Niels Bohr: Unraveling the Quantum Mysteries of the Universe
Introduction:
Niels Bohr, a towering figure in the world of physics, revolutionized our understanding of the atomic and subatomic realms in the early 20th century. Born on October 7, 1885, in Copenhagen, Denmark, Bohr's contributions to quantum theory reshaped the scientific landscape, laying the groundwork for modern physics. In this article, we delve into the life, work, and enduring legacy of Niels Bohr, exploring his groundbreaking ideas and their profound impact on our comprehension of the universe.
Early Life and Education: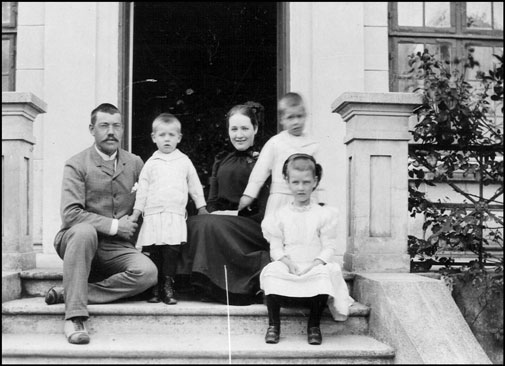
Niels Henrik David Bohr was born into an academic family; his father, Christian Bohr, was a prominent physiologist, and his mother, Ellen Adler Bohr, came from a wealthy Danish-Jewish family. From a young age, Bohr exhibited a keen interest in science, particularly in physics and mathematics. He pursued his education at the University of Copenhagen, where he initially studied physics as an undergraduate.
Bohr's academic journey took a significant turn when he traveled to England in 1911 to work with J.J. Thomson, the discoverer of the electron, at the Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge. It was during this time that Bohr became deeply involved in the emerging field of atomic physics, laying the groundwork for his future groundbreaking contributions.
Bohr's Atomic Model:
In 1913, Niels Bohr proposed his revolutionary atomic model, which incorporated principles from both classical physics and the emerging quantum theory. At the heart of Bohr's model was the idea that electrons orbit the nucleus of an atom in discrete, quantized energy levels. This concept, known as quantization, resolved the long-standing conundrum of why electrons did not spiral into the nucleus due to electromagnetic attraction, as classical physics predicted.
Bohr's model also introduced the notion of electron transitions between energy levels, accompanied by the emission or absorption of photons. This insight provided a theoretical framework for understanding the spectral lines observed in atomic spectra, a phenomenon that had puzzled physicists for decades.
The Copenhagen Interpretation:
Perhaps Bohr's most enduring contribution to physics is his formulation of the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics. Alongside Werner Heisenberg, Bohr developed this interpretative framework in the 1920s to make sense of the bizarre and counterintuitive phenomena observed at the subatomic level.
At its core, the Copenhagen interpretation posits that the act of measurement or observation fundamentally alters the state of a quantum system. Prior to measurement, a quantum entity exists in a superposition of multiple states, but upon observation, the system collapses into a single state determined by the measurement. This concept, encapsulated in the famous Schrödinger's cat thought experiment, challenged classical notions of determinism and reality, paving the way for a paradigm shift in physics.
Bohr's Bohr–Einstein Debates: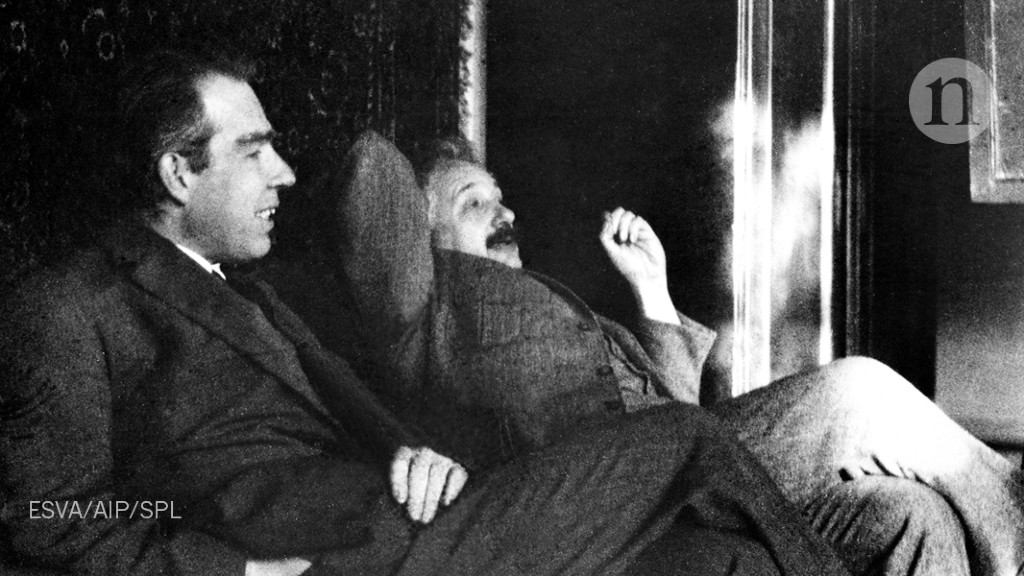
Niels Bohr's Copenhagen interpretation sparked intense debates within the scientific community, most notably with Albert Einstein. Einstein, a proponent of realism and determinism, famously clashed with Bohr over the implications of quantum mechanics, particularly regarding the completeness and accuracy of the theory.
