What is Bittensor (TAO)?
In November 2022, Sam Altman's OpenAI announced ChatGPT to the world, bringing artificial intelligence (AI) into the spotlight in the market. Over a year later, AI remains a hot topic, partly due to Altman's departure and subsequent rehiring by the OpenAI board.
News of Altman's departure sparked rumors of a significant breakthrough in artificial general intelligence (AGI), systems capable of outperforming humans in most tasks, as warned by OpenAI researchers to the board. Some believe this breakthrough is related to synthetic general intelligence (AGI), highly autonomous systems that can handle tasks better than humans in most domains.
With such rapid technological advancements, many have raised concerns about the potential risks posed by AGI. A common concern is that this highly intelligent technology lies in the hands of large, centralized organizations, such as OpenAI and its largest shareholder, Microsoft, as well as other tech companies developing AI, like Google's Bard and Elon Musk's xAI.
This has led to an increase in decentralized AI projects, with many believing that blockchain and cryptocurrencies could play a crucial role in the development of artificial intelligence. For instance, Arthur Hayes argues that AGI companies will choose Bitcoin as their transaction currency, and leading the decentralized AI field is Bittensor, a protocol focused on decentralized Machine Learning, following a similar trajectory.
What is Bittensor (TAO)?
Bittensor (TAO) is a project developed by the non-profit organization OpenTensor. Initially designed as a Polkadot parachain named Finney, the protocol decided to launch its own chain in March 2023 to reduce dependence on the Polkadot ecosystem. The current chain is named Nakamoto, modeled after the Bitcoin network.
Bittensor aims to decentralize access to Machine Learning models and train machine learning models in an anti-censorship manner. Currently, the training of Machine Learning models requires significant resources that only large corporations like Google and OpenAI can afford. Bittensor aspires to become a marketplace for machine intelligence, where intelligence is contributed to the network by highly-rated validators, and they are rewarded by the P2P network with its native token, TAO.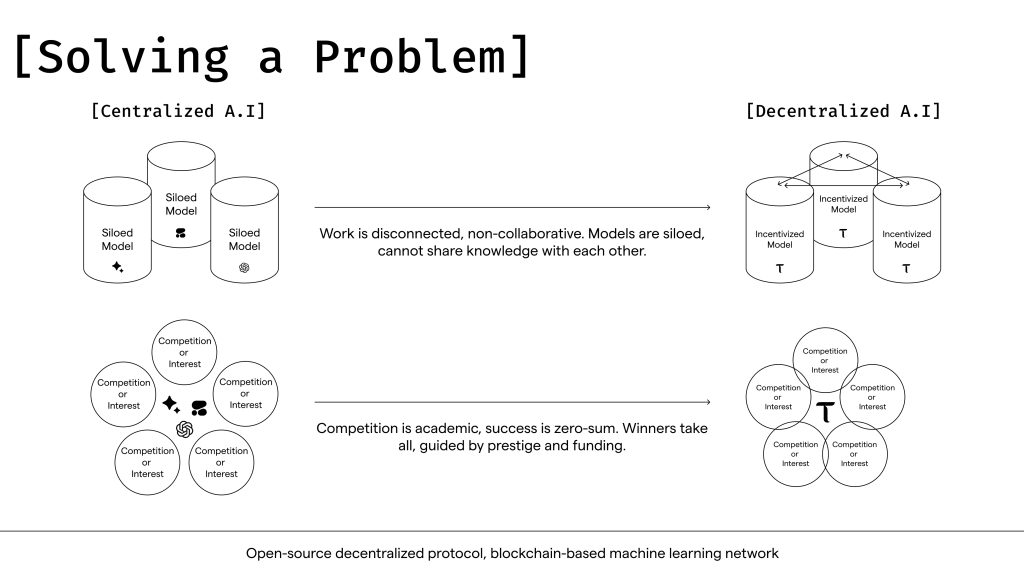
How does Bittensor work?
Bittensor consists of three core components: subnet, blockchain, and Bittensor API. According to their official documentation, Bittensor is simply “a protocol for decentralized subnets.” Subnets are a competitive mechanism based on paying incentives to users for performing a specific task. Users can create custom subnets for their own programs or join the existing competition mechanism. The Bittensor blockchain supports subnets and ensures the ecosystem is decentralized, permissionless, and collusion-resistant. Meanwhile, the Bittensor API connects subnets and blockchains, ensuring reward distribution to miners and validators across the subnet.
