How Air Travel Has Changed Over The Last 100 Years
Air travel has undergone a dramatic transformation since its inception, evolving from a daring experiment to a cornerstone of global connectivity. The changes in technology, accessibility, and experience have reshaped the way humans traverse the skies.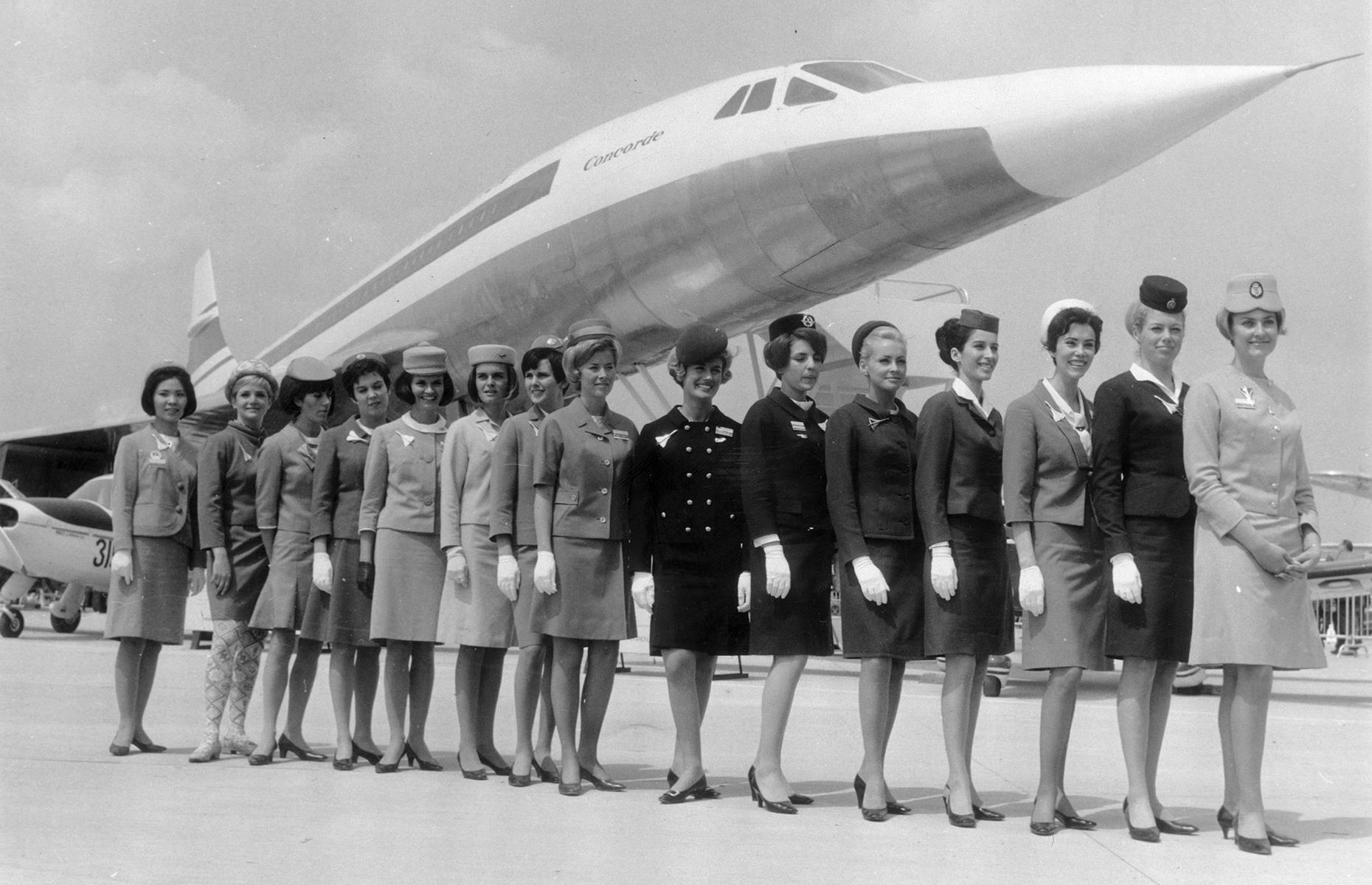 
From the first powered flights to the modern jet age, this progression reflects a fascinating blend of innovation and societal adaptation.
