The Future of Renewable Energy: Innovations and Trends
As the world grapples with the urgent need to mitigate climate change and transition away from fossil fuels, renewable energy sources have emerged as a crucial solution. In recent years, significant advancements in technology, policy, and investment have propelled the growth of renewable energy industries, transforming the global energy landscape. Looking ahead, the future of renewable energy promises even greater innovation and expansion, ushering in a new era of sustainability and clean energy abundance. One of the most exciting developments in the realm of renewable energy is the rapid advancement of solar power technology. Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels, which convert sunlight directly into electricity, have become increasingly affordable and efficient, making solar energy a competitive alternative to traditional fossil fuels in many parts of the world. Innovations such as perovskite solar cells, which promise to further improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of solar PV technology, are poised to drive continued growth in the solar energy sector in the coming years.
One of the most exciting developments in the realm of renewable energy is the rapid advancement of solar power technology. Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels, which convert sunlight directly into electricity, have become increasingly affordable and efficient, making solar energy a competitive alternative to traditional fossil fuels in many parts of the world. Innovations such as perovskite solar cells, which promise to further improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of solar PV technology, are poised to drive continued growth in the solar energy sector in the coming years.
Similarly, wind energy continues to soar to new heights, both literally and figuratively. Advances in wind turbine design and engineering have led to the development of larger, more powerful turbines capable of harnessing energy from stronger and more consistent winds at higher altitudes. Offshore wind farms, which harness the strong, steady winds found at sea, have emerged as a particularly promising frontier in the quest for clean energy. As technology continues to improve and costs continue to decline, offshore wind is expected to play an increasingly prominent role in the global energy mix.
Beyond solar and wind, other renewable energy sources such as hydropower, biomass, and geothermal energy are also poised for significant growth in the years to come. Hydropower, which has long been a mainstay of renewable energy generation, is undergoing a renaissance with the development of innovative technologies such as run-of-river and pumped storage hydroelectricity. Biomass energy, derived from organic materials such as wood, agricultural residues, and municipal solid waste, holds promise as a versatile and carbon-neutral energy source that can help mitigate waste disposal challenges while reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Geothermal energy, which harnesses heat from the Earth's interior to generate electricity and heat buildings, is also experiencing renewed interest and investment, particularly in regions with high geothermal potential. In addition to technological innovations, policy initiatives and market dynamics are driving the transition to renewable energy at an unprecedented pace. Governments around the world are increasingly implementing ambitious targets and incentives to promote renewable energy deployment and decarbonize their economies. The growing recognition of the economic, environmental, and social benefits of renewable energy is spurring investment from both public and private sources, driving down costs and accelerating deployment. Moreover, the rise of renewable energy marketplaces and innovative financing mechanisms such as green bonds and carbon markets are opening up new avenues for investment in clean energy projects and infrastructure.
In addition to technological innovations, policy initiatives and market dynamics are driving the transition to renewable energy at an unprecedented pace. Governments around the world are increasingly implementing ambitious targets and incentives to promote renewable energy deployment and decarbonize their economies. The growing recognition of the economic, environmental, and social benefits of renewable energy is spurring investment from both public and private sources, driving down costs and accelerating deployment. Moreover, the rise of renewable energy marketplaces and innovative financing mechanisms such as green bonds and carbon markets are opening up new avenues for investment in clean energy projects and infrastructure.
Looking ahead, several key trends are likely to shape the future of renewable energy. The continued electrification of transportation, heating, and industrial processes is expected to drive increased demand for renewable electricity, creating new opportunities for growth and innovation in the renewable energy sector. The integration of renewable energy into smart grids and energy storage systems is also poised to play a crucial role in enabling the reliable and resilient operation of renewable energy systems, helping to overcome challenges such as intermittency and variability.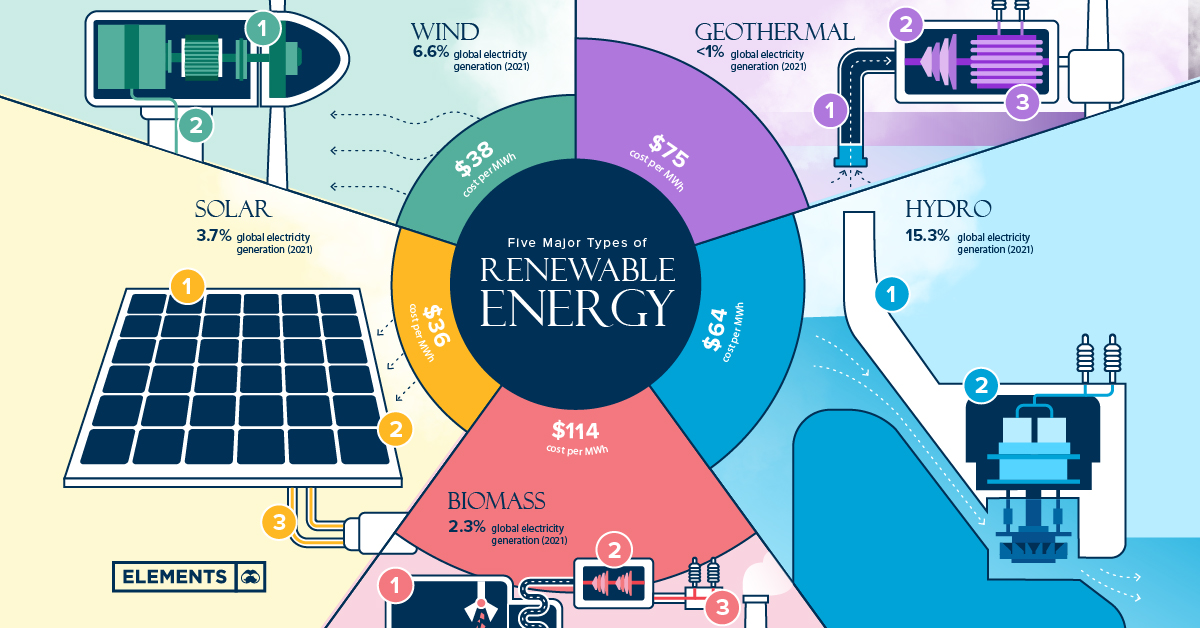 Furthermore, the democratization of energy production through distributed generation and community-owned renewable energy projects is empowering individuals and communities to take control of their energy futures, fostering greater resilience and self-reliance in the face of climate change and energy insecurity. Advances in digital technologies, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are also revolutionizing the way renewable energy systems are designed, operated, and optimized, unlocking new possibilities for efficiency, performance, and cost savings.