How do subnets work?
Subnets are Bittensor's solution for decentralizing the training of Machine Learning models. Each subnet is a closed economic market for training and cultivating different forms of machine intelligence such as: text translation, image generation, text generation, data collection, etc. Subnets are managed by their owners and will include three types of users: miners, validators, and users.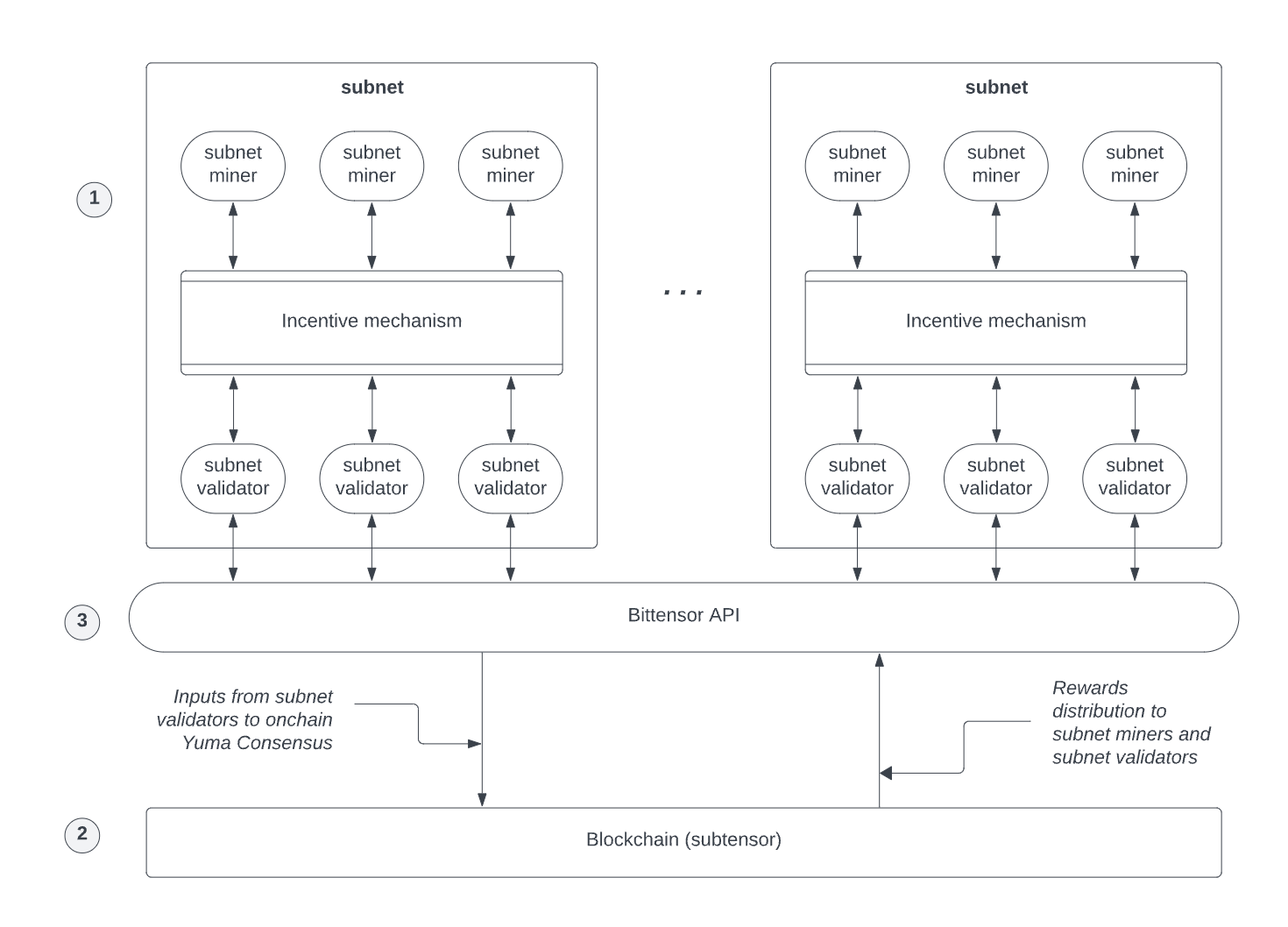
Bittensor includes miners, sometimes referred to as servers, which are off-chain Machine Learning nodes that activate the network's functions. They are responsible for handling requests from subnetworks coming from users and providing appropriate feedback based on their models. This feedback is evaluated by the subnetwork's validators, who will assign ratings to them, and miners are rewarded with Bittensor's native token, TAO. Miners continuously providing inaccurate feedback will be gradually expelled, facing reduced rewards and eventually leaving the subnetwork to ensure its quality.
