Navigating Mental Health
Understanding Mental Health:
Exploring the Basics
Mental health refers to our emotional, psychological, and social well-being, influencing how we think, feel, and act. It encompasses various factors, such as stress management, relationships, and coping with life's challenges. A crucial aspect is striking a balance between emotional stability and resilience in the face of adversity. At its core, mental health involves the interplay of biological, environmental, and genetic factors. Understanding the intricate connections between these elements is key to comprehending the complexities of mental well-being. For instance, neurotransmitters in the brain play a crucial role in regulating mood, while environmental stressors and life experiences can shape mental health outcomes. A spectrum exists, ranging from optimal mental health to diagnosed disorders. Mental well-being is not static; it can fluctuate based on life events, support systems, and individual coping mechanisms. Acknowledging that everyone experiences a range of emotions and stressors is fundamental to fostering a compassionate and informed perspective on mental health. In this exploration, it is essential to recognize the impact of societal factors, such as stigma and discrimination, on mental health. Challenging stereotypes and promoting open conversations can contribute to a more inclusive and understanding society. Ultimately, understanding mental health involves appreciating the diversity of human experiences and the various factors that contribute to the well-being of individuals. By fostering awareness and knowledge, we can collectively work towards a more empathetic and supportive approach to mental health.
Common Mental Health Disorders: Recognizing Signs and Symptoms
Mental health disorders are prevalent conditions that affect a significant portion of the global population. Recognizing the signs and symptoms is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment. Here are insights into some common mental health disorders:
1. **Depression:** - *Signs:* Persistent sadness, loss of interest, fatigue, changes in sleep or appetite. - *Symptoms:* Feelings of hopelessness, difficulty concentrating, thoughts of self-harm.
2. **Anxiety Disorders:** - *Signs:* Excessive worry, restlessness, irritability, muscle tension. - *Symptoms:* Panic attacks, phobias, obsessive-compulsive behaviors.
3. **Bipolar Disorder:** - *Signs:* Extreme mood swings, from manic (elevated) to depressive (low) episodes. - *Symptoms:* Impulsivity, racing thoughts, decreased need for sleep during manic phases.
4. **Schizophrenia:** - *Signs:* Delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thinking. - *Symptoms:* Social withdrawal, impaired cognitive function, difficulty expressing emotions.
5. **Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD):** - *Signs:* Flashbacks, nightmares, heightened startle response.
*Symptoms:* Avoidance of triggers, emotional numbness, hypervigilance. 6. **Eating Disorders:** - *Signs:* Drastic changes in eating habits, distorted body image. - *Symptoms:* Anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, binge eating disorder. Recognizing these signs and symptoms is vital, but it's equally important to understand that mental health disorders are complex and multifaceted. Diagnosis should be made by qualified professionals. Seeking help, whether through therapy, medication, or a combination of both, can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals dealing with mental health challenges. Creating a supportive environment and reducing stigma are essential steps toward fostering understanding and empathy for those facing these disorders.
Effective Coping Strategies: Building Resilience and Well-being
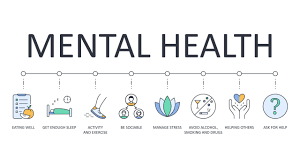
Coping strategies are vital tools for managing stress, adversity, and maintaining mental well-being. Building resilience, the ability to bounce back from challenges, is a key component of effective coping. Here's an exploration of strategies that contribute to resilience and overall mental health: 1. **Mindfulness and Meditation:** - *Practice:* Engaging in mindfulness activities, such as meditation, promotes self-awareness and reduces stress. - *Benefits:* Improved focus, emotional regulation, and a greater sense of calm. 2. **Social Support:** - *Connection:* Building and maintaining strong social connections provide a crucial support system during difficult times. - *Benefits:* Emotional support, encouragement, and a sense of belonging. 3. **Physical Exercise:** - *Activity:* Regular physical activity releases endorphins, promoting a positive mood. - *Benefits:* Stress reduction, improved sleep, and enhanced overall well-being. 4. **Cognitive Behavioral Techniques:** - *Approach:* Identifying and challenging negative thought patterns helps reshape perceptions and responses to stress. - *Benefits:* Improved problem-solving, coping skills, and a more positive mindset. 5. **Healthy Lifestyle Choices:** - *Factors:* Adequate sleep, balanced nutrition, and limiting substance use contribute to mental and physical well-being. - *Benefits:* Increased energy levels, improved mood, and better overall health. 6. **Seeking Professional Help:** - *Resources:* Consulting mental health professionals, such as therapists or counselors, offers valuable support. - *Benefits:* Access to specialized guidance, coping strategies, and tailored interventions. 7. **Engaging in Hobbies:** - *Activities:* Pursuing enjoyable hobbies provides an outlet for creativity and relaxation. - *Benefits:* Stress relief, a sense of accomplishment, and increased positive emotions. 8. **Time Management:** - *Skills:* Organizing and prioritizing tasks prevents feeling overwhelmed. - *Benefits:* Reduced stress, increased productivity, and a better work-life balance. It's important to note that effective coping strategies vary for each individual. Experimenting with different approaches and combining multiple strategies can be beneficial. Additionally, fostering resilience is an ongoing process that involves adapting and learning from experiences. Encouraging a proactive and open approach to mental well-being contributes to building a resilient and flourishing life.
