FATF Recommendations for Crypto Operations
The emergence of cryptocurrencies has revolutionized financial systems, introducing both opportunities and challenges. However, the potential for misuse in money laundering, terrorism financing, and other illicit activities has made regulation a global imperative. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), an international standards body focused on anti-money laundering (AML) and combating the financing of terrorism (CFT), has outlined specific recommendations for virtual assets (VAs) and virtual asset service providers (VASPs). 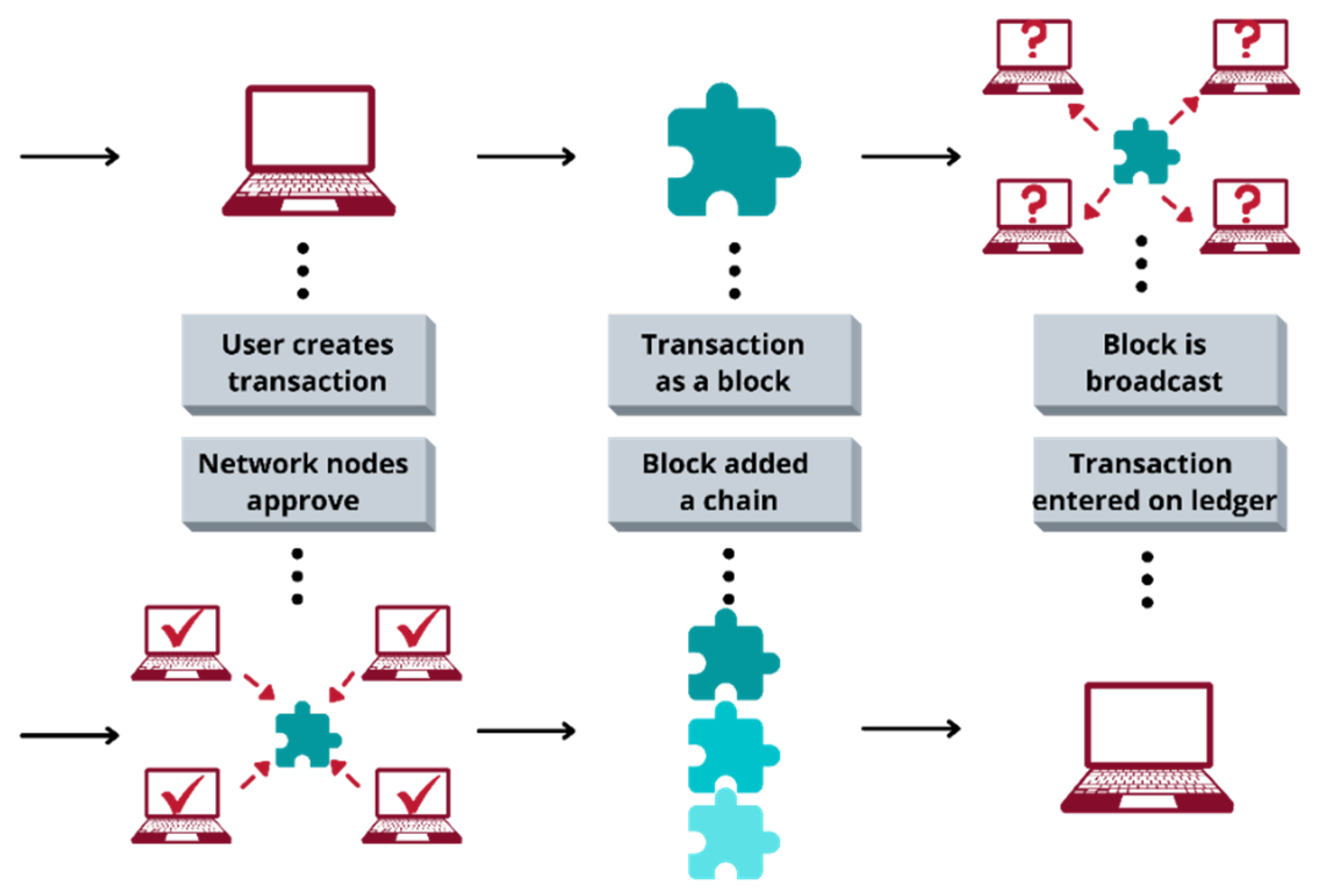
Below is a professional exploration of these recommendations and their implications for crypto operations.
1. The Foundation: FATF’s Approach to Virtual Assets
The FATF initially integrated virtual assets into its framework in 2019, expanding its AML/CFT guidelines to encompass this emerging sector. This move acknowledged the growing use of cryptocurrencies and the risks associated with anonymity and decentralization. FATF Recommendation 15 (R.15) and its Interpretative Note (INR.15) serve as the cornerstone for regulating VASPs and ensuring compliance with global standards.
