The Rise of Telemedicine: Transforming Healthcare Delivery
Introduction: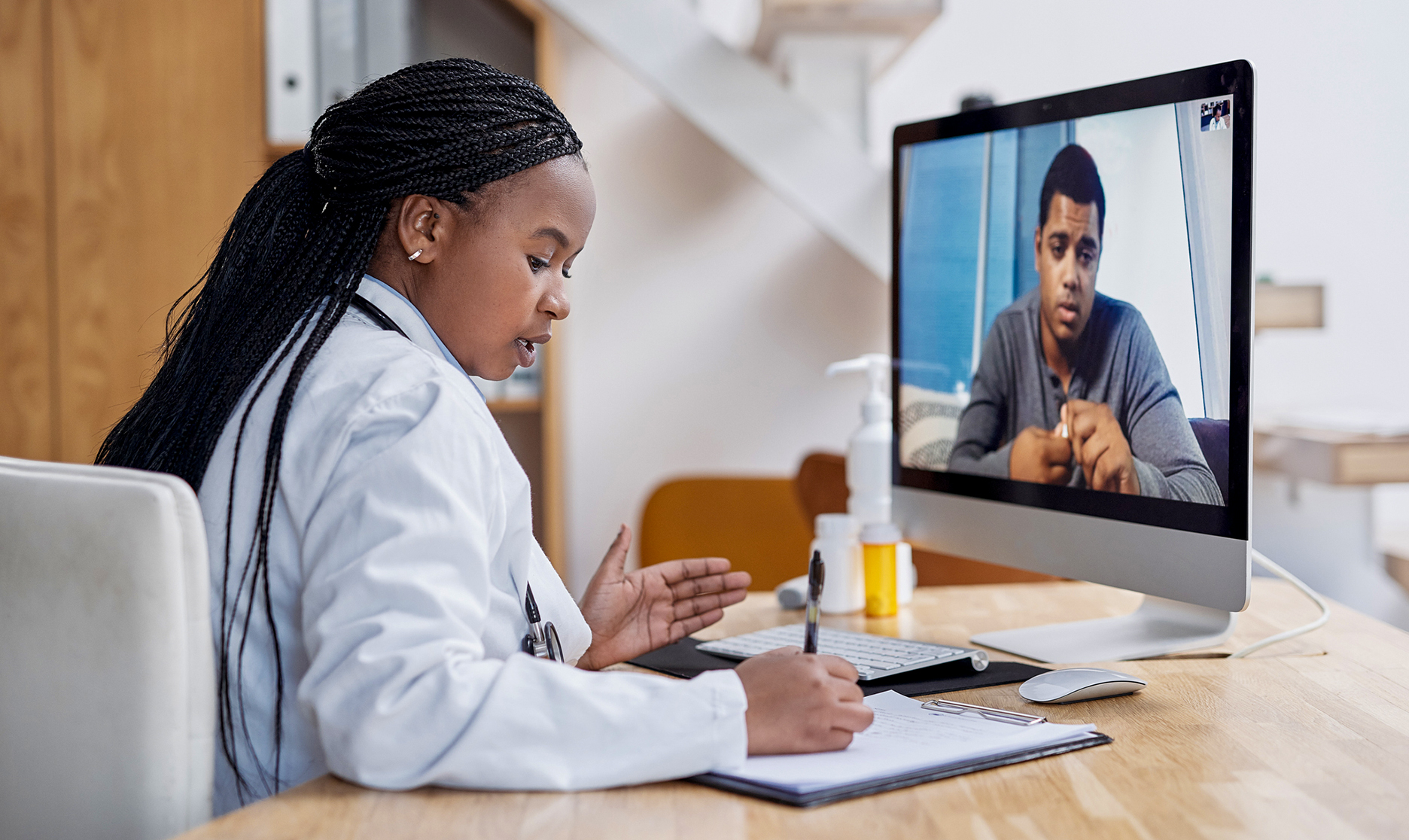
Telemedicine, once a niche concept, has rapidly emerged as a transformative force in healthcare delivery, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. By leveraging technology to facilitate remote medical consultations, diagnosis, and treatment, telemedicine has revolutionized access to healthcare, improved patient outcomes, and enhanced healthcare delivery efficiency. This article explores the evolution of telemedicine, its benefits, challenges, and its potential to reshape the future of healthcare.
