MUTATIONS AND MUTAGENESIS
Genetics is the science of heredity. Basic issues of genetics include: the phenomenon of inheritance, the molecular nature of genetic material, the ways in which genes control metabolism and development, the distribution and behavior of genes in populations. Main branches of genetics: CLASSICAL (transmission) genetics, MOLECULAR genetics studies the structure and function of genes at the molecular level, POPULATION genetics studies the behavior of genes in the population, CYTOGENETICS studies heredity at the level of chromosomes and other cell organelles, QUANTITATIVE genetics.
In every modern living cell in the world there is a central control system, a record on the basis of which the cell functions, on the basis of which it reproduces, and which controls its behavior. This control system consists of DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid
DNA contains information in the form of strings of bases: adenosine, thymine, guanine and cytosine, which are most often abbreviated as A, T, G and C. Strings of these four bases make up the genetic code, on the basis of which life functions. This code, when spelled out, usually looks like a long, meaningless string of letters: ATGCCTAAATCTG...
GENES are carriers of hereditary characteristics. They are part of the DNA molecule in the 3'-5' direction. It is hereditary material that is passed from generation to generation. They are located in the chromosomes in the so-called GEN-LOCIS. Each gene within the DNA contains information about a particular protein. Proteins are created on the basis of genes, and genes act only through the proteins made on the basis of them. In order to get from DNA to protein, a gene must go through the processes of transcription and translation. The last three letters, UAG, form the so-called stop codon, which gives a signal to the ribosome that it should stop further protein synthesis at that point.
Example of a chain: AUG GUG CCU AAU AUU AGC UAG
Met Val Pro Asn Ile Ser Stop
As you can see from the table above, some amino acids are encoded with only one code (say, UGG is the only code for tryptophan), but most have three, four, or more codes. Leucine, the most common amino acid, has as many as six different codes.
Mutation Mutation is a change in the hereditary information of an organism caused by a change in the sequence of heterocyclic bases or the number of chromosomes, which is not caused by segregation or recombination. A mutation causes a change in the hereditary information of DNA, and as a result, changes in individual characteristics can occur. Mutations are changes in the genetic code, which can occur in many ways. Every time a cell divides, say, the DNA must be copied in two copies, one copy for each new cell. Although this copying is very precise, it is still not perfect - for about every billion correctly copied bases, one is mistransmitted. Another source is damage to DNA, which can occur spontaneously through the normal life of the cell, or through external poisons or negative influences (ultraviolet radiation, for example). Through evolution, cells have developed very complex systems for repairing changes to DNA, but these systems not only have limitations, but sometimes also cause additional errors themselves.
Division by mutations of heredity
Somatic mutations are mutations that can affect all cells except gametes. Therefore, they have a reflection on the cells of the organism in which they occur. Such mutations are not hereditary. When somatic mutations occur singly, they cause little or no consequences. If they are enhanced by certain mutagens, such as energy radiation, they can become very dangerous. Thus, among other things, normal cells can be transformed into cancer cells. Somatic mutations play a major role in the aging of any organism.
Gametic mutations are mutations that are transmitted to offspring via gametes. They affect egg cells or spermatozoa and are transmitted through cell division to all other cells of the organism of the nascent organism. These mutations are very important for evolution because they are passed from generation to generation
Division by volatility
Gene mutations affect only individual genes, which is why they got their name. They are not visible under a microscope. They are usually divided into autosomal and heterosomal gene mutations, depending on which chromosome the mutated gene is located on.
Gene or point mutations are changes within a single gene. A change within one gene can lead to a change in the sequence of amino acids in a protein, and this can change the functioning of that protein and thus the structure and functioning of the entire organism. Division of gene mutations: SPONTANEOUS AND INDUCED. Spontaneous mutations occur due to errors in DNA replication (caused by biological processes). Induced mutations - caused by physical and chemical factors (they cause damage to the DNA molecule, and the repair of the damaged molecule can lead to mutations).
The causes of gene mutation are:
• Physical causes - various radiations.
• Chemical agents – various organic and inorganic compounds.
• Gene size – the larger the gene, the greater the chance for mutation.
• Genotype
• Temperature (in grape flies, the mutation rate at 27 °C is 2-3X higher than at 17 °C).
• Aging
• Mutagens
Samesense or identical mutation, when the substitution of bases in the DNA triplet does not change the arrangement of amino acids in the polypeptide.
Missense or wrong mutation - leads to the incorporation of another amino acid into the polypeptide chain.
Nonsense or senseless mutation when, for example, substitution changes the triplet for an amino acid into a code for the end of translation. Frameshift mutation - when addition or deletion causes a change (shift) within the reading of the gene code on the triplet.
