Why Bitcoin Lightning Network is Crucial for Global Payments
The global financial system is undergoing a transformation, and Bitcoin sits at the heart of this change. While Bitcoin's value and utility have revolutionized digital payments, one critical challenge has been its scalability. As more users embrace cryptocurrency, transaction speed and costs have become significant barriers. 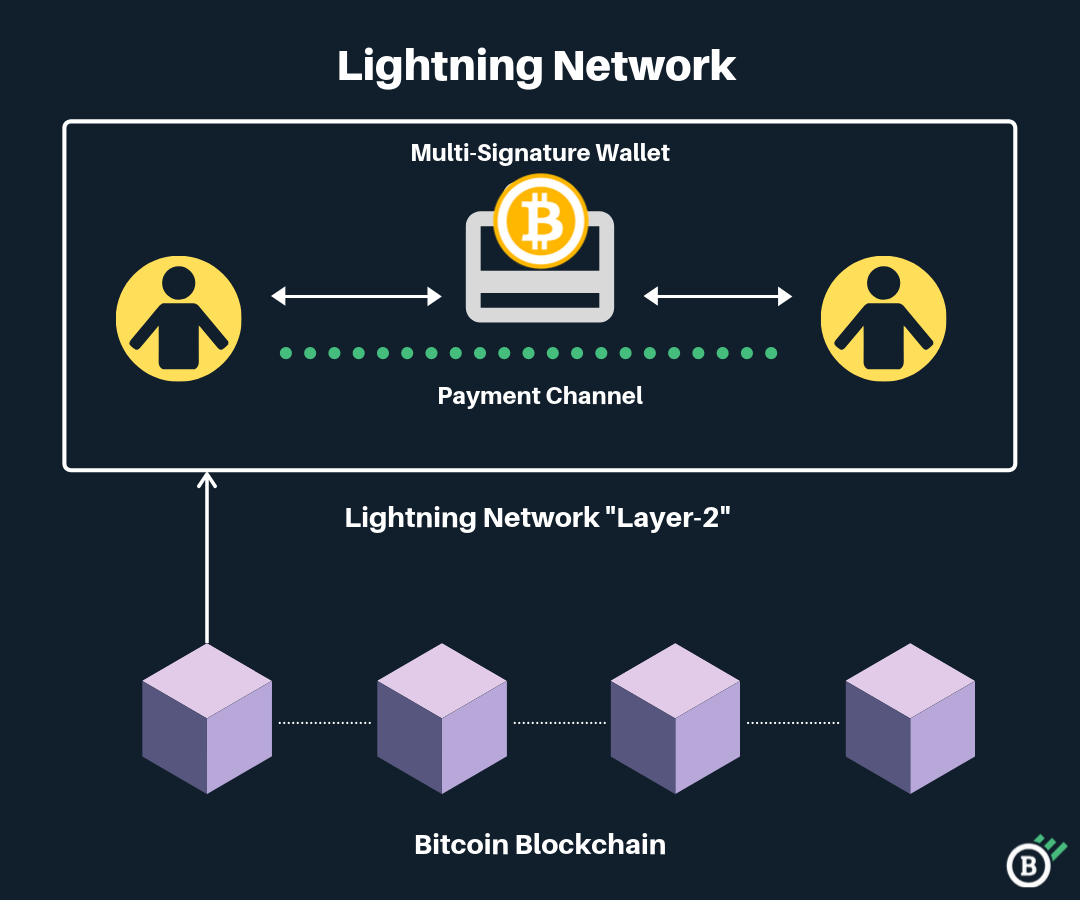 This is where the Bitcoin Lightning Network enters the picture. It promises to enhance Bitcoin’s capacity for handling global payments efficiently.
This is where the Bitcoin Lightning Network enters the picture. It promises to enhance Bitcoin’s capacity for handling global payments efficiently.
This article will explore the necessity of the Lightning Network, its role in reducing costs and increasing transaction speed, and its potential to reshape the landscape of global payments.
The Scalability Problem of Bitcoin
Bitcoin, despite its disruptive potential, faces a significant scalability problem. The underlying technology of Bitcoin—its blockchain—is designed to ensure security and transparency.
However, this design comes with trade-offs. Each block on the Bitcoin network has a limited size (1MB), and transactions must be validated by miners before they are added to the block. As Bitcoin’s popularity grows, this leads to a backlog of transactions, higher fees, and slower processing times.
Limited Transactions per Second
Bitcoin’s blockchain can only process about seven transactions per second (TPS), which pales in comparison to traditional payment networks like Visa, capable of handling thousands of TPS.
High Fees
During times of high demand, transaction fees spike, making Bitcoin transactions less viable for smaller or frequent payments.
Slow Processing Time
Confirmations on the Bitcoin blockchain can take up to 10 minutes or longer, which is impractical for everyday purchases or time-sensitive transactions.
These scalability issues have posed a significant challenge to Bitcoin’s adoption as a global payment system. The need for an efficient layer that can process more transactions at lower costs is clear.