The Evolution of Telemedicine:
The roots of telemedicine can be traced back to the early 20th century when radio and telephone communications were first utilized to provide medical consultations over long distances. However, it wasn't until the advent of the internet and digital technologies that telemedicine truly began to flourish. The development of secure communication channels, electronic health records (EHRs), and remote monitoring devices laid the groundwork for the modern telemedicine era.
Telemedicine gained momentum in the latter half of the 20th century with the introduction of videoconferencing technology, which enabled real-time audiovisual communication between patients and healthcare providers. This facilitated remote consultations, allowing patients in rural or underserved areas to access specialist care without the need for travel. Moreover, telemedicine found applications in emergency medicine, telepsychiatry, and telestroke services, where timely intervention is crucial for patient outcomes. The 21st century witnessed a surge in telemedicine adoption, driven by advancements in telecommunications, mobile computing, and healthcare informatics. The proliferation of smartphones and high-speed internet connectivity expanded access to telemedicine services, enabling patients to consult with healthcare providers from virtually anywhere. Moreover, the integration of telemedicine into electronic health record systems facilitated seamless documentation, billing, and reimbursement for telemedicine encounters, enhancing its integration into mainstream healthcare delivery.
The 21st century witnessed a surge in telemedicine adoption, driven by advancements in telecommunications, mobile computing, and healthcare informatics. The proliferation of smartphones and high-speed internet connectivity expanded access to telemedicine services, enabling patients to consult with healthcare providers from virtually anywhere. Moreover, the integration of telemedicine into electronic health record systems facilitated seamless documentation, billing, and reimbursement for telemedicine encounters, enhancing its integration into mainstream healthcare delivery.
Benefits of Telemedicine:/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/54/78/5478d7cf-4dc1-45ee-998b-ca095579ec00/telemedicine.jpg)
Telemedicine offers a multitude of benefits for patients, healthcare providers, and healthcare systems alike. For patients, telemedicine provides convenient access to medical care, particularly for those in remote or underserved areas. It eliminates the need for travel, reduces waiting times, and enables patients to consult with healthcare professionals from the comfort of their homes. This is especially significant for individuals with mobility limitations, chronic illnesses, or those at risk of infectious diseases who may benefit from remote consultations.
Furthermore, telemedicine enhances patient engagement and empowerment by facilitating greater access to health information, monitoring tools, and self-management resources. Patients can participate more actively in their care, make informed decisions, and adhere to treatment plans with the support of telemedicine-enabled education and coaching services. This proactive approach to healthcare promotes healthier lifestyles, reduces healthcare costs, and improves overall well-being. For healthcare providers, telemedicine enhances efficiency by streamlining workflows, reducing administrative burdens, and enabling more flexible scheduling. Virtual consultations allow providers to conduct patient assessments, review medical records, and prescribe treatments remotely, saving time and resources for both parties. Moreover, telemedicine enables better coordination of care among multidisciplinary teams, fostering collaboration between primary care physicians, specialists, nurses, and allied health professionals.
For healthcare providers, telemedicine enhances efficiency by streamlining workflows, reducing administrative burdens, and enabling more flexible scheduling. Virtual consultations allow providers to conduct patient assessments, review medical records, and prescribe treatments remotely, saving time and resources for both parties. Moreover, telemedicine enables better coordination of care among multidisciplinary teams, fostering collaboration between primary care physicians, specialists, nurses, and allied health professionals.
Telemedicine also improves access to specialist expertise, particularly in rural or underserved areas where healthcare resources may be limited. Through telemedicine networks and teleconsultation platforms, primary care providers can seek timely advice, second opinions, or referrals from specialists located elsewhere. This enhances diagnostic accuracy, reduces unnecessary referrals, and ensures that patients receive appropriate care in a timely manner.