The Role of Therapy:
Navigating Different Approaches
Therapy, also known as counseling or psychotherapy, plays a crucial role in addressing mental health concerns and promoting overall well-being. Navigating the various approaches to therapy involves understanding different therapeutic modalities and finding the most suitable fit for an individual's needs. Here's an overview of key aspects related to the role of therapy: 1. **Types of Therapy:** - *Psychodynamic Therapy:* Explores unconscious processes and unresolved conflicts, often focusing on the past. - *Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):* Targets negative thought patterns and behaviors to promote positive change. - *Humanistic Therapy:* Emphasizes self-exploration, personal growth, and the inherent goodness of individuals. - *Family Therapy:* Addresses dynamics within family systems to improve communication and relationships. - *Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT):* Combines cognitive-behavioral techniques with mindfulness for emotional regulation. 2. **Therapeutic Techniques:** - *Talk Therapy:* Involves open conversation between the therapist and client, providing a safe space for expression. - *Behavioral Interventions:* Focuses on modifying behaviors through reinforcement and other behavioral principles. - *Cognitive Restructuring:* Identifies and challenges negative thought patterns to promote positive thinking. - *Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques:* Integrates practices to enhance present-moment awareness and reduce stress. 3. **Role of the Therapist:** - *Supportive Guide:* Therapists serve as supportive guides, facilitating self-discovery and growth. - *Active Listener:* Attentive listening helps therapists understand clients' concerns and provide empathetic support. - *Collaborator:* Therapists collaborate with clients to set goals, develop coping strategies, and navigate challenges. 4. **Efficacy and Duration:** - *Effectiveness:* Research supports the efficacy of therapy in treating various mental health conditions. - *Duration:* The length of therapy varies based on individual needs, ranging from short-term to long-term engagements. 5. **Integration with Medication:** - *Collaboration:* Therapists often collaborate with psychiatrists when medication is part of the treatment plan. - *Complementary Approach:* Therapy and medication can complement each other, addressing different aspects of mental health. Seeking therapy is a proactive step toward understanding and addressing mental health challenges. The effectiveness of therapy depends on factors such as the therapeutic relationship, individual commitment, and the fit between the therapeutic approach and the client's needs. Overall, therapy serves as a valuable tool for self-exploration, personal growth, and navigating the complexities of mental well-being.
Breaking Stigmas: Promoting Mental Health Awareness and Support
Breaking stigmas surrounding mental health is crucial for fostering a society that values and supports the well-being of individuals facing mental health challenges. Promoting awareness and understanding contributes to reducing discrimination, encouraging open conversations, and creating an environment that supports those seeking help. Here's an in-depth exploration of the importance of breaking stigmas:
1. **Understanding Stigma:** - *Definition:* Stigma involves negative beliefs, attitudes, and stereotypes that lead to discrimination against individuals with mental health conditions. - *Impact:* Stigma can prevent people from seeking help, lead to social isolation, and perpetuate misconceptions about mental health.
2. **Educating the Public:** - *Awareness Campaigns:* Educational initiatives and campaigns help disseminate accurate information about mental health, challenging stereotypes and promoting understanding. - *Media Influence:* Responsible media portrayal of mental health issues contributes to reducing stigma by presenting realistic and empathetic narratives.
3. **Language Matters:** - *Person-First Language:* Encouraging the use of person-first language emphasizes the individual rather than their diagnosis, reducing the dehumanization associated with mental health conditions. - *Avoiding Stigmatizing Terms:* Promoting language that avoids stigmatizing terms contributes to creating a more inclusive and supportive discourse.
4. **Personal Stories and Testimonials:** - *Humanizing Experiences:* Sharing personal stories of overcoming mental health challenges humanizes the experience and demonstrates that recovery and resilience are possible. - *Role Models:* Individuals who openly discuss their mental health journeys become advocates, challenging stereotypes and inspiring others to seek help.
5. **Access to Resources and Support:** - *Community Resources:* Establishing accessible mental health resources and support services helps individuals navigate their mental health journey. - *Peer Support:* Peer-led initiatives and support groups provide individuals with shared experiences, fostering a sense of community and understanding.
6. **Integration in Education and Workplace:** - *Training Programs:* Incorporating mental health education into school curricula and workplace training programs helps reduce ignorance and promotes empathy. - *Workplace Policies:* Implementing mental health-friendly workplace policies encourages open dialogue and supports employees in seeking help.
men
7. **Legislation and Advocacy:** - *Anti-Discrimination Laws:* Enacting and enforcing laws that protect individuals with mental health conditions from discrimination is essential. - *Advocacy Initiatives:* Advocacy groups play a pivotal role in challenging discriminatory practices and influencing policy changes. Breaking stigmas requires collective efforts from individuals, communities, and institutions. By fostering a culture of empathy, understanding, and support, we can create a society where mental health is prioritized, and individuals are encouraged to seek help without fear of judgment or discrimination.