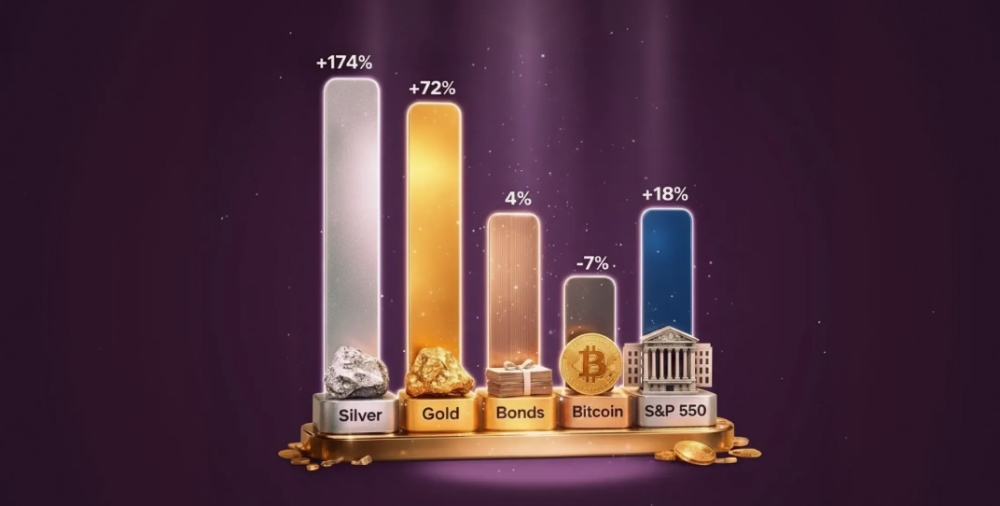
Feminism – Good or Bad?
Feminism has long been a polarizing subject, evoking passionate responses from both proponents and detractors. At its core, feminism seeks to address the systemic inequalities faced by women in a patriarchal society.
However, as discussions continue to evolve, the complexities surrounding feminism warrant a careful examination of its implications, effectiveness, and the broader social context it occupies.
Understanding Feminism: A Brief Overview
Feminism can be defined as both a social movement and a political ideology aimed at advocating for women's rights and achieving equality across all facets of life. The movement has undergone significant transformation since its inception, evolving through various waves, each addressing different sets of challenges faced by women. Notably, the key waves include:
First Wave (Late 19th - Early 20th Century):
- Focused primarily on legal issues and inequalities, particularly women's suffrage.
Second Wave (1960s - 1980s):
- Expanded its focus to issues of sexuality, family, the workplace, and reproductive rights.
Third Wave (1990s - Present):
- Emphasizes diversity and the individual experience of women, acknowledging differences based on race, class, and sexuality.
Intersectional Feminism:
- This approach addresses overlapping social identities and the resulting systemic injustices, recognizing that women experience oppression differently based on these intersections.
Examining the Pros and Cons of Feminism
The Positive Aspects
Advocacy for Equal Rights:
- Feminism has played a crucial role in advocating for women's legal rights, including the right to vote, work, and access education.
Empowerment:
- The movement empowers women to assert their individuality and make informed choices regarding their lives and bodies.
Societal Awareness:
- Feminism raises awareness of issues such as gender-based violence, workplace discrimination, and reproductive rights, prompting necessary societal changes.
Support for Marginalized Groups:
- Many feminist movements advocate for the rights of not just women, but also LGBTQ+ individuals, people of color, and other marginalized communities.
The Criticisms
Perceived Extremism:
Some critique feminist movements as being overly radical or extremist, arguing that they alienate potential allies by promoting an adversarial stance towards men.
Misrepresentation:
Critics often claim that feminism misrepresents the challenges faced by men and promotes a blame culture rather than fostering constructive dialogue.
Lack of Inclusivity:
Instances arise where certain feminist movements fail to adequately represent the voices of all women, particularly women of color and those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds.
Debate on Methods:
There is ongoing debate within feminism itself regarding effectiveness and method; for example, discussions around whether to pursue equality through political engagement versus grassroots activism.
Balancing Perspectives: Is Feminism Good or Bad?
Determining whether feminism is good or bad is not a binary question but rather a complex conversation dependent on individual perspectives and experiences. The nuances in thought and activism illustrate that while feminism has undoubtedly brought about significant strides for women's rights, there are both constructive and critical viewpoints that merit consideration.
Actionable Steps
Understanding the implications of feminism and its multifaceted nature can empower individuals to engage thoughtfully with the movement. Here are some practical steps readers can take:
Educate Yourself:
Explore feminist literature and resources to gain deeper insights into various women's experiences and the history of the movement.
Recommended reading: "The Second Sex" by Simone de Beauvoir and "We Should All Be Feminists" by Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie.
Engage in Dialogue:
Participate in discussions that include diverse perspectives on gender issues. It is imperative to listen and learn from different experiences.
Support Local Feminist Organizations:
Find and support local feminist groups or initiatives that resonate with your interests and values. Volunteering your time or resources can make a tangible impact.
Advocate for Gender Equality:
Actively support policies and legislation that promote equal rights and address gender-based discrimination in your community.
Challenge Stereotypes:
Work to challenge gender stereotypes and norms in your own life and social circles by promoting respectful and inclusive dialogues.
Stay Informed About Current Events:
Follow reputable news sources and organizations focused on women's rights and gender equality to stay updated on key issues and ongoing changes in policies.
Conclusion
Feminism is a multifaceted movement that encompasses a range of ideologies, experiences, and criticisms. Engaging with this topic can provide valuable insights into the ongoing struggle for gender equality. Whether viewed as a force for positive change or criticized for its perceived shortcomings, understanding feminism requires deep reflection and open dialogue.
References
UN Women, National Organization for Women (NOW), American Association of University Women (AAUW), World Economic Forum - Gender Gap Report, Gender Equality and Women's Empowerment - USAID, Planned Parenthood - Reproductive Rights, RAINN - Sexual Assault Prevention, Global Fund for Women, The Women's Equality Party, Feminist Majority Foundation