Consequences of gene mutation:
a) good - evolutionary progress, variability in living beings, without alternative forms of genes created by mutation, geneticists would not be able to determine which characteristics of the organism are genetically controlled.
b) bad - benign mutations - differences in the color of eyes, hair, personality traits,
pathogenic effect - occurrence of disease or even death.
c) silent mutations are not manifested in the phenotype.
Chromosomal mutations affect chromosomes and are visible under a microscope. We distinguish numerical chromosomal mutations, if a numerical chromosomal mutation has occurred, and structural chromosomal mutations, which refer to the structure of chromosomes. If one part of the chromosome is missing, we are talking about deletion, and if one part is doubled, it is called duplication. If two parts of a chromosome exchange their places, it is done in a translocation
Chromosomal mutations are major changes in the genome – the basic haploid set of chromosomes found in gametes (sex cells). They include changes in the number or structure of chromosomes.
The human karyotype consists of 23 chromosomal pairs (22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes), and we can call it a chromosomal personal map because it shows us all 46 human chromosomes in which the entire human inheritance is "packaged". Those chromosome pairs are of different sizes and have different centromere positions.
Karyotype of a male person
Structural changes of chromosomes (chromosomal aberrations)
They arise due to errors during crossover or chromosome breakage. Chromosomes can break spontaneously or due to known (eg viral infection) or unknown causes. Chromosomal aberrations appear quite often; in about one in every 500 newborns.
Deletion is the loss of a chromosomal segment as a result of chromosome breakage. Various irregularities occur depending on the size and importance of the missing part of the chromosome. Deletions are usually lethal to animal and human gametes.
Duplications
They arise when a gene is doubled, that is, it appears more than twice in a diploid. They are the result of errors during crossover. They are less harmful than deletions because there is no loss of hereditary material.
Inversions
They are created when the same chromosome breaks in two places, that segment is rotated by 180° and attached again. With inversion, there is no duplication or loss of hereditary material, but due to the reverse arrangement of genes, homologous chromosomes cannot be paired along their entire length. Inversion may or may not have unintended consequences. It can cause disorders such as severe mental retardation, small head (microcephaly), congenital heart defects and other major developmental defects.
Translocations
They arise when two segments from two different chromosomes break off and then switch positions. It can appear spontaneously at the time of conception or it can be inherited and transmitted through generations.
Changes in the number of chromosomes
A change in the number of chromosomes can affect all chromosomes in the chromosome set - euploidy, or only individual chromosomes - aneuploidy. Some cells may have a shortage of chromosomes while another may have too many. Monoploids (haploids) – organisms that have one set of chromosomes Polyploids – organisms with three or more sets of chromosomes. Aneuploidy can be caused by improper segregation of chromosomes during meiosis of polyploids. It most often affects the 13th, 18th and 21st chromosomes.
The most well-known diseases caused by autosomal aneuploidy are: Down's syndrome, Edward's syndrome and Patau's syndrome.
Down's syndrome - Trisomy of the 21st chromosome, G21
It occurs in 1 in about 700 newborns (the most common autosomal disorder). 93% of Down's syndrome cases are due to non-disjunction in meiosis. People live an average of about 18 years, are mentally retarded and have certain physical characteristics: mongoloid-set eyes, short stature, wide and short skull, folds of skin at the back of the neck, stocky limbs.
Edward's syndrome - Trisomy of the 18th chromosome
It occurs in 1 out of about 5000 births. It mostly affects the female sex. People are mentally retarded, they look like dwarfs with small noses and mouths and abnormal ears. Mortality 80-90% by the second year of life.
Patau's syndrome - Trisomy of the 13th chromosome
It occurs in 1 out of about 5000 births. People are very mentally retarded, various diseases occur. Mortality is high in the first year of life.
Turner syndrome 44+XO
The only monosomy that survives in humans. The persons are female, short, do not have ovaries, so they are sexually immature and sterile, and have a slightly reduced IQ. The disorder is caused by an error in the father's meiosis.
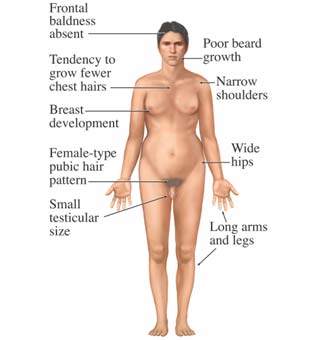
Klinefelter syndrome 44+XXY
The persons are male (due to the Y chromosome). After puberty, they develop secondary female sexual characteristics, are sterile, and have a lowered IQ.