What The Tech: Chronometers
Chronomoters would turn time into reliable navigation
For Britain to become a leading seagoing nation, it would need to be able to leverage several things reliably. It would need access to reliable and modern craft, as well as a reliable pool of well-skilled sailors and the means to navigate safely across the ocean.
While much has been written about Britain's boats and its sailors, today we’ll be looking at the evolution of reliable navigation. While many people would contribute, one British researcher would play a key role.
Nevil Maskelyne would help lay the foundations for modern research by helping to implement longitudinal navigation, while the chronometer would be a key tool for its measurement.
And, it’s a super interesting story. Let’s take a look!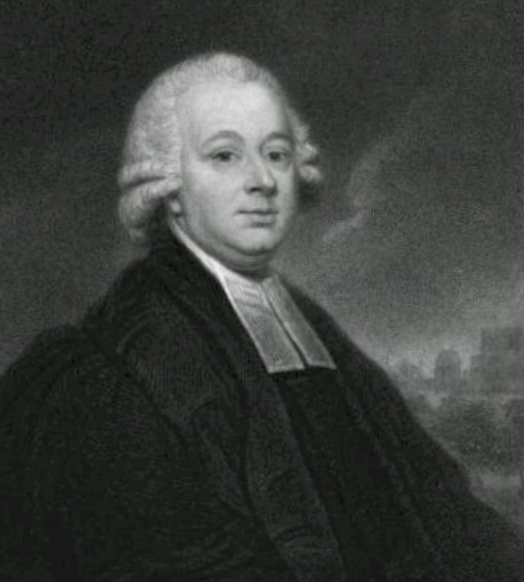 Nevil Maskelyne played a key role in longitude. Source: WIkipedia.
Nevil Maskelyne played a key role in longitude. Source: WIkipedia.
Background
Like many researchers of the day, Maskelyne wasn’t just known for his contributions to one field. Holding the prestigious rank of “Astronomer Royal”, he would first achieve fame for being the first person to measure the mass of the Earth in its entirety before providing much of the research that helped to implement lines of longitude. This research would contribute much to the art of navigation and would help establish the United Kingdom and its Royal Navy as expert seafarers.
With geography and cartography leading research fields for the time, Maskelyne would maintain an intense interest in geodetic exploration and documentation throughout his career. Before we explore this, though, let’s rewind a little.
In an age of metal ships, modern communications and GPS technology, it’s sometimes hard to grasp just how difficult seafaring life would have been even sixty years ago. A hundred years ago, though, things were much, much different, and men at sea would endure numerous hardships with no promises of a safe return.
It’s why cartography (map-making) would play such a key role in the modern world. Understanding where to go, how to get there and what was on the way gave seafarers the best chance of safely completing a voyage.
Prior to this, though many many ships would endure wrecking themselves in areas unknown. One of the most horrific mutinies of its time would occur in the wake of a shipwreck that led to a stranded crew.
Implementation
Early mariners had no issues charting their position of latitude. The ever-reliable North Star had been a beacon to seagoing nations for hundreds of years. Longitude at the time though, would provide a significant challenge as it required one thing to work reliably.
