What Is Blockchain and How Does It Work?
What Is Blockchain?
Imagine a giant, trustless, digital ledger accessible to everyone, but impossible to tamper with. That's essentially what a blockchain is. It's a fancy way of saying "public, secure record-keeping" with some unique and powerful features. Let's break it down: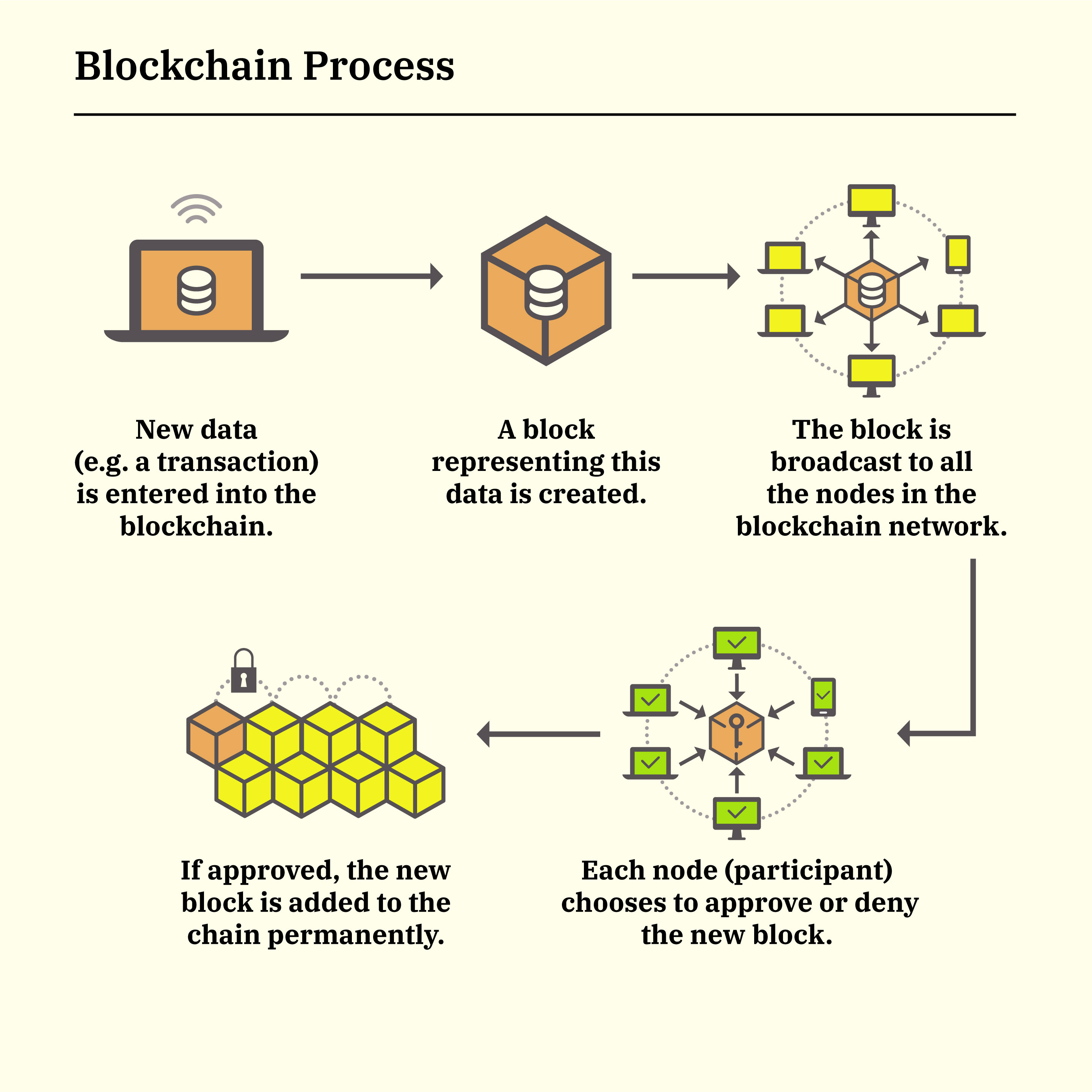
Key concept: Blocks and Chains:
- Data (transactions, records, anything digital) is grouped into "blocks."
- Blocks are linked together in a chronological chain, each block containing the unique fingerprint (hash) of the previous one.
Key features:
- Transparency: Everyone on the network can see all transactions.
- Immutability: Once data is in a block, it's practically impossible to change.
