SSD vs. Hard Disk Drive: Unveiling the Key Differences
 In the ever-evolving world of computer storage, two prominent contenders vie for supremacy: the Solid State Drive (SSD) and the Hard Disk Drive (HDD). These two storage devices have revolutionized the way we store and access data. However, they differ fundamentally in their architecture, performance, and capabilities. This article will explore and dissect the key distinctions between SSDs and HDDs to help you make an informed decision when choosing the right storage solution for your needs.
In the ever-evolving world of computer storage, two prominent contenders vie for supremacy: the Solid State Drive (SSD) and the Hard Disk Drive (HDD). These two storage devices have revolutionized the way we store and access data. However, they differ fundamentally in their architecture, performance, and capabilities. This article will explore and dissect the key distinctions between SSDs and HDDs to help you make an informed decision when choosing the right storage solution for your needs.
1. Technology Behind SSD and HDD
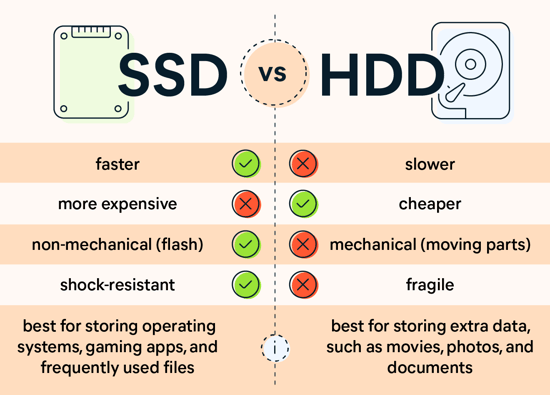
SSD: A Solid State Drive is a storage device that utilizes NAND-based flash memory to store data. Unlike HDDs, SSDs have no moving parts, which makes them more durable, reliable, and energy-efficient.
HDD: A Hard Disk Drive stores data on spinning platters coated with magnetic material. Data is read and written using a read/write head that moves across these spinning platters. The mechanical components in HDDs are the primary source of their slower performance and vulnerability to physical shock.
2. Speed and Performance
SSD: SSDs are renowned for their blazing speed. They offer near-instantaneous data access, significantly reducing boot times, application load times, and file transfers. The lack of moving parts means there’s no physical delay in data retrieval.
HDD: HDDs, due to their mechanical nature, are relatively slower. Data access involves the read/write head physically moving to the correct position on the spinning platter, resulting in slower read and write speeds compared to SSDs.
3. Reliability and Durability
SSD: SSDs are highly reliable and durable because they lack the mechanical parts that can wear out over time. They are more resistant to shocks and temperature variations, making them ideal for laptops and portable devices.
HDD: HDDs are more susceptible to wear and tear due to their mechanical components. Sudden impacts or temperature extremes can lead to data loss or drive failure. This makes HDDs less reliable for mobile applications.
4. Noise and Heat
SSD: SSDs generate no noise since they lack moving parts. They also produce minimal heat, making them suitable for quiet and power-efficient systems.
HDD: HDDs produce noise due to the spinning platters and the read/write head movement. They also generate more heat, which may require additional cooling in some setups.
5. Storage Capacity
SSD: SSDs are available in various capacities, but they are generally more expensive per gigabyte compared to HDDs. High-capacity SSDs can be costly, which can be a limiting factor for those who require massive storage space.
HDD: HDDs excel in terms of storage capacity. They offer larger capacities at more budget-friendly price points, making them the go-to choice for bulk data storage.
6. Price
SSD: SSDs tend to be pricier than HDDs. While their costs have decreased over the years, they are still more expensive on a per-gigabyte basis.
HDD: HDDs are more affordable when it comes to cost per gigabyte of storage. They are an economical choice for individuals or businesses with extensive storage needs.
Conclusion
The choice between an SSD and an HDD ultimately depends on your specific requirements. SSDs offer superior speed, reliability, and efficiency, making them an excellent choice for users seeking rapid performance and durability. On the other hand, HDDs are perfect for individuals with large storage demands who are on a budget.
In practical terms, many users opt for a combination of both types, using SSDs for their operating system and frequently used programs to enjoy speed, while relying on HDDs for archiving data and storing vast multimedia collections. The choice is yours, but understanding the differences between SSDs and HDDs is the first step toward making the right decision for your data storage needs.