Namely, the ability to accurately monitor and chart time in a wide range of conditions.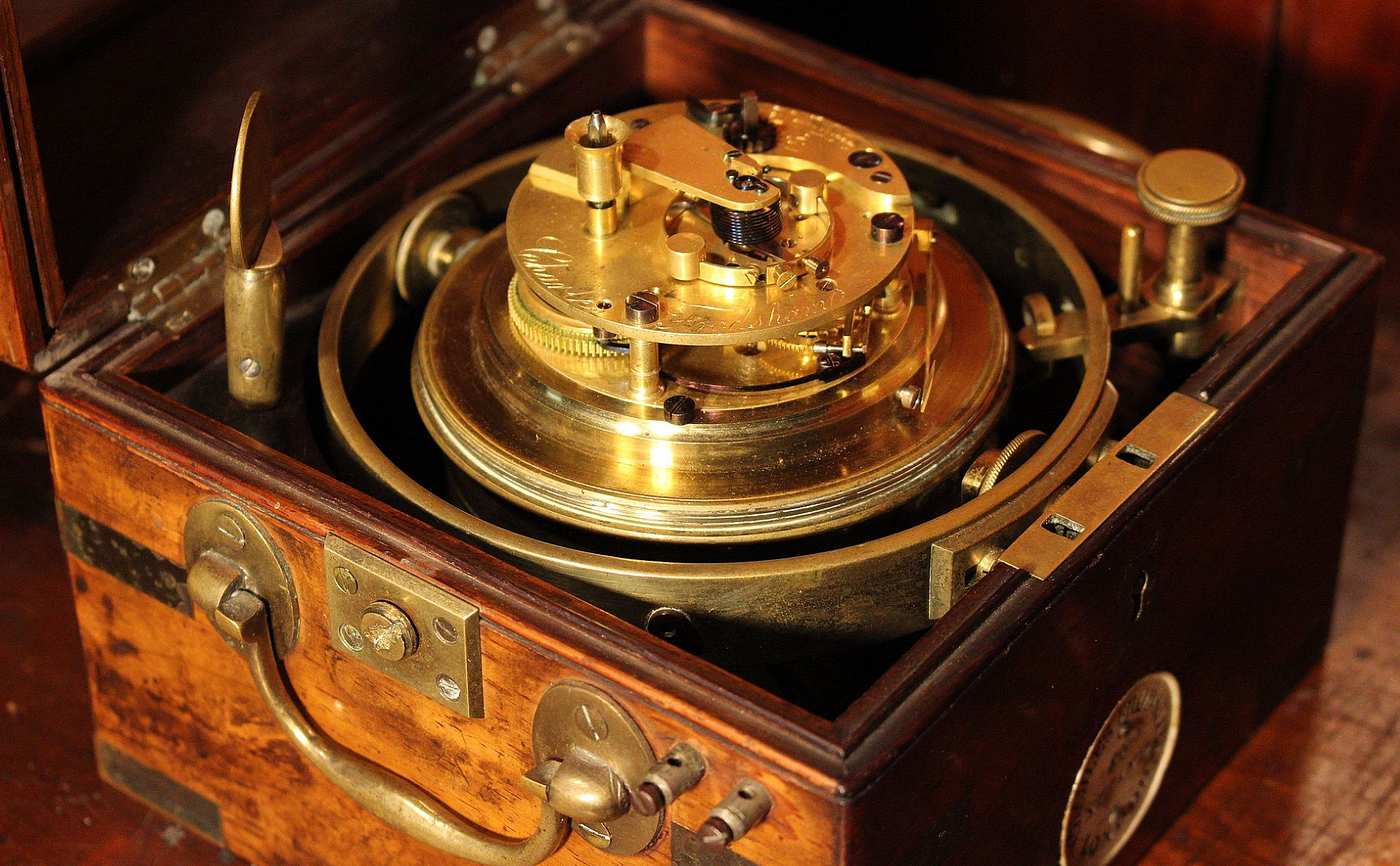 Later chronometer designs were a work of art. Source: Wikipedia.
Later chronometer designs were a work of art. Source: Wikipedia.
The marine chronometer would eventually be designed to tackle this task specifically. Highly accurate, boxed for protection and calibrated to work in a broad range of temperature conditions, the chronometer provided a technological revolution at the time and would first go to sea in the late 1700s. While the earlier designs required improvement, they were functional enough to verify the concept worked, and later research would focus on improving their timekeeping abilities and overall reliability.
As the Royal Navy travelled across the globe, marking new discoveries and exploring new areas, the chronometer would play a key role in helping many of these explorers return home safely.
Mainstream Adoption.
It’s easy to look at early chronometers and consider them to be little more than a watch, the reality is that these timepieces were some of the most precise pieces of equipment that were ever produced in their time. In today's world, we can use cheap quartz crystals to provide an accurate reference signal that lasts for as long as the device is appropriately powered.
Back then, timepieces were made using precision-built designs that were masterpieces of engineering. Even today, small, precision-built watches remain popular among many, commanding high prices in retail markets.
These products were treated according to the value that they provided to the Royal Navy. Not only would designs be “ranked” according to their durability and timekeeping standards, but they were also designed to be hot-swapped out of ships as required. This meant that they were able to be overhauled at points of failure and pressed back into service when repaired.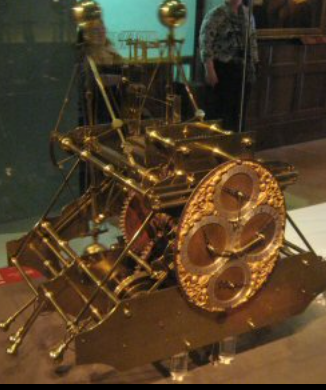 The H1 was John Harrisons first seagoing design. Source: Wikipedia
The H1 was John Harrisons first seagoing design. Source: Wikipedia
While they remained expensive, the civilian market would eventually catch on, with chronometers being fitted to merchant ships as well. The chronometer would provide the first key to unlocking the Globe, and be a natural pairing to the steam engine. When the two were combined, we’d see the foundations laid for safe and reliable navigation around the globe.
John Harrison
While Maskelyne would contribute the nautical almanac as well as strategies around its implementation it was actually John Harrison who would be responsible for much of the early design and test work.
