What is Depression and How Does It Affect You?
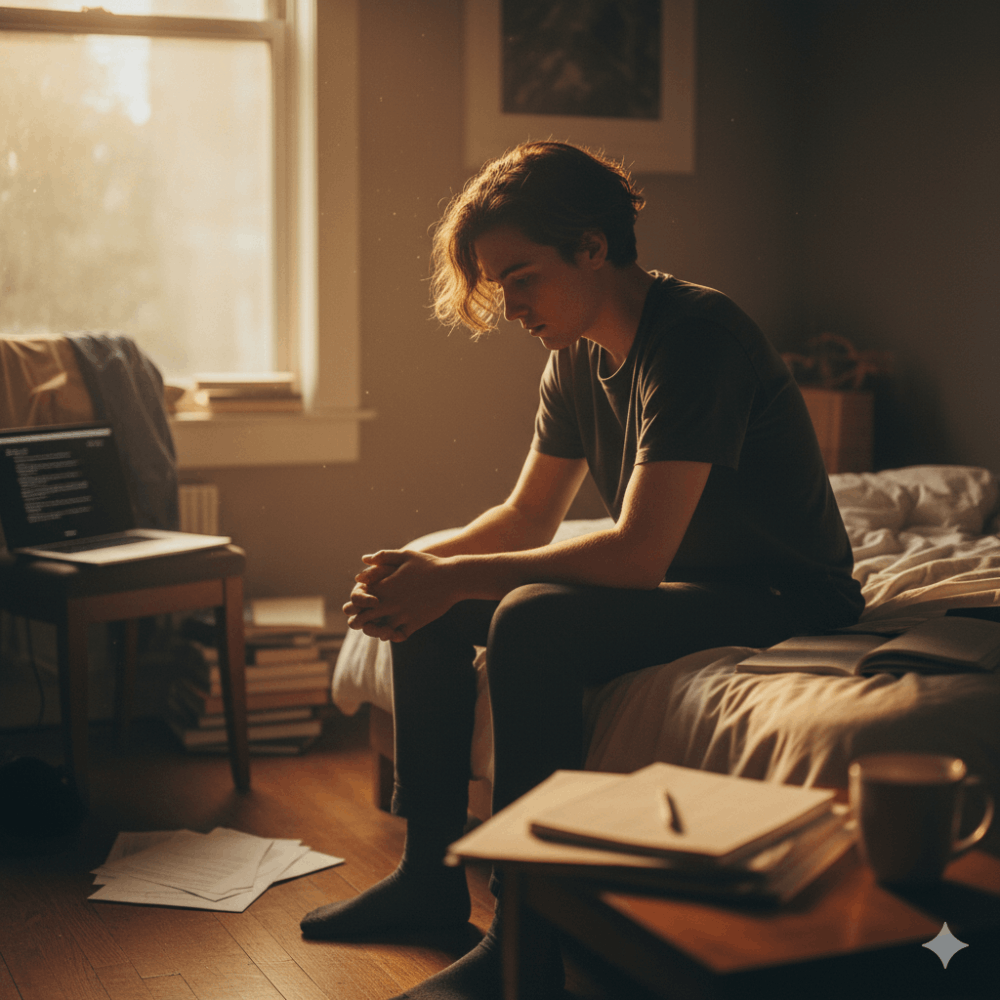
Depression is a common and serious mental health condition that affects how you feel, think, and act. It can cause persistent feelings of sadness, loss of interest, hopelessness, guilt, and low self-worth. Depression can also interfere with your daily functioning, such as work, school, relationships, and physical health.
Depression is not a sign of weakness or a character flaw. It is a treatable illness that can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, race, or background. However, many people with depression do not seek help or are unaware that they have it. Therefore, it is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of depression and seek professional help if you or someone you know is experiencing them.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Some of the common signs and symptoms of depression are:
- Feeling sad, empty, or tearful most of the time
- Losing interest or pleasure in activities that you used to enjoy
- Having trouble sleeping or sleeping too much
- Feeling restless, agitated, or slowed down
- Having low energy or fatigue
- Having difficulty concentrating, remembering, or making decisions
- Having feelings of worthlessness or excessive guilt
- Having recurrent thoughts of death or suicide
- Having changes in appetite or weight
- Having physical symptoms such as headaches, stomachaches, or pain that do not respond to treatment
These signs and symptoms can vary in severity and duration. Some people may have mild depression that lasts for a few weeks or months, while others may have severe depression that lasts for years. Some people may have episodes of depression that come and go, while others may have chronic depression that does not improve.
The Effect of Depression on different people
Depression can also affect different people in different ways. For example:
- Women may be more likely to experience symptoms such as sadness, anxiety, guilt, and changes in appetite or weight.