The Bohr–Einstein debates, which spanned several years and covered topics such as the uncertainty principle and the nature of reality, highlighted the profound philosophical implications of quantum theory. While Einstein remained skeptical of certain aspects of quantum mechanics, Bohr staunchly defended the Copenhagen interpretation, asserting that it provided the most comprehensive framework for understanding the quantum world.
Legacy and Influence:
Niels Bohr's contributions to physics reverberate across a wide array of fields, from atomic and nuclear physics to quantum information theory and beyond. His insights continue to shape our understanding of the fundamental nature of reality, inspiring generations of scientists to explore the frontiers of quantum mechanics.
In addition to his scientific endeavors, Bohr played a pivotal role in fostering international collaboration and dialogue among physicists. He established the Niels Bohr Institute in Copenhagen, which served as a hub for theoretical and experimental research in physics, attracting scholars from around the world.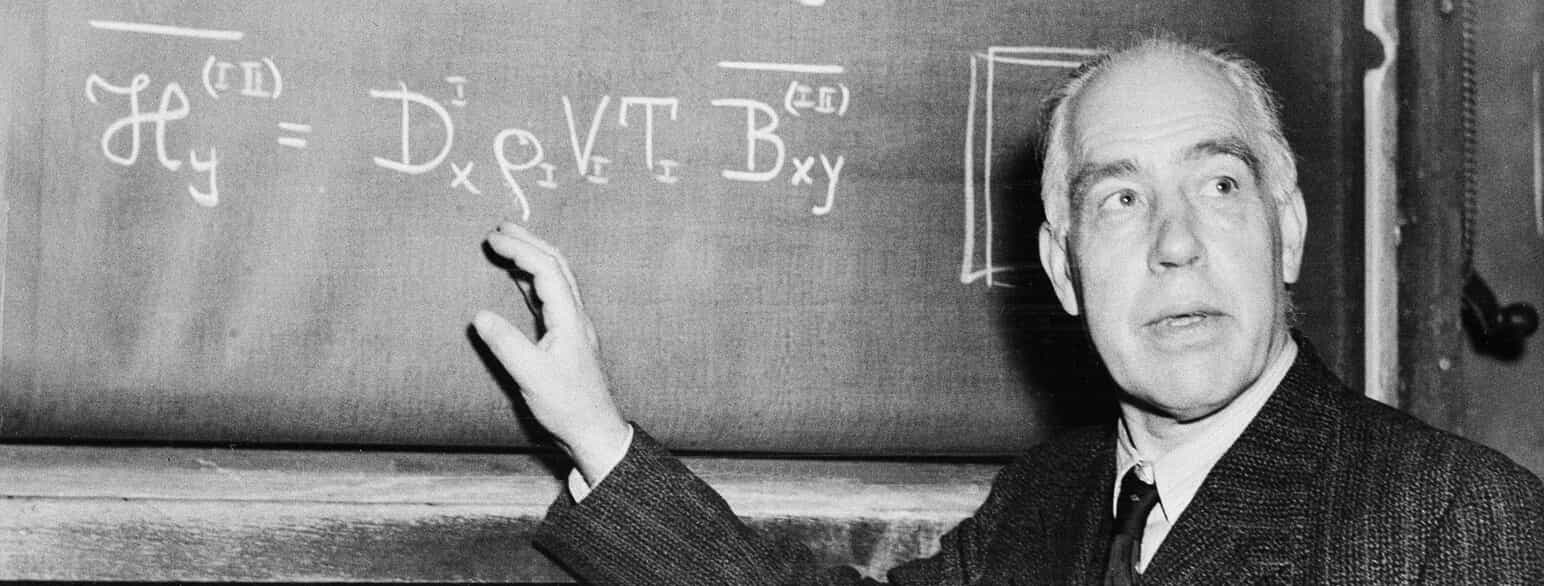 Niels Bohr's legacy as one of the preeminent figures in 20th-century physics is indelible. His atomic model, Copenhagen interpretation, and impassioned advocacy for quantum mechanics revolutionized our understanding of the quantum realm, laying the groundwork for countless discoveries and technological advancements.