Key aspects of FATF’s approach include:
Risk Assessments: Jurisdictions must conduct comprehensive evaluations of risks associated with VAs and VASPs. This helps in developing targeted mitigation strategies to curb misuse.
The Travel Rule: VASPs are required to obtain, store, and share information about the originators and beneficiaries of transactions. This ensures traceability and transparency across borders.
While FATF's standards aim to promote global uniformity, adoption varies widely. As of 2023, a significant number of jurisdictions are either partially compliant or have yet to implement these measures.
2. The Travel Rule: Strengthening Transactional Transparency
The Travel Rule has become a hallmark of FATF’s crypto guidelines. It mandates VASPs to collect and exchange specific details about transaction parties, such as:
- Names,
- Account numbers, and
- Geographical locations.
This rule aims to replicate traditional banking transparency within the digital asset ecosystem. However, its implementation has faced hurdles:
Technical Barriers: Blockchain’s decentralized nature poses challenges in enforcing data-sharing requirements.
Jurisdictional Gaps: Many countries lack legislative frameworks to mandate compliance, creating regulatory arbitrage opportunities.
Countries like Japan, South Korea, and Singapore have made significant strides in aligning with the Travel Rule, while others lag behind. These gaps underscore the need for enhanced collaboration and technological innovation.
3. Emerging Risks and FATF’s Expanded Scope
The crypto landscape is rapidly evolving, with innovations like decentralized finance (DeFi), stablecoins, and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) posing new challenges:
DeFi Platforms: Although decentralized, many DeFi arrangements involve entities that can be classified as VASPs, requiring adherence to AML/CFT obligations. The FATF emphasizes that decentralization cannot be an excuse for non-compliance.
Unhosted Wallets and P2P Transactions: These are seen as high-risk areas due to their anonymity and lack of intermediaries. FATF advises jurisdictions to impose additional scrutiny and reporting requirements for VASPs facilitating such transactions.
Stablecoins and NFTs: While stablecoins are often treated as VAs under FATF’s framework, NFTs are assessed on a case-by-case basis, particularly if they serve investment or payment purposes.
These developments highlight the FATF’s commitment to staying ahead of emerging risks and ensuring that its recommendations remain relevant.
4. Challenges and the Path Forward
The FATF faces several challenges in ensuring effective implementation of its standards:
Fragmented Implementation: As of 2023, more than half of the surveyed jurisdictions have not taken substantial steps toward implementing the Travel Rule. This creates vulnerabilities for financial crimes.
Private Sector Collaboration: Collaboration between governments and the private sector is crucial. The FATF has encouraged VASPs and technology providers to develop compliance tools and enhance industry-wide adherence.
Monitoring and Reporting: Continuous updates on jurisdictional compliance and emerging risks are vital for global coordination. FATF has committed to providing targeted assistance to low-capacity jurisdictions and improving information-sharing mechanisms.
Moving forward, the focus will be on accelerating compliance, fostering innovation in regulatory technology, and addressing the unique challenges posed by decentralized ecosystems.
Conclusion
FATF’s recommendations for crypto operations are a critical step toward ensuring that the benefits of digital assets are not overshadowed by risks of misuse. By mandating rigorous AML/CFT measures, promoting transparency through the Travel Rule, and addressing emerging risks, the FATF aims to create a robust regulatory environment. However, achieving global uniformity requires concerted efforts from all stakeholders, including governments, VASPs, and technology innovators.
The journey toward full compliance is ongoing, but with sustained focus and collaboration, the crypto ecosystem can evolve into a secure and legitimate component of the global financial system.
Reference
- FATF Official Website: FATF Standards on Virtual Assets
- Cointelegraph: FATF Crypto Standards Roadmap
- Reed Smith LLP: FATF’s Updated Guidance on Virtual Assets
- FATF Implementation Updates: Targeted Update 2023











![[ℕ𝕖𝕧𝕖𝕣] 𝕊𝕖𝕝𝕝 𝕐𝕠𝕦𝕣 𝔹𝕚𝕥𝕔𝕠𝕚𝕟 - And Now What.... Pray To The God Of Hopium?](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/79e7827b-c644-4853-b048-a9601a8a8da7/1)

















![[LIVE] Engage2Earn: Save our PBS from Trump](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/c23a1a05-c831-4c66-a1d1-96b700ef0450/1)