Introduction to the Bitcoin Lightning Network
The Bitcoin Lightning Network was introduced as a second-layer solution designed to address the scalability problem of Bitcoin. It allows users to create payment channels between two parties off-chain, enabling fast and nearly cost-free transactions. Here’s how it works:
Payment Channels
The Lightning Network uses a system of payment channels that exist between users. Once a channel is open, the participants can send Bitcoin back and forth instantly, without the need to wait for confirmations on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Instant Transactions
Transactions within the Lightning Network are processed almost instantaneously, as they do not require the same rigorous validation process as on-chain transactions.
Low Fees
Because transactions happen off-chain, the fees associated with mining and validating transactions are drastically reduced. This makes microtransactions—small, frequent payments—possible without the burden of high fees.
The Lightning Network enables Bitcoin to scale, allowing it to handle millions of transactions per second, thereby paving the way for Bitcoin’s adoption in global payment systems. But why is this particularly important for global payments?
Why Lightning Network is Key to Global Payments
In a global economy that values speed, cost-efficiency, and security, the Bitcoin Lightning Network offers several key advantages that make it crucial for international payments:
Faster Cross-Border Transactions: Traditional banking systems can take days to process international transfers. Even blockchain transactions, as mentioned, can take up to 10 minutes to confirm. With the Lightning Network, cross-border transactions happen instantly, solving one of the largest pain points in global finance.
Reduction in Fees: International payment systems typically charge significant fees for cross-border transactions. These fees accumulate over time, especially for small or frequent payments. The Lightning Network drastically reduces transaction costs, making it an ideal solution for remittances and business transactions.
Access for Unbanked Populations: One of the most promising aspects of Bitcoin and the Lightning Network is their potential to offer financial services to the unbanked. In regions where banking infrastructure is lacking, Bitcoin can serve as an accessible form of money, and the Lightning Network ensures it can be used efficiently for daily transactions.
Additionally, the Lightning Network allows for “atomic swaps,” which enable users to exchange one cryptocurrency for another without using a centralized exchange. This creates the foundation for a decentralized and borderless financial system, free from the limitations of traditional banking.
Overcoming Challenges and the Future of Bitcoin Lightning Network
While the Bitcoin Lightning Network holds immense promise, it is not without its challenges. Critics point out several potential weaknesses that must be addressed before it can be widely adopted for global payments.
Liquidity Issues: Payment channels on the Lightning Network require liquidity to function properly. If a user doesn’t have enough Bitcoin in their channel, they won’t be able to complete transactions until they add more funds. This can create friction for users making frequent payments.
Routing Problems: To send payments across the network, users rely on a series of interconnected payment channels. If there are no suitable paths between two users, payments can fail. This could create challenges for global, decentralized transactions.
User Experience and Adoption: The Lightning Network requires some technical understanding, which may deter the average user. However, ongoing development aims to simplify the user experience, making it more accessible to a broader audience.
Despite these challenges, the Lightning Network continues to evolve. Major improvements are underway to address liquidity issues, enhance routing capabilities, and make the network more user-friendly. As more developers and businesses adopt Lightning, its potential to revolutionize global payments becomes more evident.
Future Implications
Business Adoption: As more merchants and businesses integrate Lightning, Bitcoin will become more feasible as a global payment method. Businesses, both online and offline, will benefit from lower fees, faster transactions, and a global customer base.
Financial Inclusion: The Lightning Network holds significant promise for promoting financial inclusion. As mobile devices become more accessible, people in developing countries can leverage Bitcoin through Lightning to participate in the global economy.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): The integration of Bitcoin’s Lightning Network into the broader DeFi space could unlock new possibilities for decentralized lending, borrowing, and trading.
Conclusion
The Bitcoin Lightning Network is a critical innovation in the cryptocurrency space, offering solutions to Bitcoin’s scalability issues and unlocking its full potential for global payments. With its ability to process millions of transactions quickly and at low costs, the Lightning Network is positioned to become a key player in the global financial ecosystem. Its implications extend beyond just faster payments—it represents a new era of financial inclusion, reduced transaction fees, and a decentralized economy that transcends borders.
As the Lightning Network continues to grow and evolve, its role in reshaping global payments becomes increasingly clear. By addressing the limitations of traditional banking and Bitcoin’s on-chain transactions, it stands as a crucial tool for the future of decentralized global finance.
References
- Antonopoulos, A. M. (2017). Mastering Bitcoin: Unlocking Digital Cryptocurrencies. O'Reilly Media.
- Poon, J., & Dryja, T. (2016). The Bitcoin Lightning Network: Scalable Off-Chain Instant Payments.
- Bitcoin Lightning Network Stats - 1ML
- Antonopoulos, A. M. (2021). Mastering the Lightning Network. O'Reilly Media.
- The Lightning Network on Github
- Decker, C., Wattenhofer, R. (2015). A Fast and Scalable Payment Network with Bitcoin Duplex Micropayment Channels.
- Lopp, J. (2019). Bitcoin’s Scaling Struggle: A Primer on the Lightning Network.
- Antonopoulos, A. M. (2016). The Internet of Money: Volume Two. Andreas M. Antonopoulos.
- Bitcoin Magazine – Lightning Network Category
- Bitcoin Lightning Wallet: A Beginner’s Guide