The Early Days of Aviation
The origins of air travel trace back to the early 20th century, when aviation pioneers turned the dream of flight into reality.
The Wright brothers’ first successful flight in 1903 marked a pivotal moment, but commercial air travel as we know it began in the 1920s.
- Aircraft Design: Early planes were rudimentary, made primarily of wood and fabric, with open cockpits and limited capacity. Safety and reliability were major concerns.
- Passenger Experience: Flights were noisy, cold, and uncomfortable, with few passengers willing to endure the hardships for a chance to fly.
- Routes and Range: Aviation was restricted to short routes due to limited fuel capacity and the underdeveloped nature of aircraft engines.
The interwar years saw a gradual shift. Airlines like Lufthansa and Imperial Airways started offering passenger services, albeit primarily to wealthy individuals. The introduction of enclosed cabins and small luxuries marked a step forward in passenger comfort.
The Jet Age Revolution
The mid-20th century heralded a new era for air travel with the advent of jet engines. The de Havilland Comet, introduced in 1952, became the world’s first commercial jet airliner. Though early models faced challenges, the technology eventually matured, giving rise to iconic aircraft like the Boeing 707.
- Speed and Range: Jets drastically reduced travel times, allowing passengers to cross continents and oceans in hours instead of days.
- Accessibility: Air travel shifted from being an exclusive luxury to a more widely accessible mode of transport.
- Infrastructure Growth: Airports around the world expanded to accommodate the surge in air traffic, with international hubs becoming essential for global connectivity.
The 1970s saw the introduction of jumbo jets like the Boeing 747, which revolutionized air travel further by increasing passenger capacity and reducing ticket costs. The deregulation of airlines in the United States also played a significant role in making flights affordable for middle-class travelers.
Modern Air Travel: Efficiency and Connectivity
The 21st century has witnessed air travel become more streamlined, efficient, and interconnected than ever before. Technological advancements and a focus on sustainability are shaping the industry.
- Aircraft Innovations: Modern planes like the Airbus A350 and Boeing 787 Dreamliner are designed for fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and enhanced passenger comfort.
- Digital Transformation: Online booking platforms, mobile check-ins, and biometric security systems have simplified the travel experience.
- Budget Airlines: Low-cost carriers such as Ryanair and AirAsia have democratized air travel, making it accessible to millions who previously couldn't afford to fly.
Passenger Experience Today
- Enhanced in-flight entertainment systems, Wi-Fi, and improved seating configurations cater to modern travelers' expectations.
- First-class and business-class offerings have become increasingly luxurious, featuring flatbeds, private suites, and gourmet dining.
Global Connectivity
- Air travel now connects the most remote corners of the globe, facilitating economic growth, cultural exchange, and tourism.
- Airlines have formed alliances like Star Alliance and oneworld to provide seamless travel experiences across multiple carriers.
Challenges and the Future of Air Travel
Despite its achievements, the aviation industry faces significant challenges that will define its future trajectory.
- Environmental Concerns: Air travel accounts for approximately 2.5% of global CO2 emissions, prompting calls for more sustainable practices.
- The development of sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) and electric planes is underway, although these technologies are still in their infancy.
- Impact of Pandemics: Events like the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the vulnerability of air travel, leading to enhanced health and safety protocols.
- Economic Pressures: Fluctuating fuel prices, geopolitical tensions, and rising operating costs pose ongoing hurdles for airlines.
The Road Ahead
- The concept of urban air mobility, featuring flying taxis and drones, is becoming a reality, with companies like Joby Aviation leading the charge.
- Supersonic flight may make a comeback, with new designs addressing the noise and efficiency issues that plagued earlier models like the Concorde.
- Investments in artificial intelligence and automation are expected to optimize operations, from air traffic management to personalized passenger services.
Conclusion
From fragile biplanes to sophisticated jets, the journey of air travel over the last century is a testament to human ingenuity and ambition. As the industry continues to innovate, its ability to balance growth with sustainability will determine how it shapes the next 100 years.
Reference
- History of Aviation
- The Jet Age: How It Changed Air Travel
- Advancements in Aircraft Design
- Environmental Impact of Aviation
- Future of Air Travel: Trends and Innovations
- The Rise of Budget Airlines
- Pandemic Effects on Air Travel
- Urban Air Mobility: The Next Frontier
- Supersonic Travel Revival
- Sustainable Aviation Initiatives