How energy consumption is increasing day by day and different sources contributing energy
Energy consumption is increasing day by day due to the growing demand for energy from various sectors, including residential, commercial, industrial, and transportation. Here's a breakdown of how different sectors contribute to energy consumption:
- Residential sector: This sector includes homes and apartments and accounts for a significant portion of energy consumption. In the residential sector, energy is used for heating, cooling, lighting, and appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, and televisions.
- Commercial sector: This sector includes offices, schools, hospitals, and retail stores, and energy is used for lighting, heating, cooling, and powering office equipment, computers, and other electronics.
- Industrial sector: This sector includes manufacturing, construction, and mining operations, and energy is used to power machinery, equipment, and lighting.
- Transportation sector: This sector includes cars, trucks, buses, airplanes, and trains, and energy is used to power vehicles and provide fuel for transportation.
Overall, the largest contributor to energy consumption is the transportation sector, followed by the industrial sector, residential sector, and commercial sector.
The different sources of energy that contribute to the increasing energy consumption:
1.Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, are the most widely used sources of energy worldwide. These fuels were formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals that lived millions of years ago, and they provide energy by releasing the carbon stored in them when they are burned.
Fossil fuels have been a critical component of the world's energy mix for many decades, providing affordable and reliable energy for transportation, electricity generation, and manufacturing. However, the use of fossil fuels is associated with several environmental and health impacts, including air pollution, water pollution, and climate change.
Air pollution is one of the most significant environmental impacts associated with the use of fossil fuels. Burning fossil fuels releases a range of pollutants into the atmosphere, including particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds. These pollutants can cause respiratory and cardiovascular health problems, particularly for vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and people with pre-existing health conditions.
Fossil fuels also contribute to climate change by releasing large amounts of greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide, into the atmosphere. These greenhouse gases trap heat in the earth's atmosphere, causing global temperatures to rise and leading to a range of environmental impacts, such as melting glaciers, rising sea levels, and more frequent and severe weather events.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in renewable energy sources as alternatives to fossil fuels. Renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, hydro, and geothermal, do not produce greenhouse gases or air pollutants and are abundant and sustainable. Renewable energy technologies are rapidly advancing and becoming more cost-effective, making it increasingly likely that they will play a significant role in meeting the world's future energy needs.
However, the transition to renewable energy sources is likely to be gradual, as fossil fuels remain the most widely used and affordable sources of energy worldwide. Governments, industry, and consumers are working together to develop and adopt strategies for reducing the environmental impacts of fossil fuels, such as investing in carbon capture and storage technologies, improving energy efficiency, and promoting the use of cleaner forms of transportation.
Overall, while fossil fuels have played a critical role in powering economic growth and development, their continued use poses significant environmental and health challenges. As the world continues to seek ways to address these challenges, renewable energy sources are likely to play an increasingly important role in the global energy mix.
2.Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy is generated through nuclear reactions, which release energy from the nucleus of an atom. Nuclear power plants use this energy to generate electricity, which accounts for a significant portion of the world's energy consumption.
Nuclear energy is a clean source of energy that does not produce greenhouse gases, which contribute to climate change. The nuclear reaction that produces energy in nuclear power plants involves the splitting of atomic nuclei, a process known as nuclear fission. This process releases a significant amount of energy, which is used to generate steam to power turbines, which in turn generate electricity.
Despite its clean energy benefits, the use of nuclear energy remains controversial due to concerns about the safety and disposal of nuclear waste. The radioactive waste generated by nuclear power plants can remain hazardous for thousands of years, making its storage and disposal a significant challenge.
Nuclear energy also poses a risk of accidents, such as the Chernobyl and Fukushima disasters, which have had significant environmental and health impacts. These incidents have led to increased scrutiny of nuclear energy and calls for improved safety measures.
Despite these challenges, nuclear energy remains an important source of clean energy for many countries. Nuclear power plants provide reliable and affordable electricity, and many countries are investing in research and development to improve the safety and efficiency of nuclear energy.
New nuclear technologies, such as small modular reactors and advanced nuclear fuels, are being developed to address some of the concerns associated with traditional nuclear power plants. These technologies promise to be safer and more efficient than traditional nuclear power plants, while also reducing the amount of nuclear waste generated.
