The role of cryptocurrencies in global markets
Introduction
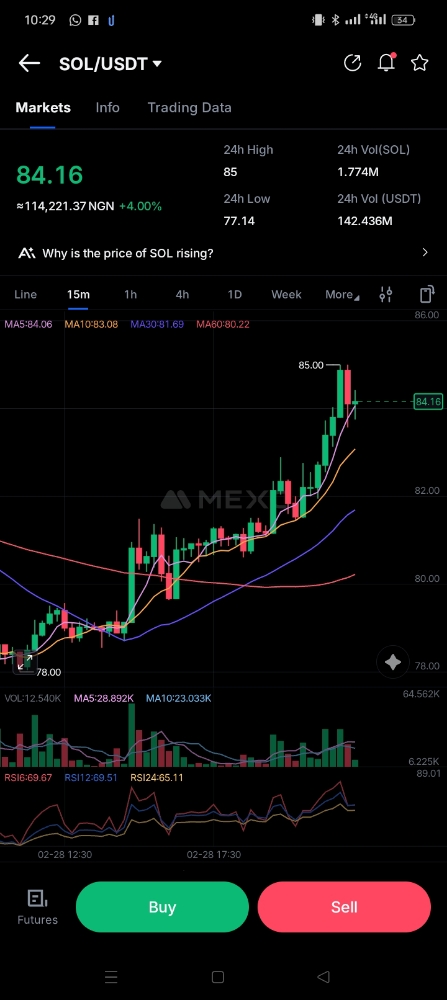
Cryptocurrencies have emerged as a disruptive force in global markets, reshaping how individuals and institutions view finance and transactions. Since the advent of Bitcoin in 2009, the cryptocurrency market has grown exponentially, with thousands of digital currencies now in existence. These decentralized, blockchain-based assets offer benefits such as transparency, security, and the potential for financial inclusion, but they also pose challenges including regulatory uncertainty and volatility. This document explores the role of cryptocurrencies in global markets, their benefits, challenges, and future implications.
The Rise of Cryptocurrencies
Early Development
Bitcoin, created by the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto, was the first cryptocurrency to leverage blockchain technology, a decentralized ledger system. Initially perceived as a niche experiment, Bitcoin gained traction due to its promise of financial autonomy and resistance to censorship.
Market Growth
Over the past decade, the cryptocurrency market has evolved into a multi-trillion-dollar industry. Ethereum, Binance Coin, Ripple, and other altcoins have expanded the ecosystem by offering additional functionalities like smart contracts and decentralized finance (DeFi).
Institutional Adoption
Institutional interest in cryptocurrencies has surged, with companies like Tesla, MicroStrategy, and Square adding Bitcoin to their balance sheets. Additionally, major financial institutions like JPMorgan Chase and Goldman Sachs now offer cryptocurrency-related services, signaling growing acceptance.
Benefits of Cryptocurrencies
Financial Inclusion
Cryptocurrencies can empower the unbanked and underbanked populations by providing access to financial services without requiring traditional banking infrastructure. Mobile wallets and blockchain networks enable users to send, receive, and store value globally.
Decentralization and Security
By operating on decentralized networks, cryptocurrencies reduce reliance on centralized intermediaries like banks. Blockchain technology ensures transparency and immutability, making transactions secure and resistant to tampering.
Borderless Transactions
Cryptocurrencies facilitate fast, low-cost cross-border transactions, making them an attractive alternative to traditional remittance systems like SWIFT. This capability is particularly valuable in regions with limited access to efficient payment systems.
Inflation Hedge
Digital assets like Bitcoin, with capped supplies, are viewed as hedges against inflation. In economies with hyperinflation, cryptocurrencies can provide a stable store of value.
Challenges in Global Markets
Regulatory Uncertainty
One of the most significant challenges facing cryptocurrencies is the lack of consistent regulatory frameworks. Governments worldwide are grappling with how to classify, tax, and oversee these digital assets.
