Radio Hackers: Electromagnetic Eavesdropping & Harmonics
In earlier articles, we covered the concept of the Van EckPhreak, which discussed how electromagnetic radiation (EMR) could be used to exploit private information. One point that we missed in that article though, was how an entire research field would come from this.
Known as Electromagnetic Eavesdropping, this technique would use the stray emissions broadcast by electronic devices to help compromise secure data. While today’s article will cover the concept of the field rather than breaking down a specific attack type, there’s still plenty for the RF enthusiast to take away from today's article. Let's take a look!
EMR & Cybersecurity
While it could be a controversial topic in the earlier days, there’s no debating that in today's world, there is a distinct overlap between cyber / hardware security and the radio spectrum. With this involving everything from NFC cards to Bluetooth, Wi-Fi & IOT devices, the overlap has become even more pronounced, with many opportunities for research and analysis.
However, it’s not just protocols like that that are open to research. For some researchers, detecting and analysing stray emissions can often be a way to recover data or uncover lesser-known exploits
To best understand this subject though, we’ll have to discuss something we’ve looked at in the publication before. The concept of harmonic frequencies, as well as where / how we can find them.
WTF Is a Harmonic?!
If you’re an amateur radio operator or military communications technician, you probably won’t need a refresher on the topic. For those who aren’t part of that community though, the concept of harmonic frequencies is that for every transmission on a fundamental frequency, we’ll also see “harmonic” frequencies at set points across the radio spectrum. Let’s get specific and check out what that means, using a frequency in the VHF band. 121.5mhz is well known to those in maritime & aviation as it used to be the emergency frequency before the digital shift.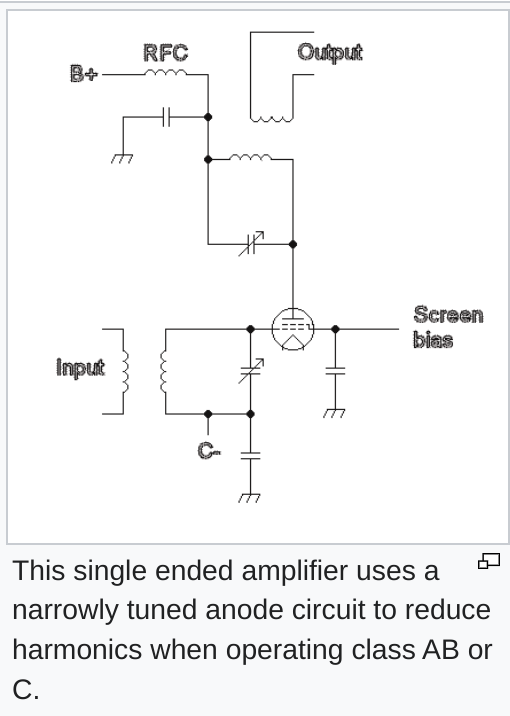 So if our fundamental frequency is 121.5mhz, we’ll see our second harmonic at 243 MHz (2 × 121.5 MHz) and our third harmonic should appear at 364.5 MHz (3 × 121.5 MHz). While it sounds pretty complex for those still learning about radio, we can work these out by using some simple math.
So if our fundamental frequency is 121.5mhz, we’ll see our second harmonic at 243 MHz (2 × 121.5 MHz) and our third harmonic should appear at 364.5 MHz (3 × 121.5 MHz). While it sounds pretty complex for those still learning about radio, we can work these out by using some simple math.
It’s worth mentioning that many electronic systems (radio transmitters in particular) apply strict filtering to harmonic frequencies. This is because badly filtered transmissions pose a very real interference threat to those operating on adjacent frequencies.
The flip side of this is that while properly built transmitting devices are usually well filtered, causing no issue with harmonic frequencies, many cheap transmitter and household consumer devices use little in the way of protection or shielding.
While that can typically cause some issues with fundamental frequencies (Baofeng radios anybody?) what it also means is that much of the natural emissions produced by things like the oscillators remain unshielded as well, and in many circumstances, it’s these stray emissions that are able to be exploited for espionage purposes.If you’d like to read more about spurious emissions from badly filtered transmitters, this Hackaday article does a great job of breaking it down.
What Kind Of Exploits?
Much of this earlier research came about as a result of the TEMPEST project, something we also touched on in the earlier article. This program was initially the domain of government actors however as technology progressed and became more prolific, more and more of this research started to enter the public domain. By the time the 90s rolled around, civilian researchers were also contributing both data and exploits to attack and protect various electronic devices.
If you aren’t familiar with some of these techniques you’d be forgiven for thinking you were reading from the set of a James Bond movie, as TEMPEST research covered light, audio, vibrations and pretty much everything in between. In its earliest stages, the research was complex and labour-intensive, with a significant entry barrier in terms of the technical skills required. While that hasn’t changed in the modern world, one thing that has changed is the technology that’s available to assist with this type of work. When paired with modern strategies like machine learning, there’s still plenty to be gained by using the radio spectrum for research purposes.
