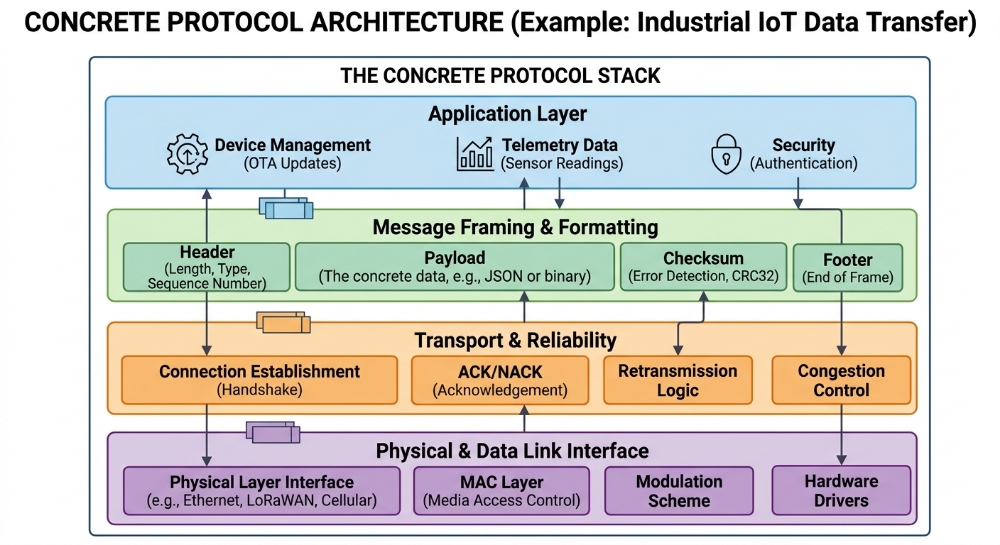
What is Ethereum?
12
Ethereum is a groundbreaking blockchain platform that was introduced in 2015 by a developer named Vitalik Buterin. While it is true that Ethereum has its native cryptocurrency called Ether (ETH), it is important to note that Ethereum is much more than just a cryptocurrency network. Here is a more comprehensive explanation of Ethereum:
- Smart Contracts: One of the most distinctive features of Ethereum is its ability to support smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with predefined rules and conditions. These contracts automatically execute when the specified conditions are met, without the need for intermediaries like banks or lawyers. This feature has opened up a wide range of possibilities for decentralized applications (DApps) across various industries, from finance and gaming to supply chain management and healthcare.
- Decentralized Applications (DApps): Ethereum serves as the foundation for a burgeoning ecosystem of decentralized applications. These DApps run on the Ethereum blockchain, leveraging smart contracts to provide transparency, security, and trust. Some popular DApps include Uniswap (a decentralized exchange), Compound (a lending and borrowing platform), and CryptoKitties (a blockchain-based game).
- ERC-20 Tokens: Ethereum's standard protocol for creating tokens, known as ERC-20, has become the industry standard for creating and launching new cryptocurrencies. This has led to the creation of thousands of tokens, many of which are used for various purposes such as crowdfunding, governance, and even as representations of assets like real estate or commodities.
- Network Upgrades: Ethereum has undergone several network upgrades or hard forks to improve its functionality and scalability. Notable upgrades include Ethereum Homestead, Ethereum Metropolis, and Ethereum Serenity (the ongoing upgrade to transition from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake).
- Scalability Challenges: Ethereum has faced challenges with scalability due to its initial Proof of Work consensus mechanism. As mentioned, the network can become congested during periods of high demand, resulting in high transaction fees (gas fees) and slower processing times. To address these issues, Ethereum is transitioning to a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism with the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. PoS is expected to increase transaction throughput and reduce energy consumption.
- Ethereum's Role in Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Ethereum has played a pivotal role in the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi). DeFi encompasses a wide range of financial services and applications built on blockchain technology. These include lending, borrowing, trading, and yield farming, among others. Ethereum-based projects like MakerDAO, Aave, and Compound have been instrumental in the growth of DeFi.
- Layer 2 Solutions: To alleviate network congestion and reduce transaction costs, various Layer 2 scaling solutions have been developed on top of Ethereum. These solutions, such as Optimistic Rollups and zk-Rollups, aim to increase the throughput of the network by processing transactions off-chain or in a more efficient manner while still relying on the security of the Ethereum mainnet.
In summary, Ethereum is not just a cryptocurrency but a robust and versatile blockchain platform that has revolutionized the way applications are built and executed. Its ecosystem continues to evolve, and its transition to Proof of Stake is anticipated to address scalability and environmental concerns while maintaining its position as a leading platform for decentralized innovation.