What is censorship resistance in blockchain technology?
What is censorship resistance in blockchain technology?
What is censorship resistance?
Censorship resistance is known as the ability of a system, usually a communications or information distribution network, to resist attempts to censor, modify, or stop the flow of information.
In the field of digital technology, encrypted communication tools, social networking platforms or cryptocurrency systems. These systems ensure the free flow of information even in the face of censorship attempts by spreading control among large numbers of participants and encrypting conversations.
Censorship-resistant systems are necessary to protect the right to freedom of expression, ensure access to information in repressive governments, and encourage creativity by guarding against arbitrary limits on expression and communication. In the digital age, it is a powerful weapon to advance democracy, human rights and the free flow of ideas.
What effects do traditional systems of censorship have?
In traditional systems, censorship weakens the foundations of established institutions by preventing free speech, maintaining inequalities in power, and distorting the course of history.
First, it restricts the right to free speech, which is essential for many traditional communities. Ideas stagnate when voices are silenced, hindering progress both intellectually and culturally. Censorship can prevent the transmission of knowledge and values from one generation to the next and undermine social cohesion in traditional systems where oral traditions and storytelling are essential.
Additionally, censorship often perpetuates power relations found in established hierarchies. By determining what information is acceptable, those in positions of power strengthen their grip on the narrative, leading to the silence of dissenting voices, stifling critical thought and maintaining long-standing inequalities.
In addition, censorship has the power to distort historical accounts by reshaping perceptions of the past and collective memory. Governments and other institutions can influence public opinion by restricting access to information, hiding inconvenient facts, and promoting a distorted version of events.
For example, the 2008 financial crisis occurred when risk experts' warnings about the dangers associated with subprime mortgage-backed securities were stolen or ignored at financial institutions. This lack of transparency about real risks partly led to the housing market bubble and subsequent crash.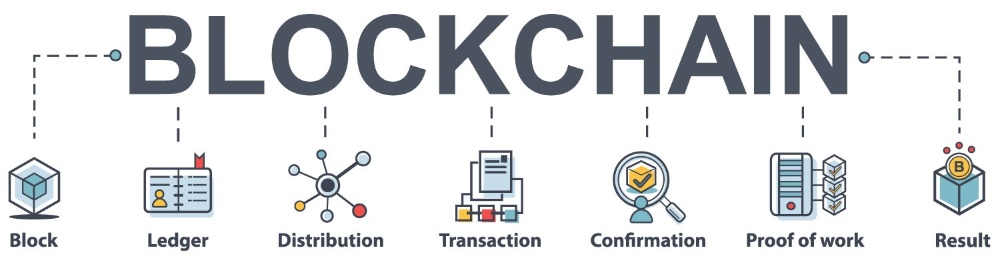
The various anti-censorship capabilities provided by blockchain technology are crucial to protecting freedom of speech and the transfer of information.
Although they have strong anti-censorship capabilities, it is crucial to remember that blockchains have limits. Governments or other influential organizations may attempt to impose restrictions on network access or even take tighter control over permissioned blockchains. However, the fundamental structure of blockchains makes them an effective tool for promoting free expression and transparent information sharing.
Anti-censorship features in blockchain include:
decentralization
Blockchains rely on a distributed network of computers or nodes, unlike traditional systems with centralized authorities. This means that no party has complete control over the network, making it difficult to remove or filter content.
immutable ledger
Data entered into the blockchain cannot be removed or modified later. The cryptographic hash of each link in the chain is the one before it, preventing manipulation and ensuring data integrity. Information censors find it very difficult to influence due to this immutability feature.
transparency
All data and transactions on public blockchains are accessible to all network users. Because of this transparency, attempts at censorship are discouraged because it makes data manipulation obvious.
encryption
Strong encryption techniques are often used by blockchains to protect communications and transactions. Due to this encryption, data confidentiality and integrity is ensured, making it difficult for censors to intercept or modify data without permission.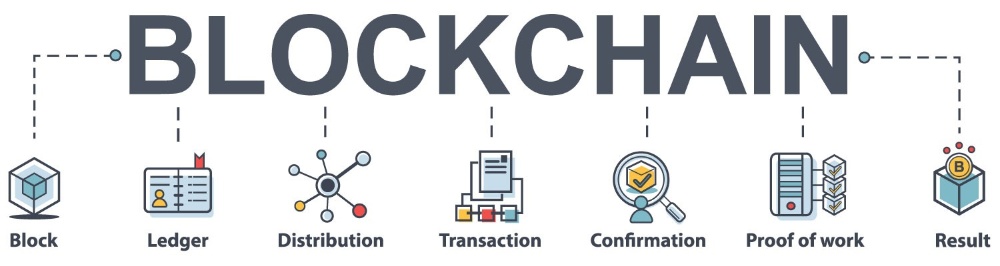
Bitcoin's decentralized consensus mechanism, pseudonymity, and decentralized governance allow it to withstand censorship attempts by any central authority and maintain the immutability of its transactions.
On the Bitcoin network, miners race to add transactions to the blockchain and verify them by solving difficult mathematical puzzles. Since the network cannot be controlled by a single party, censorship becomes a challenging endeavor. Any attempt to filter a transaction will have to exceed the total processing capacity of the network, which will become increasingly difficult as the network grows.
Additional censorship resistance is added by the fraudulent nature of Bitcoin. Since transactions are broadcast to the entire network and documented on a general ledger, anyone can participate without needing permission. Any central authority would find it difficult to selectively ban sender or content-based transactions due to this transparency.
Additionally, Bitcoin's resistance to censorship is due to its decentralized governance architecture, where decisions are made by consensus among network users. Changes to the protocol require broad consensus among participants, making it impervious to censorship efforts by any individual or organization.


![[ℕ𝕖𝕧𝕖𝕣] 𝕊𝕖𝕝𝕝 𝕐𝕠𝕦𝕣 𝔹𝕚𝕥𝕔𝕠𝕚𝕟 - And Now What.... Pray To The God Of Hopium?](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/79e7827b-c644-4853-b048-a9601a8a8da7/1)





















![[LIVE] Engage2Earn: auspol follower rush](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/c1a761de-5ce9-4e9b-b5b3-dc009e60bfa8/1)