- Security: Cryptographic hashing and distributed nature make it hack-resistant.
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the network, preventing manipulation.
How it works:
- Data in, Block made: Transactions or records are bundled into blocks.
- Unique fingerprint: Each block gets a special code called a "hash."
- Linked in a chain: The hash of the previous block is included in the current one, creating a chain. Altering a block messes up its hash and the whole chain.
- Network of verifiers: Computers called "nodes" hold copies of the chain and verify each block's integrity.
- Adding new blocks: New transactions are broadcasted, nodes validate them, and if approved, a new block is added to the chain, following the same verification process.
Beyond Bitcoin:
While best known for Bitcoin, blockchain has potential applications in many areas like:
- Supply chain management: Tracking goods to ensure authenticity and transparency.
- Healthcare: Securing medical records and protecting patient privacy.
- Voting systems: Creating tamper-proof voting systems.
- Identity management: Giving individuals control over their digital identities.
Blockchain is still young, but it holds the potential to transform how we store, share, and trust information.
What Is Decentralization in Blockchain?
In the world of blockchains, decentralization reigns supreme. It's the magic ingredient that makes this technology tick, removing the need for a central authority and placing the power in the hands of the network itself. Imagine a system where trust isn't handed over to a single entity, but distributed among everyone participating. That's decentralization in a nutshell.
Here's how it works:
Centralized vs. Decentralized:
Think of traditional systems like banks or governments. They operate centrally, with a single authority controlling the data and decision-making. This can lead to:
- Single point of failure: If the central authority is compromised, the entire system is vulnerable.
- Limited transparency: You have to trust the central authority to be honest and act in your best interests.
- Potential for manipulation: The central authority could potentially alter data or control access.
Now, enter decentralization. Instead of a single authority, the power is spread across a network of computers, called nodes. These nodes:
- Hold a copy of the blockchain: Every node has the complete history of transactions, ensuring transparency and redundancy.
- Verify transactions: Nodes collectively validate new transactions before they're added to the blockchain, preventing fraud and errors.
- Reach consensus: Nodes use specific protocols to agree on the state of the blockchain, preventing manipulation or forking.
Benefits of Decentralization:
- Enhanced security: No single point of failure makes the system more resistant to attacks and technical issues.
- Increased transparency: Everyone can see what's happening on the blockchain, fostering trust and accountability.
- Greater resilience: Decentralized systems are more adaptable and can continue to function even if some nodes go offline.
- Reduced censorship: No single entity can control or censor information on the blockchain.
Real-world applications:
Decentralization isn't just a theoretical concept. It's powering various innovative applications, including:
- Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies use decentralization to create secure and transparent digital payment systems.
- Decentralized finance (DeFi): DeFi applications allow users to borrow, lend, and trade financial assets without relying on traditional intermediaries.
- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs): NFTs use decentralization to create unique digital assets with verifiable ownership.
- Supply chain management: Decentralized platforms can track the movement of goods and materials in a transparent and tamper-proof manner.
The future of decentralization:
Decentralization is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to revolutionize various industries and reshape how we interact with technology. As the technology evolves, we can expect to see even more innovative applications emerge, empowering individuals and creating a more open and equitable digital landscape.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain, at its core, is like a secure, public, and unbreakable record-keeping system. Imagine a giant, digital ledger accessible to everyone, where all transactions and information are stored in chronological order and permanently preserved. But unlike a regular ledger, altering something in a blockchain is nearly impossible, making it incredibly reliable and trustworthy.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-blockchain-5088260_4-35c5d84ddc4345d1a3fe029fa7a90e47.png)
Here's how the magic happens:
1. Data in, Block created: Every piece of information, like a transaction or record, is grouped into a "block." Think of these blocks as individual pages in the ledger.
2. Fingerprint created: Each block gets a unique digital fingerprint called a "hash." This hash is like a special code generated based on the block's data. Any change in the data would result in a completely different hash, making it easy to detect tampering.
3. Chain reaction: Blocks are linked together in a chronological order, with each block containing the hash of the previous one. This creates a chain, making it impossible to alter a block without changing all the subsequent ones.
4. Network of verifiers: Computers called "nodes" maintain the blockchain. These nodes hold copies of the entire chain and constantly verify the integrity of each block using the hashes.
5. Adding new blocks: When new information needs to be recorded, it's sent to the network. Nodes validate the information, and if approved, it's added to a new block at the end of the chain, following the same hashing and verification process.