Validators perform the task of verifying the quality of work done. The subnetwork owner can provide a template for validation, but validators can also express their own views through personal validation about what the subnetwork should learn. This increases diversity in learning and reduces the risk of centralization in a network where models are forced in a specific direction.
Finally, users of the subnetwork submit requests to the subnetwork as end-users, and corresponding miners respond to these requests. Users can access these subnetworks through BitAPAI (accessible through popular programming languages like Python, Node.js, Golang, and Rust). This service is currently free to encourage development on the platform, although limits have been set to prevent API abuse. However, requests can be made to increase limits, depending on further questions and approval from the BitAPAI team.
The project is built on top of Bittensor, creating a decentralized and incentivized ecosystem for machine learning and artificial intelligence.
Project built on Bittensor
Despite being a young protocol, there are already a number of projects starting to build on the Bittensor network, relying on the services of specific subnets, with most targeting text or image generation. A popular type of project are ChatGPT-style bots such as ChatNI, Chat with Hal, and Chattensor, all of which act as chat support assistants where users can type questions or requests and receive answers from bot.
Another popular project built on Bittensor is ReplyTensor, which uses an image and text generation subnet to generate automated responses on Twitter, Telegram, and Discord. ReplyTensor is developed by Neural Internet, an AI research decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) and one of the main builders on Bittensor's resources.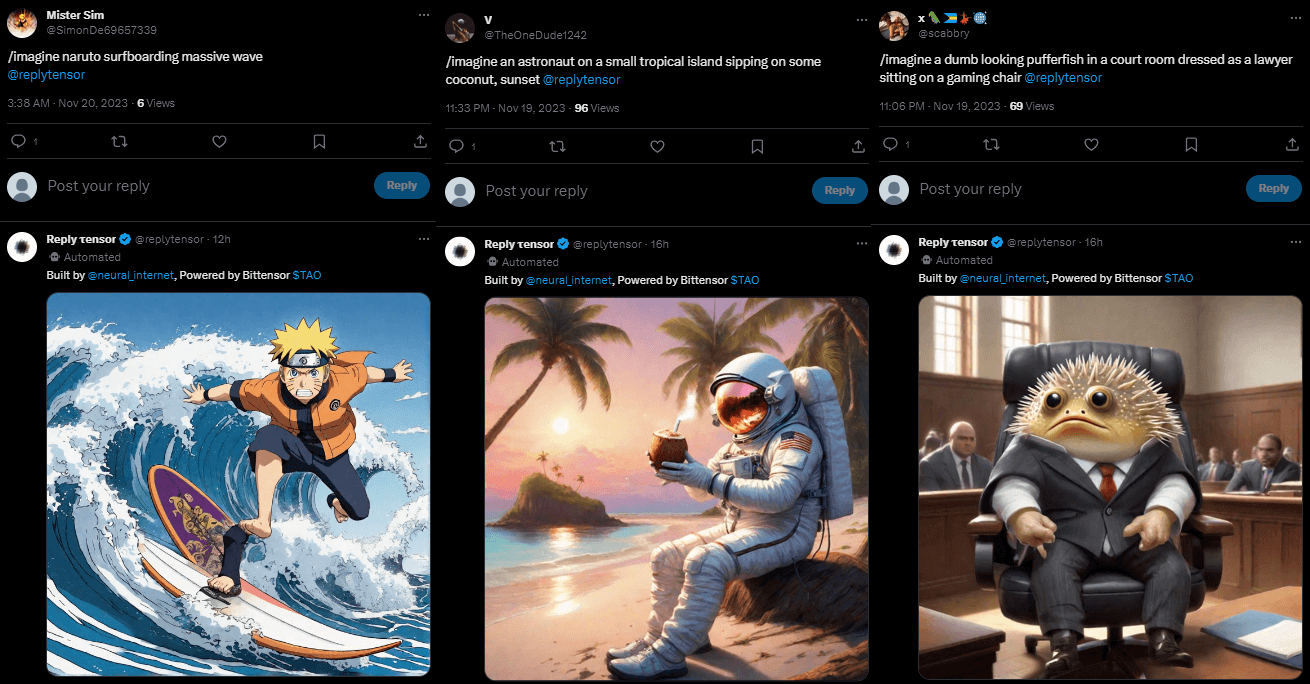