His H4 design contained many years of research into design and would be lauded for its features and overall design in later years. It’s fair to say though, that Harrison’s work would take a long time to achieve appropriate recognition. In the early stages, his work received much resistance, and while he’d eventually achieve recognition from the government in later life, it came at the cost of near ridicule when his work was originally released.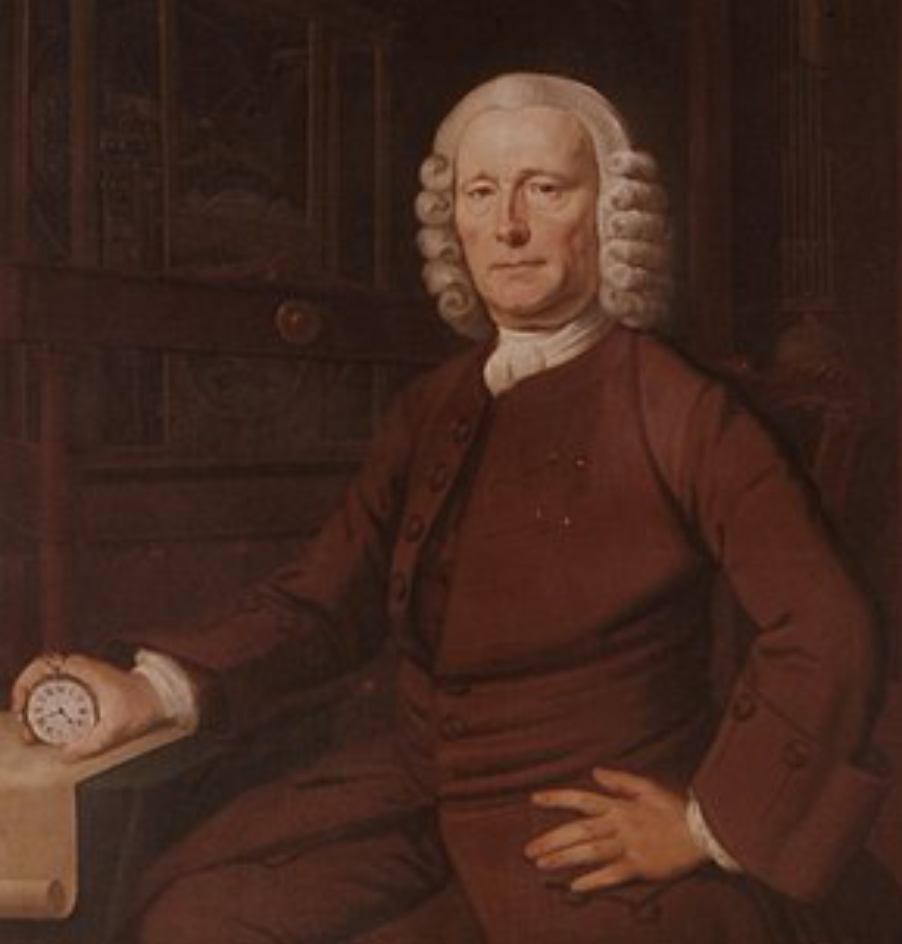 John Harrison would also play a key role in developing the chronometer. Source: Wikipedia.
John Harrison would also play a key role in developing the chronometer. Source: Wikipedia.
In 2002, Harrison would place at number 39 in a list of the most influential Britons in a series carried out by the British BBC, establishing his role in the history books and validating his work hundreds of years after his death.
Redundancy & Replacement
We give little thought to the art of timekeeping in the modern world, as for the most part, we’ve automated this to the point where it simply isn’t a problem anymore.
There’s no denying though, that it’s still relevant in today’s world. Computers work on internet-synchronized timing systems, while many communications, like mobile phones and satellite, tend to rely on accurate timekeeping as well.
Eventually, it would be a pairing of both of these systems that would give us a reduced need for accurate time management on a personal basis. While radio-based time management was a thing in the early 1900s, the development of space-based satellite constellations would provide the biggest move toward making chronometer-based navigation techniques obsolete. GPS would change navigation, forever. Source: Wikipedia.
GPS would change navigation, forever. Source: Wikipedia.
The launch of the US-designed Global Position System would use a satellite constellation to broadcast a signal that consisted of time and identification values that allowed for the accurate calculation of position anywhere on the globe.
Eventually, civilian access to the GPS constellation would make the older, time-based methods of navigation obsolete. This would bring in a new era of safety and navigational accuracy for both ship and aircraft.
What The Tech?! is our recurring, twice-monthly piece that focuses on the technology that helped shape our modern world.
If you found this article insightful, informative, or entertaining, we kindly encourage you to show your support. Clapping for this article not only lets the author know that their work is appreciated but also helps boost its visibility to others who might benefit from it.
🌟 Enjoyed this article? Join the community! 🌟
📢 Join our OSINT Telegram channel for exclusive updates or
📢 Follow our crypto Telegram for the latest giveaways
🐦 Follow us on Twitter and
🟦 We’re now on Bluesky!
🔗 Articles we think you’ll like:
- What The Tech?! Space Shuttles
- Shodan: A Map of the Internet
✉️ Want more content like this? Sign up for email updates



































