Key features of blockchain:
- Transparency: Everyone on the network can see all the transactions and information stored in the chain, promoting trust and accountability.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded in a block, it's extremely difficult to change or delete, making it tamper-proof and reliable.
- Security: The cryptographic hashing and distributed nature of the network make it highly resistant to hacking and fraud.
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the blockchain, eliminating the risk of manipulation or censorship.
Beyond the hype:
Blockchain isn't just about Bitcoin. This technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries, including:
- Supply chain management: Tracking goods and materials to ensure authenticity and transparency.
- Healthcare: Securing medical records and ensuring patient privacy.
- Voting systems: Creating tamper-proof and auditable voting processes.
- Identity management: Giving individuals control over their digital identities.
Remember: Blockchain is still evolving, but its potential for secure and transparent record-keeping is undeniable. As it matures, we can expect even more innovative applications to emerge, changing the way we interact with information and trust online systems.
What Is a Consensus Mechanism?
In the fascinating world of blockchains, where trust and security reign supreme, consensus mechanisms play a crucial role. They act as the silent orchestrators, ensuring all the nodes on the network agree on the current state of the ledger, preventing confusion and fraud. Imagine a group of people trying to build a shared document, but without a designated leader. That's essentially what a consensus mechanism achieves in a blockchain, but with much more sophistication and security.
Here's what you need to know about these fascinating protocols:
What is a consensus mechanism?
Simply put, a consensus mechanism is a set of rules or procedures that ensures all the nodes on a blockchain network agree on the validity of new transactions and the state of the overall ledger. Without such a mechanism, the network would be vulnerable to inconsistencies and manipulation.
Why are they important?
Decentralization is the backbone of blockchains, meaning there's no central authority to dictate what's true and what's not. This is where consensus mechanisms step in. They ensure that even though there's no single leader, everyone on the network agrees on the same truth, keeping the ledger consistent and reliable.
Common types of consensus mechanisms:
- Proof of Work (PoW): This popular mechanism, used by Bitcoin, makes nodes solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions. The first node to solve the puzzle gets to add the new block to the chain and earn rewards. This system is secure but also energy-intensive.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): This more eco-friendly alternative allows nodes to participate in the validation process based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold (their stake). Nodes with larger stakes have a higher chance of being chosen to validate transactions.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): In this system, nodes elect representatives (called validators) to validate transactions on their behalf. This improves efficiency but introduces an element of centralization.
Beyond the basics:
Each consensus mechanism has its own strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different situations. Choosing the right one depends on factors like scalability, security, and energy efficiency. As blockchain technology evolves, new and innovative consensus mechanisms are constantly being developed.
Real-world impact:
Consensus mechanisms aren't just theoretical concepts; they play a vital role in various real-world applications of blockchain technology. From ensuring the security of cryptocurrencies to powering decentralized platforms, these protocols are shaping the future of trust and transparency online.
Remember: Consensus mechanisms are the hidden heroes of the blockchain world, guaranteeing a unified and secure network. As you delve deeper into this fascinating technology, understanding these critical protocols will unlock a whole new level of appreciation for its capabilities.
Types of Consensus Mechanisms
1. Proof of Work (PoW):
- Concept: In PoW, miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles in order to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. The first miner to solve the puzzle wins the right to add the block and earn a reward in cryptocurrency.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/proof-work_final-6196eaf3c78f4f22959b261c6d611421.jpg)
- Strengths: Highly secure and resistant to attacks due to its computational difficulty.
- Weaknesses: Energy-intensive and slow, as it requires a lot of computing power to solve the puzzles.
2. Proof of Stake (PoS):
- Concept: In PoS, validators are chosen based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold (their stake). The more stake a validator has, the higher the chance they will be chosen to validate a transaction and earn a reward.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Term-Definitions_Proof_Of_Stake_V1-2fe2af764d9c404e8c387224e4f69f60.jpg)
- Strengths: More energy-efficient and faster than PoW, as it doesn't require solving complex puzzles.
- Weaknesses: Can be susceptible to attacks if a few validators hold a majority of the stake.
3. Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS):
- Concept: In DPoS, token holders elect a limited number of representatives (called delegates or block producers) to validate transactions on their behalf. This creates a faster and more efficient system than PoS, but it also introduces an element of centralization.