Challenges and Considerations:
Despite its many benefits, telemedicine also presents challenges and considerations that must be addressed for its widespread adoption and effectiveness. One significant challenge is ensuring equitable access to telemedicine services, particularly for vulnerable populations who may lack access to reliable internet connectivity or digital literacy skills. The "digital divide" exacerbates healthcare disparities, limiting access to telemedicine for marginalized communities, older adults, and individuals with disabilities.
Moreover, concerns regarding patient privacy, data security, and regulatory compliance require careful attention to safeguard patient information and uphold ethical standards. Telemedicine platforms must comply with healthcare privacy regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) to protect patient confidentiality and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive health data. Additionally, telemedicine providers must implement robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard against data breaches, hacking attempts, and other cyber threats that could compromise patient safety and trust.
Telemedicine in the COVID-19 Era:
The COVID-19 pandemic served as a catalyst for the rapid expansion of telemedicine, as social distancing measures and lockdowns necessitated alternative methods of healthcare delivery. Telemedicine emerged as a critical tool for triaging COVID-19 cases, providing continuity of care for chronic conditions, and reducing the burden on healthcare facilities overwhelmed by the pandemic. Remote monitoring technologies enabled early detection of COVID-19 symptoms and facilitated remote patient monitoring for those recovering at home.
Moreover, policymakers and healthcare organizations relaxed regulatory barriers and expanded reimbursement policies to facilitate broader telemedicine adoption, accelerating its integration into mainstream healthcare delivery. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) expanded telehealth coverage and reimbursement rates for Medicare beneficiaries, enabling more providers to offer telemedicine services and receive payment for virtual consultations. Private insurers followed suit, expanding telehealth coverage and waiving cost-sharing requirements to make telemedicine more accessible and affordable for patients.
Telemedicine played a pivotal role in maintaining essential healthcare services during the pandemic, enabling patients to access medical care while minimizing the risk of exposure to COVID-19. Virtual consultations allowed patients to consult with healthcare providers, refill prescriptions, and receive follow-up care without leaving their homes. Remote monitoring technologies enabled healthcare providers to monitor patients' vital signs, symptoms, and medication adherence remotely, facilitating early intervention and preventing complications.
Future Directions:
As we look to the future, telemedicine holds immense potential to transform healthcare delivery and improve patient outcomes. Advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and wearable technologies promise to further enhance telemedicine capabilities, enabling more personalized and proactive approaches to healthcare. AI-powered virtual assistants, chatbots, and decision support tools can augment clinical decision-making, automate administrative tasks, and provide personalized health recommendations based on patients' unique needs and preferences.
Moreover, telemedicine has the potential to address longstanding healthcare disparities by increasing access to care for underserved populations and facilitating greater collaboration among healthcare providers across geographic boundaries. Telemedicine networks and teleconsultation platforms enable healthcare providers to share knowledge, exchange expertise, and collaborate on complex cases, regardless of their physical location. This enhances diagnostic accuracy, treatment effectiveness, and patient outcomes, particularly in regions with limited access to specialist care.
However, realizing this potential requires continued investment in technology infrastructure, regulatory frameworks, and stakeholder engagement to ensure that telemedicine evolves in a manner that prioritizes patient-centered care, equity, and quality. Policymakers must address barriers to telemedicine adoption, such as reimbursement disparities, licensure requirements, and interstate practice regulations, to promote a conducive environment for telemedicine innovation and expansion.
Conclusion:
Telemedicine represents a paradigm shift in healthcare delivery, offering a transformative solution to address the evolving needs of patients and healthcare systems. By harnessing the power of technology to overcome geographic barriers, improve access to care, and enhance care coordination, telemedicine has the potential to revolutionize the way healthcare is delivered, experienced, and perceived. As we navigate the complexities of modern healthcare, telemedicine stands as a beacon of innovation and progress, offering hope for a future where quality healthcare is accessible to all, regardless of location or circumstance. With continued investment, collaboration, and commitment, telemedicine can pave the way for a more accessible, equitable, and patient-centered healthcare system for generations to come.








































