- Men may be more likely to experience symptoms such as anger, irritability, loss of interest, and substance abuse.
- Older adults may be more likely to experience symptoms such as memory loss, confusion, social withdrawal, and physical complaints.
- Children and adolescents may be more likely to experience symptoms such as irritability, mood swings, poor school performance, and changes in behavior.
Depression in Children and Teens
Depression in Children and Teens Depression is a serious mental health problem that affects millions of people around the world. It can cause persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities that used to be enjoyable. Depression can also interfere with daily functioning, such as school, work, and relationships.
While depression can affect anyone at any age, it is not uncommon for children and teens to experience depression. In fact, an estimated 3.2 percent of American children and adolescents have been diagnosed with depression. However, depression in children and teens may look different from depression in adults. Here are some of the signs and symptoms of depression in children and teens, as well as the possible causes and treatments.
Signs and Symptoms of Depression in Children and Teens
Depression can manifest differently in different people, depending on their age, personality, and circumstances. However, some common signs and symptoms of depression in children and teens include:
- Persistent feelings of sadness, emptiness, or irritability
- Loss of interest or pleasure in hobbies, sports, or other activities
- Trouble sleeping or sleeping too much
- Changes in appetite or weight
- Fatigue or low energy
- Feelings of worthlessness, guilt, or self-blame
- Difficulty concentrating, thinking, or making decisions
- Frequent complaints of physical pain, such as headaches or stomachaches
- Withdrawal from family, friends, or social situations
- Poor academic performance or frequent absences from school
- Anger outbursts, aggression, or risky behaviors
- Self-harm or suicidal thoughts or attempts
It is important to note that not all children and teens who have these symptoms are depressed. Some of these behaviors may be normal reactions to stressors or developmental changes. However, if these symptoms are severe, persistent, or interfere with daily functioning, it may indicate a depressive disorder that requires professional help.
Causes of Depression in Children and Teens :
There is no single cause of depression in children and teens. Rather, it is likely the result of a combination of biological, psychological, and environmental factors.
Some of the possible factors that may contribute to depression in children and teens include:
- Genetic predisposition: Having a family history of depression may increase the risk of developing depression.
- Brain chemistry: Imbalances in neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, may affect mood regulation and emotional processing.
- Hormonal changes: Puberty, menstruation, and other hormonal fluctuations may affect mood and stress levels.
- Stressful life events: Experiencing trauma, loss, abuse, neglect, bullying, divorce, or other stressful situations may trigger or worsen depression.
- Co-occurring mental health conditions: Having other mental health problems, such as anxiety, ADHD, autism spectrum disorder.
Depression in adults:
Depression in adults is a common and serious mental health condition that affects how people feel, think, and act. It can cause persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, guilt, and worthlessness. It can also cause persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, anger, or loss of interest in things that used to be enjoyable.
What to do if you think you may have depression :
Depression is not a sign of weakness or a character flaw. It is a treatable illness that can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, race, or background.
Remember that depression is not your fault and that you are not alone. You are a valuable and worthy person who deserves happiness and well-being. With proper treatment and support, you can overcome depression and live a fulfilling and productive life.
- If you think you may have depression, it is important to seek professional help as soon as possible. the first step is to talk to your doctor or a mental health professional. They can assess your symptoms and provide you with a diagnosis and a treatment plan.
- Treatment for depression may include medication, psychotherapy (counseling), or a combination of both. Treatment can help you feel better and improve your quality of life. There are effective treatments available for depression, such as medication, psychotherapy, lifestyle changes, or alternative therapies. The sooner you start treatment, the better your chances of recovery and preventing complications.
- Depression is not something that you have to suffer alone. There are many resources and support groups available to help you cope with your condition and recover from it.
- You can also take some steps to help yourself by :
- Seeking social support from family, friends, or others who understand what you are going through
- Engaging in physical activity that you enjoy and that makes you feel good
- Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or massage
- Avoiding alcohol and drugs that can worsen your mood and interfere with your treatment
- Setting realistic and achievable goals for yourself and celebrating your progress
- Challenging negative thoughts and replacing them with positive ones
- Seeking help if you have thoughts of harming yourself or others
These signs and symptoms can vary in severity and duration. Some people may have mild depression that lasts for a few weeks or months, while others may have severe depression that lasts for years. Some people may have episodes of depression that come and go, while others may have chronic depression that does not improve.
Remember that depression is not your fault and that you are not alone. With proper treatment and support, you can overcome depression and live a fulfilling and happy life.
you can check out this article also
Depression in Women: 5 Things You Should Know
Mental Health Information
Depression and Older Adults