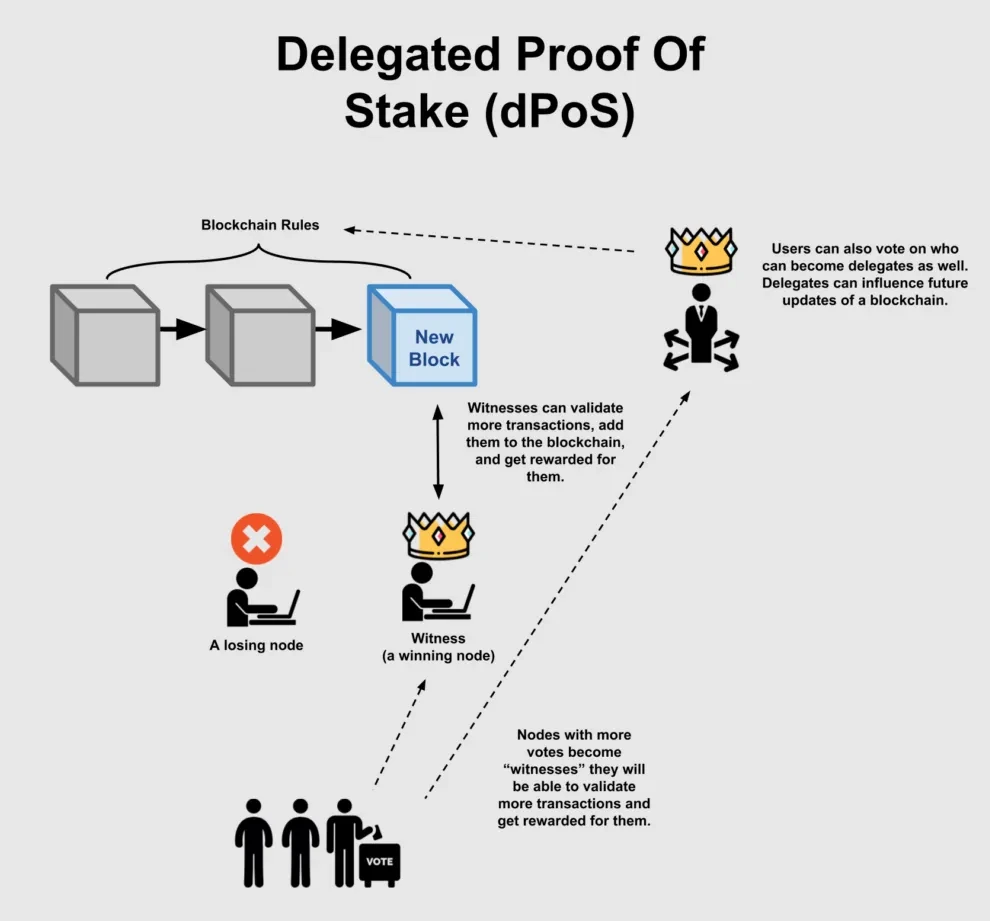
- Strengths: Faster and more efficient than PoS, as it only requires a small number of delegates to validate transactions.
- Weaknesses: Can be less secure than PoS, as it relies on a smaller group of delegates who could potentially collude to manipulate the network.
4. Proof of Authority (PoA):
- Concept: In PoA, only pre-selected and trusted nodes are allowed to validate transactions. This makes PoA very fast and efficient, but it also makes it the most centralized type of consensus mechanism.
- Strengths: Very fast and efficient, as only a small number of trusted nodes need to validate transactions.
- Weaknesses: Not as secure as other consensus mechanisms, as it relies on trusting a small group of nodes.
5. Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET):
- Concept: In PoET, validators are chosen based on a random lottery, where the winner is the first node to wait for a pre-determined amount of time. This makes PoET very fair and resistant to manipulation, but it can also be slow and inefficient.
- Strengths: Very fair and resistant to manipulation, as validators are chosen at random.
- Weaknesses: Can be slow and inefficient, as it can take a long time for a winner to be chosen.
These are just a few of the many different types of consensus mechanisms that are used in blockchains. The best type of consensus mechanism for a particular blockchain will depend on its specific needs and goals.
Check Out My Latest Blogs:
1- Don't Get Hooked:Crypto Phishing Scams (Great)
2- Demystifying the Portal to Web3: Your Guide to Web3 Wallets (Great)
3- A beginner-friendly guide to sidechains: Everything you need to know about it (Brilliant)
4- How to Grow Your Savings (Brilliant)
Show some love in the comments and reactions, friends! Every like and word fuels the conversation and makes this blog even more awesome!