- United States: The SEC, CFTC, and IRS have differing views on cryptocurrencies, creating a fragmented regulatory landscape.
- China: The Chinese government has banned cryptocurrency trading and mining, citing financial stability concerns.
- European Union: The EU is working on the Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation to establish a unified approach.
Volatility
Cryptocurrencies are notorious for price volatility. Sudden market swings can result in significant financial losses, deterring risk-averse investors and businesses.
Environmental Impact
The energy-intensive process of cryptocurrency mining, particularly for proof-of-work (PoW) systems like Bitcoin, has raised concerns about environmental sustainability. Renewable energy adoption and alternative consensus mechanisms like proof-of-stake (PoS) are mitigating this issue.
Security Risks
While blockchain technology is inherently secure, cryptocurrencies are not immune to hacking, fraud, and scams. High-profile exchange hacks and Ponzi schemes have tarnished the industry’s reputation.
Cryptocurrencies in Specific Markets
Payments and Remittances
Cryptocurrencies are revolutionizing payments by reducing transaction times and fees. Platforms like Ripple and Stellar focus on cross-border remittances, enabling near-instantaneous money transfers.
Investment and Speculation
Cryptocurrencies have become popular investment vehicles, with retail and institutional investors seeking high returns. The rise of cryptocurrency derivatives and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) has further legitimized the asset class.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi platforms offer decentralized lending, borrowing, and trading services without intermediaries. Smart contract platforms like Ethereum power the DeFi ecosystem, unlocking new possibilities in finance.
Tokenization of Assets
Blockchain technology allows for the tokenization of real-world assets such as real estate, art, and commodities. Tokenization increases liquidity and accessibility by enabling fractional ownership.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Governments are exploring CBDCs to modernize monetary systems. While CBDCs are distinct from cryptocurrencies, they draw inspiration from blockchain technology and share some characteristics.
Global Impact
Emerging Markets
Cryptocurrencies have significant potential in emerging markets, where traditional financial systems are often underdeveloped. In countries like Venezuela and Zimbabwe, citizens turn to cryptocurrencies as a lifeline against hyperinflation and economic instability.
Remittance Economies
Countries heavily reliant on remittances, such as the Philippines and El Salvador, benefit from the lower costs and faster transaction times offered by cryptocurrencies. El Salvador’s adoption of Bitcoin as legal tender highlights this trend.
Financial Innovation
Cryptocurrencies are driving innovation across industries, from supply chain management to digital identity verification. Blockchain’s transparency and security are being leveraged to solve real-world problems beyond finance.
Future Prospects
Technological Advancements
Improvements in blockchain scalability, interoperability, and energy efficiency will shape the future of cryptocurrencies. Layer-2 solutions like the Lightning Network and advancements in PoS blockchains are key developments.
Regulatory Evolution
As governments establish clearer regulatory frameworks, investor confidence in cryptocurrencies is likely to increase. Collaboration between regulators and industry stakeholders is essential for balanced oversight.
Integration with Traditional Finance
The integration of cryptocurrencies with traditional financial systems will continue to grow. Banks and payment processors are increasingly incorporating blockchain-based solutions to enhance efficiency and security.
Adoption by Businesses
More businesses are expected to accept cryptocurrencies as payment, driven by customer demand and the potential for cost savings. Integration with e-commerce platforms and point-of-sale systems will facilitate widespread adoption.
Social and Cultural Impacts
Cryptocurrencies have the potential to democratize finance, empowering individuals with greater control over their assets. However, addressing inequality and ensuring equitable access will remain challenges.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrencies have already left an indelible mark on global markets, offering innovative solutions to long-standing challenges in finance and beyond. While their transformative potential is undeniable, the journey is fraught with hurdles, including regulatory ambiguity, volatility, and environmental concerns. As technology evolves and regulatory frameworks mature, cryptocurrencies are poised to play an even more significant role in reshaping the global economic landscape. Balancing innovation with responsible governance will be crucial to unlocking the full potential of this revolutionary technology.