Due to the complexity of these types of cyberattacks though there’s little in the way of validated information about them occurring in the wild. Given the earliest research occurred in the 1980s, it’s reasonable to assume that while some of these attack vectors nights have been used, there’s little incentive for both victim and attacker to provide any form of validation.
Despite this, we still see much in the way of research into these fields at events like Defcon, that are implemented to encourage free thinking and collaborative working. This alone is pretty interesting to follow.
How Can I Learn?
While these might be state-based attacks that are out of the realm of the hobbyist-level researcher, the reality is that for those who are interested, it’s still a pretty viable field for independent research. Technology is responsible for changing much in the world of technology over the past 20 years, however, the importance of the radio spectrum in today's world is probably even more relevant than it was previously.
We can see this in the explosion of IOT devices over the past few years, many of which use some form of RF protocol to communicate. This could be purely for data transmission or it could entail some form of remote update or administrator access, similar to the Over-The-Air updates that we see in modern motor vehicles. It’s fair to say that while for many, the radio spectrum is out of sight and out of mind, it’s still an important domain to understand, particularly for military purposes.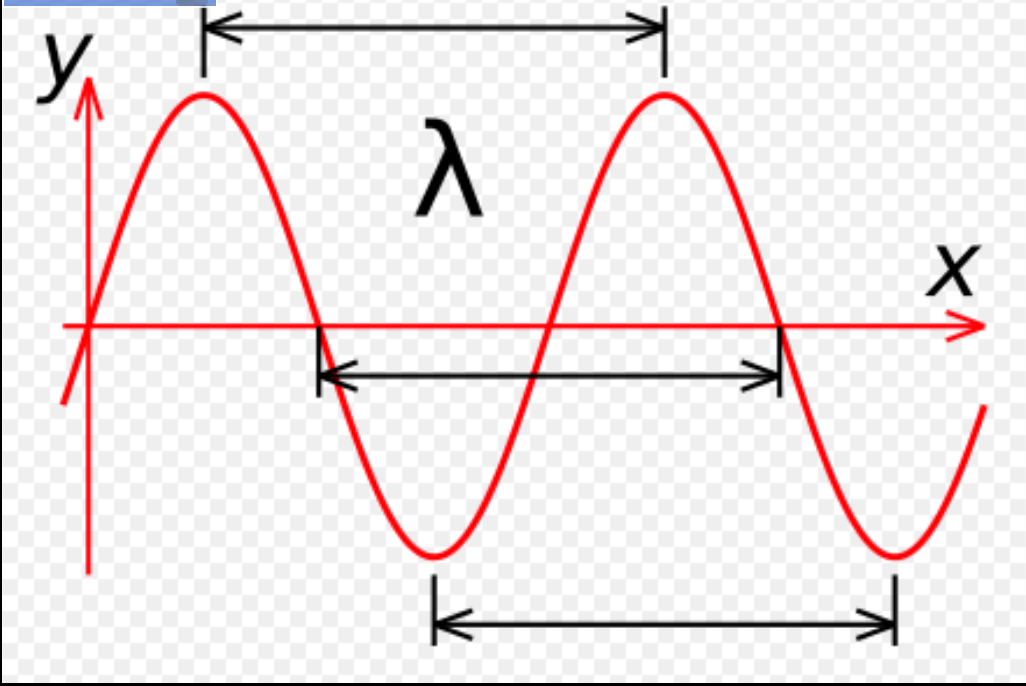 So for learning purposes, there are a few things beginners can look at to deepen their understanding of this topic. Firstly, understanding the relationship between frequencies and wavelength as well as identifying harmonic frequencies is a great place to start.
So for learning purposes, there are a few things beginners can look at to deepen their understanding of this topic. Firstly, understanding the relationship between frequencies and wavelength as well as identifying harmonic frequencies is a great place to start.
Next up understanding how different signal types propagate in different mediums is also a useful skill to understand. Grasping this will help you understand what is good for high-speed data or transmitting underwater to submarines or how to overcome propagation issues in built-up or marginal areas.
Lastly, understanding how to capture, identify and decode different signal types is also helpful. This means you’ll be better equipped to understand different transmissions that you might see on your SDR display as well as having a clear understanding of both harmonic and fundamental frequencies.
To operate within the radio spectrum ideally, we’ll need to understand it properly first.
If you found this article insightful, informative, or entertaining, we kindly encourage you to show your support. Clapping for this article not only lets the author know that their work is appreciated but also helps boost its visibility to others who might benefit from it.
🌟 Enjoyed this article? Join the community! 🌟
📢 Join our OSINT Telegram channel for exclusive updates or
📢 Follow our crypto Telegram for the latest giveaways
🐦 Follow us on Twitter and
🟦 We’re now on Bluesky!
🔗 Articles we think you’ll like:
- What The Tech?! Rocket Engines
- OSINT Investigators Guide to Self Care & Resilience
✉️ Want more content like this? Sign up for email updates