Exploring the Role of Technology in Revolutionizing Financial Trading
Trading is the act of buying and selling financial instruments such as stocks, bonds, commodities, or currencies to make a profit. It's a dynamic and complex field that requires a combination of skill, knowledge, and sometimes luck. Over the years, trading has evolved significantly, with the advent of technology playing a crucial role in shaping how trades are executed and managed. Here, we'll delve into trading and the various tools used in this practice.
Understanding Trading:
- Market Dynamics: Successful trading requires a deep understanding of market dynamics. This includes factors such as supply and demand, market sentiment, economic indicators, geopolitical events, and more. Traders analyze these factors to identify potential opportunities and risks.
- Risk Management: Managing risk is paramount in trading. Traders employ various strategies to minimize losses, including setting stop-loss orders, diversifying their portfolios, and using leverage cautiously.
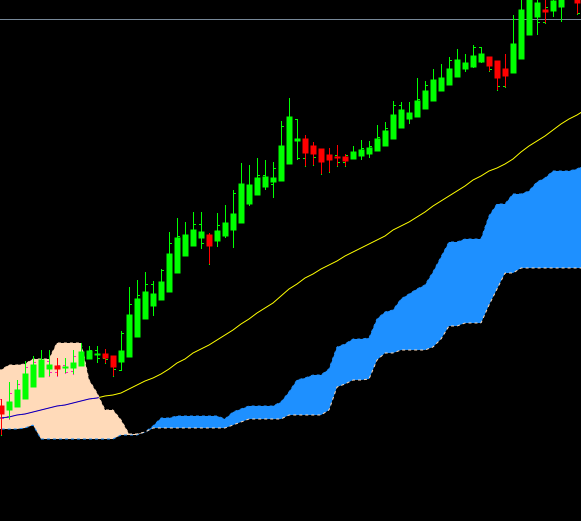
- Technical Analysis: Many traders utilize technical analysis, which involves studying past market data (such as price and volume) to forecast future price movements. Chart patterns, indicators, and trend analysis are common tools in technical analysis.
- Fundamental Analysis: Fundamental analysis involves evaluating the intrinsic value of an asset by analyzing economic, financial, and other qualitative factors. This can include examining company financials, industry trends, macroeconomic indicators, and geopolitical events.
- Trading Strategies: There are numerous trading strategies employed by traders, including day trading, swing trading, trend following, scalping, and algorithmic trading. Each strategy has its own risk profile and requires different skills and tools.
Trading Tools:
- Trading Platforms: Online trading platforms serve as the interface between traders and the financial markets. These platforms provide access to market data, charting tools, order execution, and account management. Examples include MetaTrader, Thinkorswim, and TradingView.
- Charting Software: Charting software allows traders to visualize market data and perform technical analysis. These tools often include a wide range of technical indicators, drawing tools, and customization options to analyze price movements effectively.
- Algorithmic Trading Software: Algorithmic trading, or automated trading, involves using computer algorithms to execute trades automatically based on predefined criteria. Algorithmic trading software allows traders to backtest strategies, optimize parameters, and execute trades at high speeds.
- News and Analysis Platforms: Access to real-time news and analysis is essential for staying informed about market developments. Many traders use news terminals or financial news websites to monitor breaking news, economic reports, and expert analysis.
- Risk Management Tools: Risk management tools help traders assess and mitigate risks associated with their trades. This includes position-sizing calculators, risk-reward calculators, and volatility indicators.
- Social Trading Platforms: Social trading platforms allow traders to interact with and copy the trades of other investors. These platforms facilitate knowledge sharing and idea generation among traders.
- Educational Resources: Continuous learning is vital for traders to stay ahead in the markets. Educational resources such as online courses, webinars, trading books, and forums provide valuable insights and knowledge to improve trading skills.
In conclusion, trading is a multifaceted activity that requires a combination of skill, knowledge, and the right tools. Whether you're a novice trader or an experienced investor, leveraging trading tools effectively can enhance your decision-making process and potentially improve your trading outcomes. However, it's important to remember that trading carries inherent risks, and prudent risk management is essential for long-term success in the markets.