Niels Bohr's legacy as one of the preeminent figures in 20th-century physics is indelible. His atomic model, Copenhagen interpretation, and impassioned advocacy for quantum mechanics revolutionized our understanding of the quantum realm, laying the groundwork for countless discoveries and technological advancements.
As we reflect on Bohr's life and work, we are reminded of the enduring power of curiosity, creativity, and collaboration in the pursuit of scientific knowledge. Niels Bohr's quest to unravel the mysteries of the universe continues to inspire and captivate minds, ensuring his place among the pantheon of scientific luminaries for generations to come.
Bohr's later years were marked by his continued dedication to advancing the frontiers of physics while also actively engaging in efforts to promote international cooperation in science. Amidst the tumultuous backdrop of World War II, Bohr, who had Jewish ancestry, found himself in a precarious position due to the Nazi occupation of Denmark. Recognizing the grave threat posed by the Nazi regime, Bohr and his family fled Denmark in 1943, eventually finding refuge in the United States.
In the United States, Bohr contributed to the Manhattan Project, the top-secret initiative to develop the atomic bomb. While Bohr's exact role and influence within the project remain a subject of historical debate, his insights into atomic physics undoubtedly informed the scientific endeavors of the Manhattan Project's researchers.
Following the end of World War II, Niels Bohr emerged as a leading advocate for the peaceful application of atomic energy and a vocal proponent of arms control and disarmament. He recognized the immense potential of nuclear technology to address pressing societal challenges, such as energy production and medical treatment, while also emphasizing the urgent need to prevent the proliferation of nuclear weapons.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/physicist-niels-bohr-514891628-5a6e41193418c60036a1ee35.jpg) Bohr's efforts to promote international cooperation in science and foster dialogue among nations culminated in his role as a key figure in the establishment of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in 1945. He believed fervently in the power of education and cultural exchange to bridge divides and promote mutual understanding among peoples.
Bohr's efforts to promote international cooperation in science and foster dialogue among nations culminated in his role as a key figure in the establishment of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in 1945. He believed fervently in the power of education and cultural exchange to bridge divides and promote mutual understanding among peoples.
Throughout his illustrious career, Niels Bohr received numerous accolades and honors in recognition of his scientific achievements and humanitarian efforts. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922 for his pioneering work on atomic structure and spectral lines, cementing his status as one of the foremost physicists of his era. Despite his towering intellect and profound impact on the course of 20th-century physics, Bohr remained remarkably humble and approachable, earning the admiration and respect of colleagues and students alike. His deep-seated commitment to scientific inquiry, coupled with his unwavering advocacy for global cooperation and peace, exemplifies the best qualities of the scientific endeavor.
Despite his towering intellect and profound impact on the course of 20th-century physics, Bohr remained remarkably humble and approachable, earning the admiration and respect of colleagues and students alike. His deep-seated commitment to scientific inquiry, coupled with his unwavering advocacy for global cooperation and peace, exemplifies the best qualities of the scientific endeavor.
Niels Bohr's legacy endures not only in the annals of scientific history but also in the hearts and minds of all those who continue to be inspired by his quest to unravel the mysteries of the universe. As we commemorate the 150th anniversary of his birth, we celebrate not only the extraordinary intellect and achievements of Niels Bohr but also his enduring spirit of curiosity, compassion, and collaboration, which continues to illuminate the path forward for humanity.





