Furthermore, the democratization of energy production through distributed generation and community-owned renewable energy projects is empowering individuals and communities to take control of their energy futures, fostering greater resilience and self-reliance in the face of climate change and energy insecurity. Advances in digital technologies, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are also revolutionizing the way renewable energy systems are designed, operated, and optimized, unlocking new possibilities for efficiency, performance, and cost savings.
Challenges and Opportunities
However, despite the remarkable progress made in the renewable energy sector, several challenges remain that must be addressed to realize its full potential. One of the most significant challenges is the need to overcome existing infrastructural and regulatory barriers that hinder the widespread adoption of renewable energy technologies. Outdated grid infrastructure, regulatory frameworks that favor fossil fuels, and entrenched interests in the energy industry pose obstacles to the transition to renewables. Addressing these barriers will require bold policy interventions, investments in infrastructure upgrades, and efforts to level the playing field for renewable energy in energy markets.
Additionally, the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind presents challenges for grid stability and reliability. While advancements in energy storage technologies such as batteries hold promise for mitigating the impacts of intermittency, further research and development are needed to improve the efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness of energy storage systems. Moreover, innovative approaches such as demand response, grid-scale energy management, and the integration of diverse renewable energy sources can help enhance grid flexibility and resilience, ensuring reliable and secure energy supply in a renewable-powered future. Another challenge facing the renewable energy transition is the need to address social and environmental considerations associated with renewable energy deployment. While renewable energy offers significant environmental benefits compared to fossil fuels, it is not without its own environmental impacts. Large-scale renewable energy projects can have adverse effects on ecosystems, biodiversity, and local communities if not carefully planned and managed. As such, it is essential to prioritize sustainable siting, environmental conservation, and community engagement in renewable energy development efforts to minimize negative impacts and maximize co-benefits for both people and the planet.
Another challenge facing the renewable energy transition is the need to address social and environmental considerations associated with renewable energy deployment. While renewable energy offers significant environmental benefits compared to fossil fuels, it is not without its own environmental impacts. Large-scale renewable energy projects can have adverse effects on ecosystems, biodiversity, and local communities if not carefully planned and managed. As such, it is essential to prioritize sustainable siting, environmental conservation, and community engagement in renewable energy development efforts to minimize negative impacts and maximize co-benefits for both people and the planet.
Moreover, the transition to renewable energy must be inclusive and equitable, ensuring that all communities have access to clean, affordable, and reliable energy services. Historically marginalized communities, including low-income neighborhoods and indigenous populations, have borne the brunt of environmental injustice and energy poverty. By prioritizing equity, diversity, and inclusion in renewable energy policies and initiatives, we can ensure that the benefits of the clean energy transition are shared equitably among all members of society, leaving no one behind.
Despite these challenges, the future of renewable energy is brighter than ever before, with unprecedented opportunities for innovation, investment, and collaboration. By harnessing the power of renewable energy, we can build a more resilient, sustainable, and prosperous world for future generations. With bold leadership, collective action, and a shared commitment to a clean energy future, we can overcome the challenges ahead and usher in a new era of renewable energy abundance and prosperity for all. In conclusion, the future of renewable energy is not just about technology; it is about people, communities, and the planet. By embracing renewable energy as a cornerstone of our energy future, we can create a world that is cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable for generations to come. The time to act is now. Let us seize the opportunity before us and work together to build a brighter, greener future for all.
In conclusion, the future of renewable energy is not just about technology; it is about people, communities, and the planet. By embracing renewable energy as a cornerstone of our energy future, we can create a world that is cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable for generations to come. The time to act is now. Let us seize the opportunity before us and work together to build a brighter, greener future for all.




































