Mastering Financial Balance: Understanding the 50/30/20 Budget Rule with Example
Mastering Financial Balance
Understanding the
50/30/20 Budget Rule
with Practical Example
 Managing personal finances effectively is essential for achieving financial stability and building wealth. While budgeting may seem daunting, adopting a simple and flexible approach can make it more manageable. One such approach is the 50/30/20 budget rule, which provides a clear framework for allocating income to different expense categories. In this article, we'll delve into the 50/30/20 budget rule, explaining its principles and providing practical examples to help you apply it to your financial planning.
Managing personal finances effectively is essential for achieving financial stability and building wealth. While budgeting may seem daunting, adopting a simple and flexible approach can make it more manageable. One such approach is the 50/30/20 budget rule, which provides a clear framework for allocating income to different expense categories. In this article, we'll delve into the 50/30/20 budget rule, explaining its principles and providing practical examples to help you apply it to your financial planning.
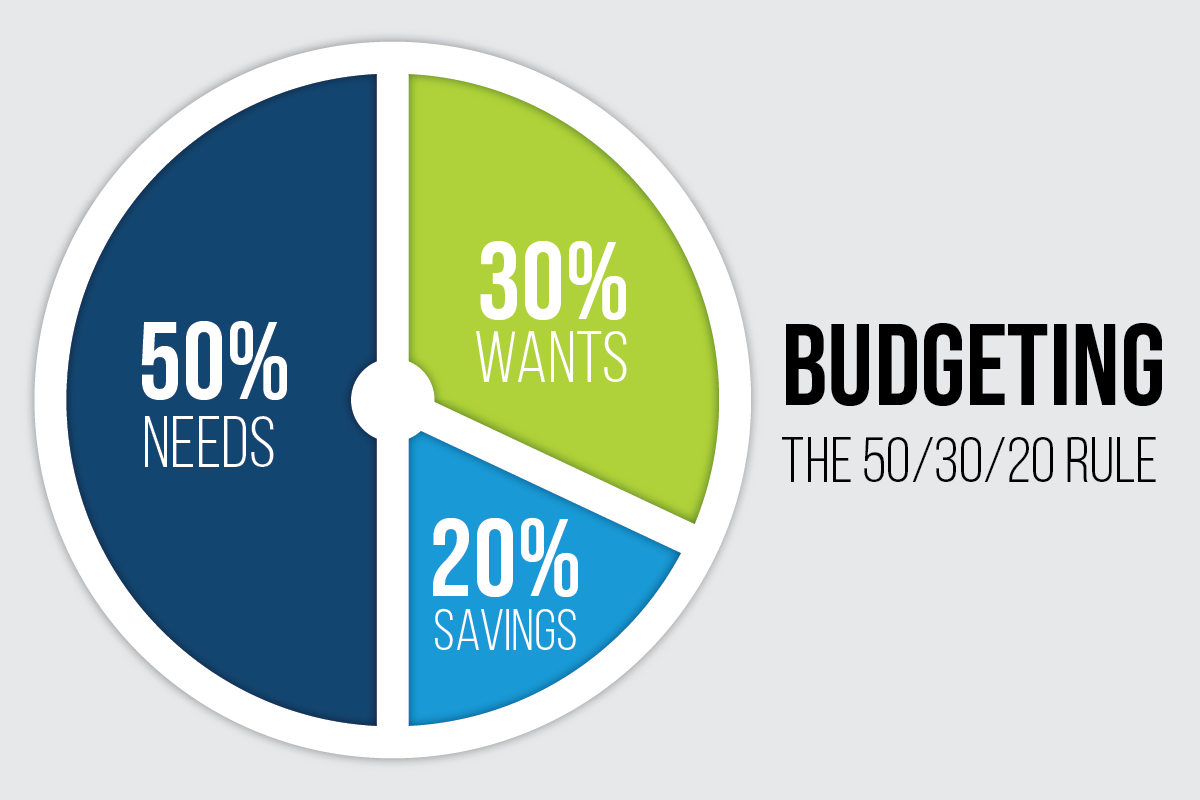
Understanding the 50/30/20 Budget Rule
The 50/30/20 budget rule is a simple guideline for allocating your income across three main expense categories: needs, wants, and savings. According to this rule:
- 50% of your income should be allocated to essential needs, such as housing, utilities, groceries, transportation, and healthcare.
- 30% of your income can be allocated to discretionary wants, such as dining out, entertainment, travel, shopping, and hobbies.
- 20% of your income should be allocated to savings and financial goals, such as emergency funds, retirement savings, debt repayment, and investments.
By following this budgeting rule, you can achieve a balance between meeting your immediate financial obligations, enjoying discretionary spending, and building a secure financial future.
Practical Example

To illustrate how the 50/30/20 budget rule works in practice, let's consider a hypothetical scenario:
- Monthly Income: $4,000
- Needs (50%): $2,000
- Rent/Mortgage: $1,000
- Utilities: $200
- Groceries: $300
- Transportation: $200
- Healthcare: $300
- Wants (30%): $1,200
- Dining Out: $200
- Entertainment: $100
- Travel: $300
- Shopping: $300
- Hobbies: $200
- Savings (20%): $800
- Emergency Fund: $200
- Retirement Savings: $300
- Debt Repayment: $200
- Investments: $100
In this example, the individual earns a monthly income of $4,000. They allocate 50% of their income ($2,000) to essential needs, such as housing, utilities, groceries, transportation, and healthcare. They allocate 30% of their income ($1,200) to discretionary wants, such as dining out, entertainment, travel, shopping, and hobbies. Finally, they allocate 20% of their income ($800) to savings and financial goals, such as emergency funds, retirement savings, debt repayment, and investments.
By adhering to the 50/30/20 budget rule, the individual ensures that their financial priorities are aligned, allowing them to cover essential expenses, enjoy discretionary spending, and work towards long-term financial security. The 50/30/20 budget rule offers a straightforward and flexible framework for managing personal finances effectively. By allocating 50% of your income to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings and financial goals, you can achieve a balance between meeting immediate financial obligations, enjoying discretionary spending, and building a secure financial future. Whether you're just starting your financial journey or looking to refine your budgeting strategy, the 50/30/20 budget rule provides a practical and accessible approach to achieving financial balance and stability.
The 50/30/20 budget rule offers a straightforward and flexible framework for managing personal finances effectively. By allocating 50% of your income to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings and financial goals, you can achieve a balance between meeting immediate financial obligations, enjoying discretionary spending, and building a secure financial future. Whether you're just starting your financial journey or looking to refine your budgeting strategy, the 50/30/20 budget rule provides a practical and accessible approach to achieving financial balance and stability.
Thank you for reading!
Find useful articles to read: HERE