What is a Computer? A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
A computer is an indispensable part of modern life, playing a pivotal role in various aspects of our daily activities. In this article, we will delve into the intricate world of computers, exploring their definition, components, historical evolution, and diverse applications.
Definition
At its core, a computer is an electronic device capable of processing data according to a set of instructions. It can perform a wide range of tasks, from simple calculations to complex operations, and has become an essential tool in fields such as science, business, education, and entertainment.
Components of a Computer:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Often referred to as the brain of the computer, the CPU is responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations.
- Memory (RAM and Storage): Random Access Memory (RAM) is used for temporary data storage, while storage devices like hard drives or solid-state drives store data for the long term.
- Motherboard: This is the main circuit board connecting all the computer's components, facilitating communication between them.
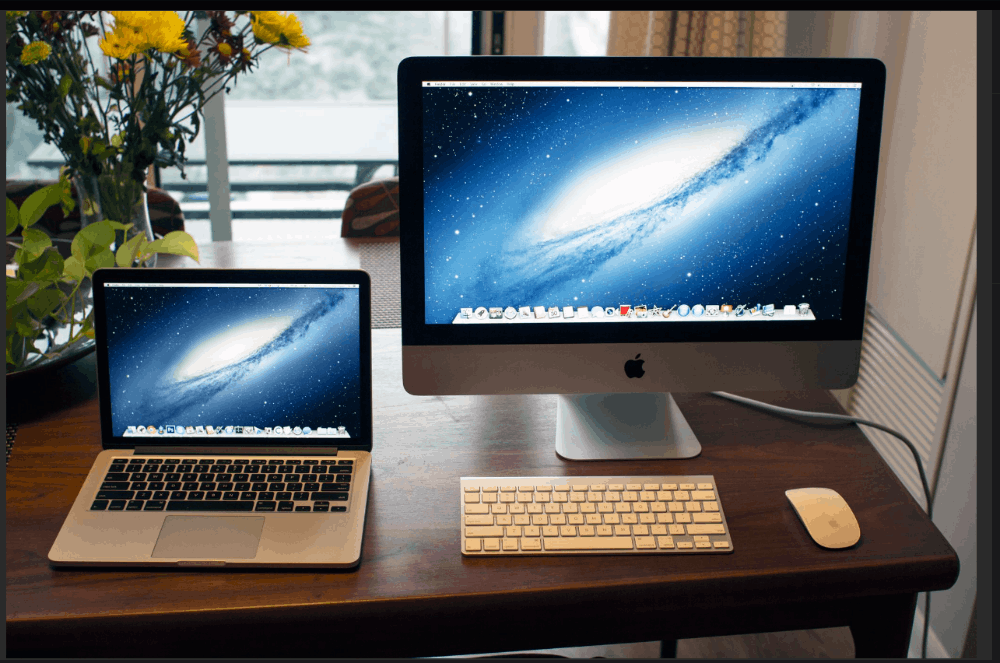
- Input Devices: Devices like keyboards and mice allow users to input data into the computer.
- Output Devices: Monitors, printers, and speakers are examples of output devices that display or produce results from the computer's processes.
- Peripheral Devices: Additional devices like scanners, external drives, and webcams enhance the computer's functionality.
1. Central Processing Unit (CPU):
The CPU, often considered the heart of the computer, is responsible for executing instructions from programs. It performs arithmetic and logic operations, managing data and controlling other components of the system. The speed and efficiency of a computer are often associated with the capabilities of its CPU.
2. Memory (RAM and Storage):
Random Access Memory (RAM) is volatile memory that provides the computer with quick access to currently running applications and data. Storage, on the other hand, includes devices like hard disk drives (HDDs) or solid-state drives (SSDs) for long-term data storage. The combination of RAM and storage contributes to the overall performance and responsiveness of the computer.
3. Motherboard:
The motherboard is a crucial component that houses the CPU, memory, and other essential connectors. It serves as a communication hub, facilitating the flow of data between various components. Expansion slots on the motherboard allow users to add additional features or upgrade their system.
4. Input and Output Devices:
Input devices, such as keyboards, mice, and touchscreens, enable users to interact with the computer. Output devices, including monitors, printers, and speakers, provide feedback and present the results of computer processes.
5. Types of Computers:
- Personal Computers (PCs): Widely used for general-purpose computing.
- Servers: Designed to manage network resources and provide services.
- Mainframes: Powerful computers used for large-scale data processing.
- Supercomputers: Specialized for complex scientific and engineering tasks, like weather modeling and molecular simulations.
6. Applications of Computers:
- Business: Used for data analysis, accounting, and communication.
- Education: Facilitates research, online learning, and collaborative projects.
- Healthcare: Critical for medical imaging, patient records, and research.
- Entertainment: Powers gaming, multimedia creation, and streaming services.
- Communication: The internet, email, and social media are reliant on computer networks.
7. Challenges:
- Cybersecurity: The increasing connectivity brings forth security threats and the need for robust protective measures.
- Ethical Concerns: Issues arise with the development and deployment of technologies like artificial intelligence, raising questions about privacy and bias.
8. Future Trends:
- Quantum Computing: Promises to revolutionize computing by leveraging quantum bits (qubits) for faster and more efficient calculations.
- Edge Computing: Involves processing data closer to the source (e.g., devices) to reduce latency and enhance efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence: Continues to evolve, impacting areas such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision.
Understanding these details provides a comprehensive overview of the intricate world of computers and their far-reaching impact on society.
Historical Evolution
The history of computers spans centuries, from ancient abacuses to the sophisticated devices we use today. Major milestones include the invention of mechanical calculators in the 17th century, the development of electronic computers in the mid-20th century, and the subsequent rise of personal computers in the late 20th century. The evolution of computers continues with the advent of quantum computing and artificial intelligence.
Types of Computers
Computers come in various forms, ranging from personal computers (desktops and laptops) to servers, mainframes, and supercomputers. Each type serves specific purposes, with supercomputers, for example, being designed for high-performance computing tasks such as scientific simulations and complex calculations.
Applications of Computers
Computers have permeated every facet of modern life. They are used in business for data analysis and management, in education for research and learning, in healthcare for diagnostics and research, and in entertainment for gaming and multimedia production. The internet, powered by computers, has revolutionized communication and information access globally.
Challenges and Future Trends
Despite their ubiquity, computers face challenges such as cybersecurity threats and ethical concerns related to artificial intelligence. Looking forward, emerging technologies like quantum computing, edge computing, and the continued development of artificial intelligence are poised to shape the future landscape of computing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, computers have evolved from rudimentary devices to complex systems integral to our daily lives. Understanding their components, history, and diverse applications provides a comprehensive perspective on the significance of computers in the contemporary world. As technology continues to advance, the role of computers is likely to expand, influencing and enhancing various aspects of human existence.