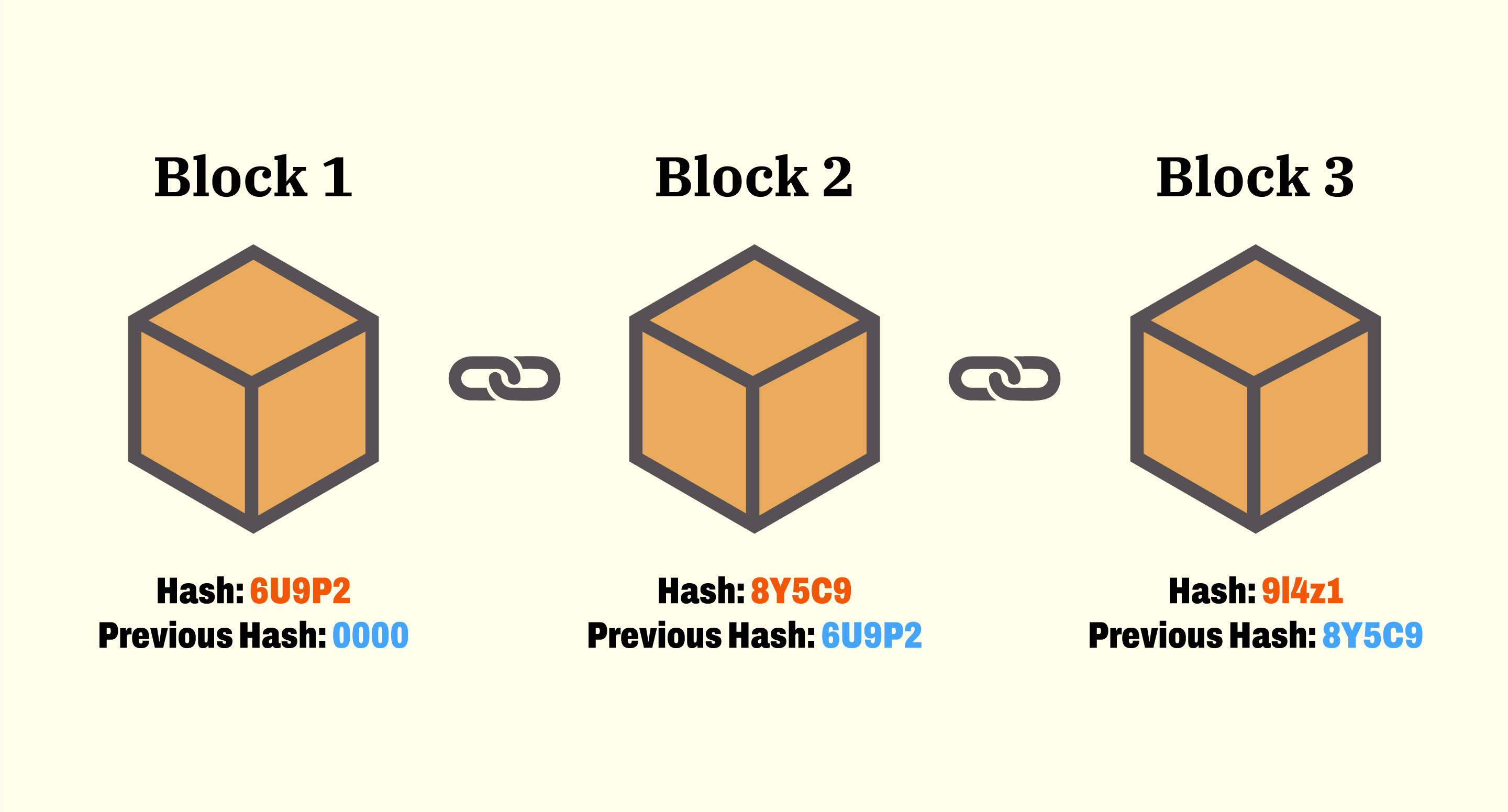 Conclusion: Shaping the Future of Technology
Conclusion: Shaping the Future of Technology
In conclusion, blockchain technology has already left an indelible mark on various industries, and its journey is far from over. The ongoing developments, challenges, and emerging trends indicate that blockchain will continue to evolve, shaping the future of technology. As scalability solutions, regulatory frameworks, and ethical considerations progress, blockchain's potential to revolutionize the way we interact with data and conduct transactions becomes even more promising. The journey of blockchain is a dynamic and transformative one, with a future that holds endless possibilities.





