Overall, nuclear energy remains a controversial but important source of clean energy. As the world seeks to address the urgent challenge of climate change, the role of nuclear energy in the global energy mix is likely to be an ongoing topic of debate and discussion.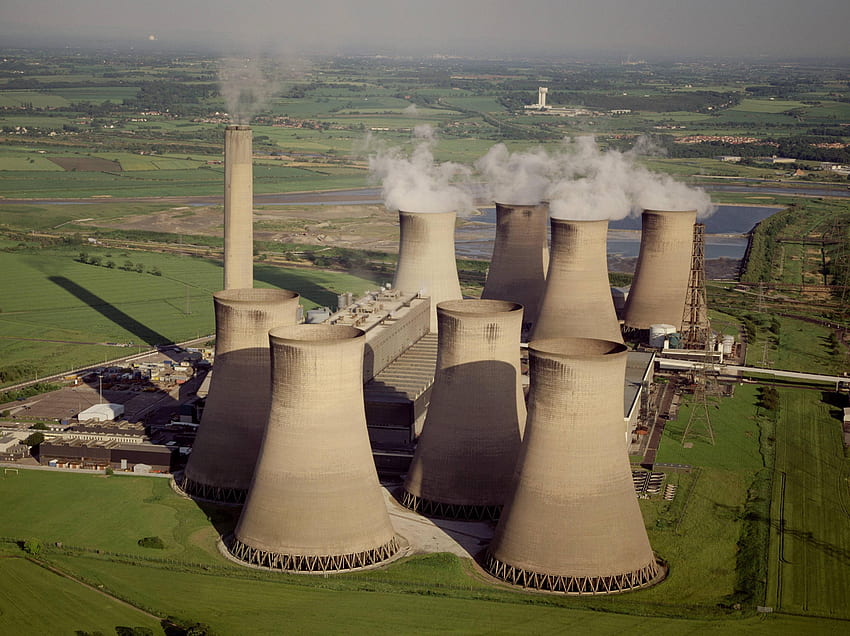
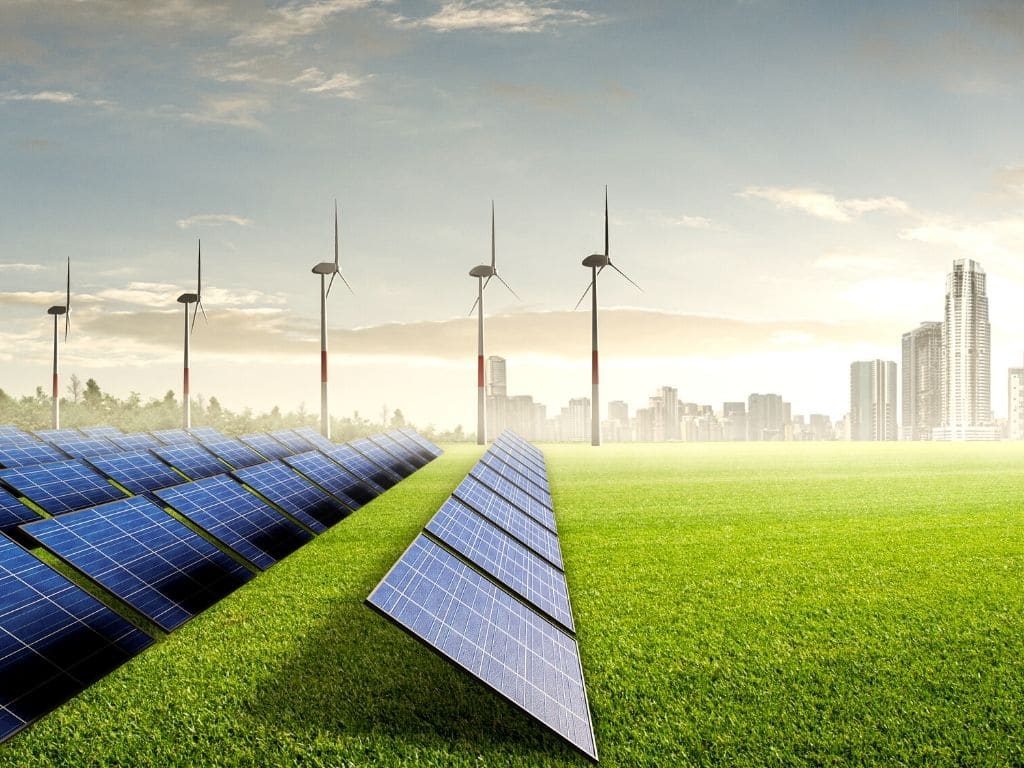
3.Renewable Energy
Renewable energy is energy that is derived from natural resources that are replenished over time, such as sunlight, wind, water, and geothermal heat. Renewable energy sources are an important part of the world's energy mix, as they provide a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
Solar energy is one of the most widely used renewable energy sources, and it is generated by converting the energy from the sun into electricity using solar panels. Wind energy is also a significant source of renewable energy, generated by harnessing the power of wind turbines to generate electricity.
Hydroelectric power is generated by using the power of moving water to turn turbines and generate electricity. Geothermal energy is generated by tapping into the heat that is naturally produced by the earth's core, and using it to generate electricity.
Renewable energy sources have several advantages over fossil fuels, including lower greenhouse gas emissions, reduced air pollution, and improved energy security. The use of renewable energy can also help to reduce the impact of climate change, which is caused by the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Renewable energy technologies are rapidly advancing, and many countries are investing heavily in research and development to improve the efficiency and affordability of these technologies. In recent years, the cost of renewable energy has decreased significantly, making it increasingly competitive with fossil fuels.
However, the transition to renewable energy sources is not without its challenges. The intermittency of some renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, can make it difficult to ensure a consistent supply of electricity. The deployment of renewable energy technologies can also face opposition from local communities and environmental groups.
Overall, renewable energy sources are an important part of the world's energy mix and will play a critical role in the transition to a more sustainable energy future. As renewable energy technologies continue to advance, it is likely that they will become increasingly cost-effective and widely adopted, helping to reduce the environmental and economic impacts of fossil fuels.