TAO Token and its Tokenomics
Like the Bitcoin network that Bittensor is modeled after, the design of the TAO token closely follows that of Bitcoin with a total supply of 21 million. Aiming for as fair a launch as possible, Bittensor does not have any presales or private investors, with even the founders and founding team having to mine their own tokens. Likewise, TAO also follows Bitcoin's Halving model, emissions are also halved every 10.5 million blocks. The first halving is scheduled to take place in September 2025, with a total of 64 halving events.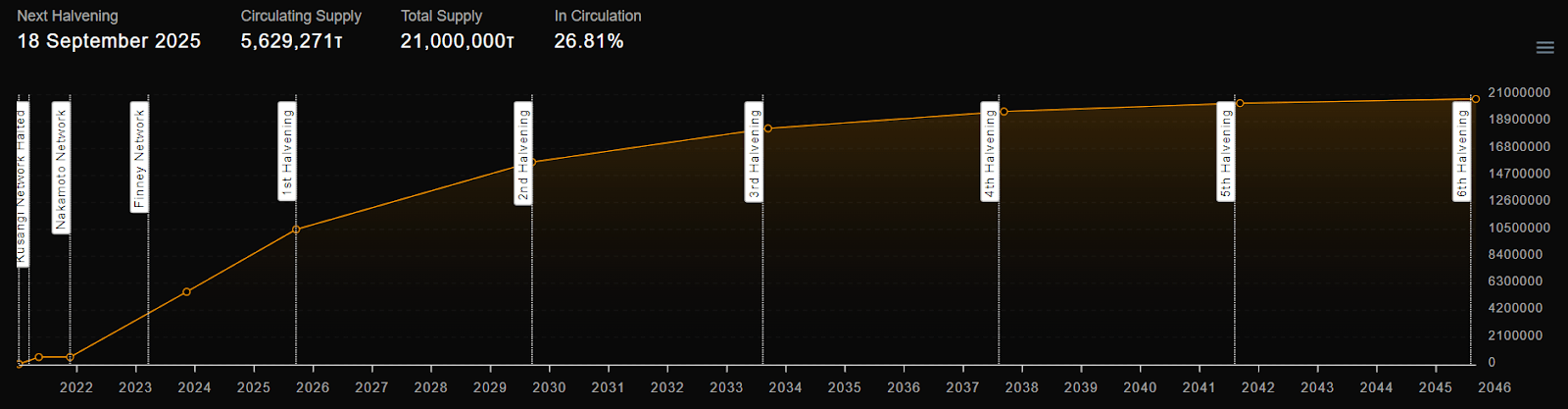
In addition to the native TAO token, TAO also exists as an ERC-20 version on the Ethereum mainnet as wrapped TAO (wTAO). WTAO can be connected back to the Bittensor network via the TAO Bridge. However, please note that TAO Bridge is a community-run project and is not officially run by the Bittensor team.
Future outlook for Bittensor
The current state of Machine Learning training is hampered by a siled approach and a lack of composability. As the Bittensor network continues to grow and develop, they aspire to one day become the center of all things machine intelligence, with users, start-ups and even large corporations Harness the network for machine intelligence capabilities, with all services paid for in TAO tokens.






![[LIVE] Engage2Earn: auspol follower rush](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/c1a761de-5ce9-4e9b-b5b3-dc009e60bfa8/1)




![[ℕ𝕖𝕧𝕖𝕣] 𝕊𝕖𝕝𝕝 𝕐𝕠𝕦𝕣 𝔹𝕚𝕥𝕔𝕠𝕚𝕟 - And Now What.... Pray To The God Of Hopium?](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/79e7827b-c644-4853-b048-a9601a8a8da7/1)






















